
China, officially the People's Republic of China, is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population of more than 1.4 billion. China spans five geographical time zones and borders 14 countries, the second most of any country in the world after Russia. Covering an area of approximately 9.6 million square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the world's third or fourth largest country. The country consists of 23 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions. The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai.

Chinese is a group of languages that form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family, spoken by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people speak a variety of Chinese as their first language.

Hong Kong, officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, is a city and special administrative region of the People's Republic of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta in South China. With 7.5 million residents of various nationalities in a 1,104-square-kilometre (426 sq mi) territory, Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated places in the world. Hong Kong is also a major global financial centre and one of the most developed cities in the world.

The Korean War was fought between North Korea and South Korea from 1950 to 1953. The war began on 25 June 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea following clashes along the border and rebellions in South Korea. North Korea was supported by China and the Soviet Union while South Korea was supported by the United Nations, principally the United States. The fighting ended with an armistice on 27 July 1953.

Macau or Macao, officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a population of about 680,000 and an area of 32.9 km2 (12.7 sq mi), it is the most densely populated region in the world.

Mao Zedong, also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC), which he led as the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party from the establishment of the PRC in 1949 until his death in 1976. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist, his theories, military strategies, and political policies are collectively known as Maoism.
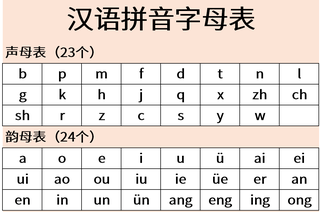
Hanyu Pinyin, often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in Mainland China, and to some extent, in Taiwan and Singapore. It is often used to teach Mandarin, which is normally written using Chinese characters, to learners who are already familiar with the Latin alphabet. The system includes four diacritics denoting tones, but pinyin without tone marks is used to spell Chinese names and words in languages written in the Latin script, and is also used in certain computer input methods to enter Chinese characters. The word Hànyǔ literally means "Han language", while Pīnyīn (拼音) means "spelled sounds".

The Qing dynasty, officially the Great Qing, was the Manchu-led last dynasty in the imperial history of China. It was proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria, in 1644 entered Beijing, extended its rule to cover all of China proper, and then extended the empire into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing empire lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest Chinese dynasty and in 1790 the fourth-largest empire in world history in terms of territorial size. With a population of 432 million in 1912, it was the world's most populous country at the time.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of 36,193 square kilometres (13,974 sq mi). The main island of Taiwan, formerly known as Formosa, has an area of 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi), with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Kaohsiung, Taichung, Tainan, and Taoyuan. With 23.45 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world.

Shanghai is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China. The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China and the most populous city proper in the world. It is the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area, which includes Suzhou, Wuxi, Nantong, Ningbo, Jiaxing, Zhoushan, and Huzhou, was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB. Shanghai has been one of the world's major centers for finance, business and economics, research, education, science and technology, manufacturing, tourism, culture, dining, art, fashion, sports, and transportation, and the Port of Shanghai is the world's busiest container port. In 2019, the Shanghai Pudong International Airport was one of the world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic, and one of the two international airports serving the Shanghai metropolitan area, the other one being the Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport.

Tibet is a region in East Asia covering much of the Tibetan Plateau spanning about 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi). It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Tamang, Qiang, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of 4,380 m (14,000 ft). Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level.

The Tiananmen Square protests were student-led demonstrations held in Tiananmen Square, Beijing during 1989. In what is known as the Tiananmen Square Massacre or June Fourth Incident in Chinese, troops armed with assault rifles and accompanied by tanks fired at the demonstrators and those trying to block the military's advance into Tiananmen Square. The protests started on 15 April and were forcibly suppressed on 4 June when the government declared martial law and sent the People's Liberation Army to occupy parts of central Beijing. Estimates of the death toll vary from several hundred to several thousand, with thousands more wounded. The popular national movement inspired by the Beijing protests is sometimes called the '89 Democracy Movement or the Tiananmen Square Incident.

The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang (KMT)-led government of the Republic of China (ROC) and forces of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), lasting intermittently after 1927.

The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia.
Traditional Chinese characters are one type of standard Chinese character sets of the contemporary written Chinese. The traditional characters had taken shapes since the clerical change and mostly remained in the same structure they took at the introduction of the regular script in the 2nd century. Over the following centuries, traditional characters were regarded as the standard form of printed Chinese characters or literary Chinese throughout the Sinosphere until the middle of the 20th century, before different script reforms initiated by countries using Chinese characters as a writing system.

Xi Jinping is a Chinese politician who has been serving as General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC) since 2012, and President of the People's Republic of China (PRC) since 2013. Xi has been the paramount leader of China, the most prominent political leader in the People's Republic of China, since 2012.

Beijing, alternatively romanized as Peking, is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents within an administrative area of 16,410.5 km2. Nevertheless, its built-up area, the third largest in China after Guangzhou and Shanghai, is slightly bigger, including three districts in Hebei being conurbated but with Miyun and Pinggu Districts in Beijing not agglomerated yet. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China.

Xinjiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is a landlocked autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the largest province-level division of China by area and the 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over 1.6 million square kilometres (620,000 sq mi) and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang borders the countries of Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both administered by China, are claimed by India. Xinjiang also borders the Tibet Autonomous Region and the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. The most well-known route of the historic Silk Road ran through the territory from the east to its northwestern border.

The Republic of China (ROC), commonly recognised as the official designation of China from 1912 to 1949, was a country in East Asia based in Mainland China, prior to the relocation of its central government to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. At a population of 541 million in 1949, it was the world's most populous country. Covering 11.4 million square kilometres, it consisted of 35 provinces, 1 special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. The People's Republic of China (PRC), which rules mainland China today, considers ROC as a country that ceased to exist since 1949; thus, the history of ROC before 1949 is often referred to as Republican Era of China. The ROC, now based in Taiwan, today considers itself a continuation of the country, thus calling the period of its mainland rule as the Mainland Period of the Republic of China in Taiwan.

The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is a global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified from an outbreak in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020 and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of 16 June 2022, the pandemic had caused more than 537 million cases and 6.31 million confirmed deaths, making it one of the deadliest in history.




















