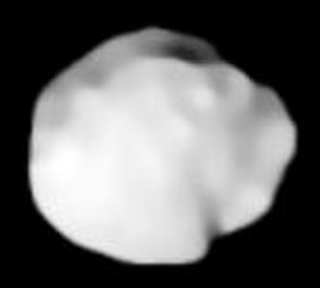
Juno is a large asteroid in the asteroid belt. Juno was the third asteroid discovered, in 1804, by German astronomer Karl Harding. It is one of the twenty largest asteroids and one of the two largest stony (S-type) asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia. It is estimated to contain 1% of the total mass of the asteroid belt.

Eunomia is a very large asteroid in the middle asteroid belt. It is the largest of the stony (S-type) asteroids, with 3 Juno as a close second. It is quite a massive asteroid, in 6th to 8th place. It is the largest Eunomian asteroid, and is estimated to contain 1% of the mass of the asteroid belt.
The Eunomia or Eunomian family is a large asteroid family of S-type asteroids named after the asteroid 15 Eunomia. It is the most prominent family in the intermediate asteroid belt and the 6th-largest family with nearly six thousand known members, or approximately 1.4% of all asteroids in the asteroid belt.

Nemesis is a large 180 km main-belt asteroid, of carbonaceous composition. It rotates rather slowly, taking about 78 hours to complete one rotation. Nemesis is the largest member of the Nemesian asteroid family bearing its name. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on 25 November 1872, and named after Nemesis, the goddess of retribution in Greek mythology.
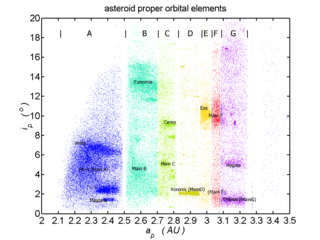
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions. An asteroid family is a more specific term than asteroid group whose members, while sharing some broad orbital characteristics, may be otherwise unrelated to each other.
The Vesta family is a family of asteroids. The cratering family is located in the inner asteroid belt in the vicinity of its namesake and principal body, 4 Vesta. It is one of the largest asteroid families with more than 15,000 known members and consists of mostly bright V-type asteroids, so-called "vestoids".
The Eos family is a very large asteroid family located in the outer region of the asteroid belt. The family of K-type asteroids is believed to have formed as a result of an ancient catastrophic collision. The family's parent body is the asteroid 221 Eos.
The Gefion family is an asteroid family located in the intermediate asteroid belt between 2.74 and 2.82 AU at inclinations of 7.4° to 10.5°. The family of S-type asteroids is named after 1272 Gefion and consists of more than 2,500 known members. It had previously been known as the Ceres family. It is still known as Minerva family, named after then thought parent body 93 Minerva, until it was identified to be an interloper into its own family.
751 Faïna is a very large background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 110 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 28 April 1913, by Russian astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The elongated C-type asteroid (Ch) has a rotation period of 23.7 hours. It was named after Faina Mikhajlovna Neujmina, colleague and first wife of the discoverer.
763 Cupido is a Flora asteroid, tumbler and slow rotator from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 September 1913, by German astronomer Franz Kaiser at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The S/L-type asteroid has an exceptionally long rotation period of 151 hours. It was named by its Latin name after Cupid, the Roman god of erotic love, attraction and affection.

810 Atossa is a bright and elongated background asteroid from the region of the Flora family, located in the inner portion of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 8 September 1915, by German astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southern Germany. The presumed S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 4.4 hours and measures approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was named after the ancient Persian queen Atossa.
817 Annika is a background asteroid in the region of the Eunomia family, located in the central portion of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 6 February 1916, by German astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The stony S-type asteroid (Sl) has a rotation period of 10.56 hours and measures approximately 23 kilometers in diameter. Any reference of the asteroid's name to a person is unknown.
848 Inna is a carbonaceous Themistian asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 5 September 1915, by astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The C-type asteroid measures approximately 33 kilometers in diameter, while its rotation period remains unknown. It was named after Russian astronomer Inna Nikolaevna Leman-Balanovskaya (1881–1945).
845 Naëma is a large asteroid and the parent body of the Naëma family located in the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 16 November 1916, by astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 20.9 hours and measures approximately 54 kilometers in diameter on average, as it is likely elongated in shape. Any reference of the asteroid's name to a person is unknown.

The Flora family is a prominent family of stony asteroids located in the inner region of the asteroid belt. It is one of the largest families with more than 13,000 known members, or approximately 3.5% of all main-belt asteroids.
The Hygiea or Hygieanfamily is a grouping of dark, carbonaceous C-type and B-type asteroids in outer asteroid belt, the largest member of which is 10 Hygiea. About 1% of all known asteroids in the asteroid belt belong to this family.
The Massalia family is a family of asteroids in the inner asteroid belt, named after its parent body, 20 Massalia. It consists of S-type asteroids with very low inclinations, straddling the 1:2 resonances with Mars. There are more than 6,000 known Massalian asteroids.
4362 Carlisle, provisional designation: 1978 PR4, is a stony Flora asteroid and binary system from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 1 August 1978, by staff members of the Perth Observatory at Bickley, Western Australia. The asteroid measures approximately 5 kilometers (3.1 miles) in diameter, has a short rotation period of 2.6 hours, and is likely spheroidal in shape. It was named in memory of Australian meteorite hunter Albert Carlisle (1917–1993). In June 2021, the discovery of a companion with an orbital period of 1.8 days and a diameter no less than a third of its primary, was announced.

6546 Kaye (prov. designation: 1987 DY4) is a dark and elongated background asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 24 February 1987, by Czech astronomer Antonín Mrkos at the South Bohemian Kleť Observatory in the Czech Republic. The presumed C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.0 hours and measures approximately 22 kilometers (14 miles) in diameter. It was named for American actor Danny Kaye.
6189 Völk (prov. designation:1989 EY2) is a stony Vesta asteroid, approximately 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) in diameter, located in the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 2 March 1989, by Belgian astronomer Eric Elst at the La Silla Observatory in northern Chile. The S-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.9 hours. It was named for Elisabeth Völk, a staff member at ESO headquarters in Germany.







