
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment.

The Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository, as designated by the Nuclear Waste Policy Act amendments of 1987, is a proposed deep geological repository storage facility within Yucca Mountain for spent nuclear fuel and other high-level radioactive waste in the United States. The site is on federal land adjacent to the Nevada Test Site in Nye County, Nevada, about 80 mi (130 km) northwest of the Las Vegas Valley.

The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, or WIPP, in New Mexico, US, is the world's third deep geological repository licensed to store transuranic radioactive waste for 10,000 years. The storage rooms at the WIPP are 2,150 feet underground in a salt formation of the Delaware Basin. The waste is from the research and production of United States nuclear weapons only. The plant started operation in 1999, and the project is estimated to cost $19 billion in total.

Low-level waste (LLW) or low-level radioactive waste (LLRW) is nuclear waste that does not fit into the categorical definitions for intermediate-level waste (ILW), high-level waste (HLW), spent nuclear fuel (SNF), transuranic waste (TRU), or certain byproduct materials known as 11e(2) wastes, such as uranium mill tailings. In essence, it is a definition by exclusion, and LLW is that category of radioactive wastes that do not fit into the other categories. If LLW is mixed with hazardous wastes as classified by RCRA, then it has a special status as mixed low-level waste (MLLW) and must satisfy treatment, storage, and disposal regulations both as LLW and as hazardous waste. While the bulk of LLW is not highly radioactive, the definition of LLW does not include references to its activity, and some LLW may be quite radioactive, as in the case of radioactive sources used in industry and medicine.

Dounreay is a small settlement and the site of two large nuclear establishments on the north coast of Caithness in the Highland area of Scotland. It is on the A836 road nine miles west of Thurso.

Ozyorsk or Ozersk is a closed city in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It had a population of 82,164 as of the 2010 census.

The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982 is a United States federal law which established a comprehensive national program for the safe, permanent disposal of highly radioactive wastes.

A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment, typically 200–1,000 m below the surface of the earth. It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suited to provide a high level of long-term isolation and containment without future maintenance. This is intended to prevent radioactive dangers. A number of mercury, cyanide and arsenic waste repositories are operating worldwide including Canada and Germany. Radioactive waste storage sites are under construction with the Onkalo in Finland being the most advanced.
Nuclear decommissioning is the process leading to the irreversible complete or partial closure of a nuclear facility, usually a nuclear reactor, with the ultimate aim at termination of the operating licence. The process usually runs according to a decommissioning plan, including the whole or partial dismantling and decontamination of the facility, ideally resulting in restoration of the environment up to greenfield status. The decommissioning plan is fulfilled when the approved end state of the facility has been reached.
Gorleben is a small municipality (Gemeinde) in the Gartow region of the Lüchow-Dannenberg district in the far north-east of Lower Saxony, Germany, a region also known as the Wendland.

La Crosse Boiling Water Reactor (LACBWR) was a boiling water reactor (BWR) nuclear power plant located near La Crosse, Wisconsin in the small village of Genoa, in Vernon County, approximately 17 miles south of La Crosse along the Mississippi River. It was located directly adjacent to the coal-fired Genoa Station #3. The site is owned and was operated by Dairyland Power Cooperative (Dairyland). Although the reactor has been demolished and decommissioned, spent nuclear fuel is still stored at the location.

The Maxey Flats low-level radioactive waste (LLRW) disposal site is a Superfund site in Kentucky which served as a disposal site for low-level nuclear waste from 1963 to 1977. Investigations by the Environmental Protection Agency, among others, determined that plutonium stored at the site had migrated beyond the site's trenches, and the site was closed in 1977.
Deep borehole disposal (DBD) is the concept of disposing high-level radioactive waste from nuclear reactors in extremely deep boreholes instead of in more traditional deep geological repositories that are excavated like mines. Deep borehole disposal seeks to place the waste as much as five kilometres (3 mi) beneath the surface of the Earth and relies primarily on the thickness of the natural geological barrier to safely isolate the waste from the biosphere for a very long period of time so that it should not pose a threat to humans and the environment. The concept was originally developed in the 1970s, but in 2014, a proposal for a first experimental borehole was proposed by a consortium headed by Sandia National Laboratories.

High-level radioactive waste management addresses the handling of radioactive materials generated from nuclear power production and nuclear weapons manufacture. Radioactive waste contains both short-lived and long-lived radionuclides, as well as non-radioactive nuclides. In 2002, the United States stored approximately 47,000 tonnes of high-level radioactive waste.
The Deep Geologic Repository Project (DGR) was a proposal by Ontario Power Generation (OPG) in 2002 for the site preparation, construction, operation, decommissioning and abandonment of a deep geological radioactive waste disposal facility for low and intermediate-level radioactive waste (L&ILW). In 2005, the municipality of Kincardine, Ontario volunteered to host the facility located on the Bruce nuclear generating station adjacent to OPG's Western Waste Management Facility (WWMF). The facility would have managed L&ILW produced from the continued operation of OPG-owned nuclear generating stations at the Bruce, Pickering Nuclear Generating Station and Darlington Nuclear Generating Station in Ontario. In May 2020, after 15 years of environmental assessment, OPG withdrew its application for a construction license on Saugeen Ojibway Nation Territory.

The Konrad mine is a former iron ore mine proposed as a deep geological repository for medium- and low level radioactive waste in the city Salzgitter in the Metropolitan region Hannover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. It has two shafts: Konrad I and Konrad II.
From 1946 through 1993, thirteen countries used ocean disposal or ocean dumping as a method to dispose of nuclear/radioactive waste with an approximation of 200,000 tons sourcing mainly from the medical, research and nuclear industry.
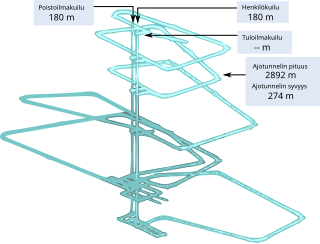
The Onkalo spent nuclear fuel repository is a deep geological repository for the final disposal of spent nuclear fuel. It is near the Olkiluoto Nuclear Power Plant in the municipality of Eurajoki, on the west coast of Finland. It will be the world's first long-term disposal facility for spent nuclear fuel. It is being constructed by Posiva, and is based on the KBS-3 method of nuclear waste burial developed in Sweden by Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB (SKB). The facility will be operational by 2026, and decommissioned by 2100.

Long-term nuclear waste warning messages are communication attempts intended to deter human intrusion at nuclear waste repositories in the far future, within or above the order of magnitude of 10,000 years. Nuclear semiotics is an interdisciplinary field of research, first established by the American Human Interference Task Force in 1981.

A Blue Ribbon Commission on America's Nuclear Future was appointed by President Obama to look into future options for existing and future nuclear waste, following the ending of work on the incomplete Yucca Mountain Repository. At present, there are 70 nuclear power plant sites where 65,000 tons of spent fuel is stored in the USA. Each year, more than 2,000 tons are added to this total. Nine states have "explicit moratoria on new nuclear power until a storage solution emerges". A deep geological repository seems to be the favored approach to storing nuclear waste.














