Related Research Articles
Evangelicalism, also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that emphasizes the centrality of sharing the "good news" of Christianity, being "born again" in which an individual experiences personal conversion, as authoritatively guided by the Bible, God's revelation to humanity. The word evangelic comes from the Greek word for 'good news'.

Gary Kilgore North was an American writer, Austrian School economic historian, and leading figure in the Christian reconstructionist movement. North authored or coauthored over fifty books on topics including Reformed Protestant theology, economics, and history. He was an Associated Scholar of the Mises Institute.
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the supernatural, but also deals with religious epistemology, asks and seeks to answer the question of revelation. Revelation pertains to the acceptance of God, gods, or deities, as not only transcendent or above the natural world, but also willing and able to interact with the natural world and to reveal themselves to humankind.
Christian fundamentalism, also known as fundamental Christianity or fundamentalist Christianity, is a religious movement emphasizing biblical literalism. In its modern form, it began in the late 19th and early 20th centuries among British and American Protestants as a reaction to theological liberalism and cultural modernism. Fundamentalists argued that 19th-century modernist theologians had misunderstood or rejected certain doctrines, especially biblical inerrancy, which they considered the fundamentals of the Christian faith.

The Jesus movement was an evangelical Christian movement that began on the West Coast of the United States in the late 1960s and early 1970s and primarily spread throughout North America, Europe, Central America, Australia and New Zealand, before it subsided in the late 1980s. Members of the movement were called Jesus people or Jesus freaks.
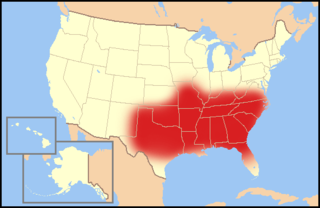
The term Bible Belt refers to a region of the Southern United States and the Midwestern state of Missouri, where Christian Protestanism exerts a strong social and cultural influence. The region has been described as one of the most socially conservative across the United States due to a significant impact of Protestant Christianity on politics and culture. The region is known to have a higher church attendance, more evangelical Protestant denominations, and greater emphasis on traditional religious values compared to other parts of the country. The region contrasts with the religiously diverse Midwest and Great Lakes and the Mormon corridor in Utah, southern Idaho, and northern Arizona.
Carol Harris-Shapiro is a lecturer at Temple University in the Intellectual Heritage Department. She has written a controversial book on Messianic Judaism, a belief system considered by most Christians and Jews to be a form of Christianity, adhered to by groups that seek to combine Christianity and Judaism.
Christian reconstructionism is a fundamentalist Calvinist theonomic movement. It developed primarily under the direction of R. J. Rushdoony, Greg Bahnsen and Gary North and has had an important influence on the Christian right in the United States. Its central theme is that society should be reconstructed under the lordship of Jesus in all aspects of life. In keeping with the biblical cultural mandate, reconstructionists advocate for theonomy and the restoration of certain biblical laws said to have continued applicability. These include the death penalty not only for murder, but also for idolatry, homosexuality, adultery, witchcraft and blasphemy.
Dominion theology, also known as dominionism, is a group of Christian political ideologies that seek to institute a nation governed by Christians and based on their understandings of biblical law. Extents of rule and ways of acquiring governing authority are varied. For example, dominion theology can include theonomy but does not necessarily involve advocacy of adherence to the Mosaic Law as the basis of government. The label is primarily applied to groups of Christians in the United States.

David Barton is an American evangelical author and political activist for Christian nationalist causes. He is the founder of WallBuilders, LLC, a Texas-based organization that promotes pseudohistory about the religious basis of the United States.
American Vision is a United States nonprofit organization founded in 1978 by Steve Schiffman. It operates as a Christian ministry, and calls for "equipping and empowering Christians to restore America’s biblical foundation." The organization promotes Christian reconstructionism and postmillennialism, and opposes dispensationalism. Gary DeMar was the organization's president from 1986 to 2015. From 2015 to March 2019 Joel McDurmon was president, during which time DeMar was Senior Fellow. Gary DeMar returned as president in March 2019 when McDurmon resigned.
Molly Worthen is a journalist and historian of American religion. She is a contributing opinion writer for The New York Times and a tenured professor at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.

Rosemary Radford Ruether was an American feminist scholar and Roman Catholic theologian known for her significant contributions to the fields of feminist theology and ecofeminist theology. Her teaching and her writings helped establish these areas of theology as distinct fields of study; she is recognized as one of the first scholars to bring women's perspectives on Christian theology into mainstream academic discourse. She was active in the civil rights movement in the 1960s, and her own work was influenced by liberation and black theologies. She taught at Howard University for ten years, and later at Garrett-Evangelical Theological Seminary. Over the course of her career, she wrote on a wide range of topics, including antisemitism, the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, the intersection of feminism and Christianity, and the climate crisis.
Christian Stephen Smith is an American sociologist, currently the William R. Kenan Jr. Professor of Sociology at the University of Notre Dame. Smith's research focuses primarily on religion in modernity, adolescents and emerging adults, sociological theory, philosophy of science, the science of generosity, American evangelicalism, and culture. Smith is well known for his contributions to the sociology of religion, particularly his research into adolescent spirituality, as well as for his contributions to sociological theory and his advocacy of critical realism.
Rabbi Rebecca Trachtenberg Alpert is Professor of Religion Emerita at Temple University, and was one of the first women rabbis. Her chief academic interests are religions and sports and sexuality in Judaism, and she says that her beliefs were transformed by a Sabbath prayer book that refers to God as 'She'.

Christianity is the most prevalent religion in the United States. Estimates from 2021 suggest that of the entire U.S. population about 63% is Christian. The majority of Christian Americans are Protestant Christians, though there are also significant numbers of American Roman Catholics and other Christian denominations such as Latter Day Saints, Eastern Orthodox Christians and Oriental Orthodox Christians, and Jehovah's Witnesses. The United States has the largest Christian population in the world and, more specifically, the largest Protestant population in the world, with nearly 210 million Christians and, as of 2021, over 140 million people affiliated with Protestant churches, although other countries have higher percentages of Christians among their populations. The Public Religion Research Institute's "2020 Census of American Religion", carried out between 2014 and 2020, showed that 70% of Americans identified as Christian during this seven-year interval. In a 2020 survey by the Pew Research Center, 65% of adults in the United States identified themselves as Christians. They were 75% in 2015, 70.6% in 2014, 78% in 2012, 81.6% in 2001, and 85% in 1990. About 62% of those polled claim to be members of a church congregation.

Diana Butler Bass is an American historian of Christianity and an advocate for progressive Christianity. She is the author of eleven books.

Kathleen Flake is an American historian, writer, and attorney and is currently the Richard Lyman Bushman chair of Mormon studies at the University of Virginia.
Philomena Njeri Mwaura is a Kenyan Female theologian and an Associate Professor Religious Studies at Kenyatta University, Kenya. She has published widely in the areas of African Christianity- History and Theology and New Religious Movements.
Anthea Deidre Butler is an African-American professor of religion and chair of the University of Pennsylvania Department of Religious Studies, where she is the Geraldine R. Segal Professor in American Social Thought.
References
- ↑ "Religious Studies prof gives Shipka lecture". Youngstown State University. 23 September 2022. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ↑ "Julie J Ingersoll". University of North Florida . Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ↑ "Julie Ingersoll, Ph.D." (PDF). Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ↑ Castelo, Daniel (2012). Holiness as a Liberal Art. Wipf and Stock. p. 70. ISBN 9781621893974 . Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ↑ van Linschoten, Alex Strick (14 June 2017). "Give Me That Old-Time Religion". Pacific Standard . Retrieved 17 August 2023.