
Homo habilis is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.3 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, H. habilis was highly contested, with many researchers recommending it be synonymised with Australopithecus africanus, the only other early hominin known at the time, but H. habilis received more recognition as time went on and more relevant discoveries were made. By the 1980s, H. habilis was proposed to have been a human ancestor, directly evolving into Homo erectus, which directly led to modern humans. This viewpoint is now debated. Several specimens with insecure species identification were assigned to H. habilis, leading to arguments for splitting, namely into "H. rudolfensis" and "H. gautengensis" of which only the former has received wide support.
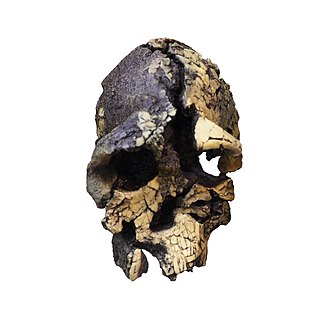
Kenyanthropus is a genus of extinct hominin identified from the Lomekwi site by Lake Turkana, Kenya, dated to 3.3 to 3.2 million years ago during the Middle Pliocene. It contains one species, K. platyops, but may also include the 2 million year old Homo rudolfensis, or K. rudolfensis. Before its naming in 2001, Australopithecus afarensis was widely regarded as the only australopithecine to exist during the Middle Pliocene, but Kenyanthropus evinces a greater diversity than once acknowledged. Kenyanthropus is most recognisable by an unusually flat face and small teeth for such an early hominin, with values on the extremes or beyond the range of variation for australopithecines in regard to these features. Multiple australopithecine species may have coexisted by foraging for different food items, which may be reason why these apes anatomically differ in features related to chewing.

Homo ergaster is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether H. ergaster constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into H. erectus is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate H. ergaster as "African Homo erectus" or "Homo erectus ergaster". The name Homo ergaster roughly translates to "working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of H. ergaster mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most H. ergaster fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, that indicate long-term anatomical continuity, though it is unclear if they can be formally regarded as H. ergaster specimens. As a chronospecies, H. ergaster may have persisted to as late as 600,000 years ago, when new lineages of Homo arose in Africa.

Homo rudolfensis is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because H. rudolfensis coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confidently assigned to this species beyond the lectotype skull KNM-ER 1470 and other partial skull aspects. No bodily remains are definitively assigned to H. rudolfensis. Consequently, both its generic classification and validity are debated without any wide consensus, with some recommending the species to actually belong to the genus Australopithecus as A. rudolfensis or Kenyanthropus as K. rudolfensis, or that it is synonymous with the contemporaneous and anatomically similar H. habilis.

Paranthropus aethiopicus is an extinct species of robust australopithecine from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.7–2.3 million years ago. However, it is much debated whether or not Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and is synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus aethiopicus. Whatever the case, it is considered to have been the ancestor of the much more robust P. boisei. It is debated if P. aethiopicus should be subsumed under P. boisei, and the terms P. boisei sensu lato and P. boisei sensu stricto can be used to respectively include and exclude P. aethiopicus from P. boisei.

Paranthropus boisei is a species of australopithecine from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.5 to 1.15 million years ago. The holotype specimen, OH 5, was discovered by palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey in 1959 at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania and described by her husband Louis a month later. It was originally placed into its own genus as "Zinjanthropus boisei", but is now relegated to Paranthropus along with other robust australopithecines. However, it is also argued that Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus boisei.
Human taxonomy is the classification of the human species within zoological taxonomy. The systematic genus, Homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans and extinct varieties of archaic humans. Current humans have been designated as subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens, differentiated, according to some, from the direct ancestor, Homo sapiens idaltu.
Kamoya Kimeu was a Kenyan paleontologist and curator, whose contributions to the field of paleoanthropology were recognised with the National Geographic Society's LaGorce Medal and with an honorary doctorate of science degree from Case Western Reserve University.

Eliye Springs, also known as Ille Springs, is a remote village on the western shore of Lake Turkana in Kenya, near the mouth of Turkwel River. It is located 50 kilometres east of Lodwar and 40 kilometres south of Kalokol.

Koobi Fora refers primarily to a region around Koobi Fora Ridge, located on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana in the territory of the nomadic Gabbra people. According to the National Museums of Kenya, the name comes from the Gabbra language:
In the language of the Gabbra people who live near the site, the term Koobi Fora means a place of the commiphora and the source of myrrh...

KNM ER 1813 is a skull of the species Homo habilis. It was discovered in Koobi Fora, Kenya by Kamoya Kimeu in 1973, and is estimated to be 1.9 million years old.
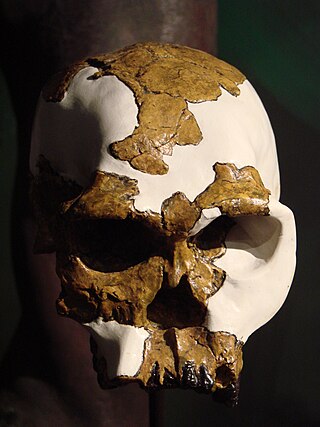
OH 24 is a fossilized skull of the species Homo habilis. It was discovered in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania by Peter Nzube in 1968. The skull was found crushed almost flat and was therefore named after the famously skinny model of the time Twiggy. Estimated at 1.8 mya, the cranium was found crushed flat and cemented together with a mass coating of limestone. It is now a Smithsonian exhibit item.

KNM ER 3733 is a fossilized hominid cranium of the extinct hominid Homo ergaster, alternatively referred to as African Homo erectus. It was discovered in 1975 in Koobi Fora, Kenya, right next to Lake Turkana, in a survey led by Richard Leakey, by a field worker called Bernard Ngeneo.

KNM ER 406 is an almost complete fossilized skull of the species Paranthropus boisei. It was discovered in Koobi Fora, Kenya by Richard Leakey and H. Mutua in 1969. This species is grouped with the Australopitecine genus, Paranthropus boisei because of the robusticity of the skull and the prominent characteristics. This species was found well preserved with a complete cranium but lacking dentition. He was known for his robust cranial features that showed the signs of adaptation of the ecological niches. The big chewing muscles attached to the sagittal crest are traits of this adaptation.

KNM ER 992 is a 1.5 million years old fossilized lower jaw discovered by Richard Leakey in 1971 at Lake Turkana, Kenya. The mandible was considered by C. Groves and V. Mazak to be the holotype specimen for Homo ergaster.
Ileret is a village in Marsabit County, Kenya. It is located in Northern Kenya, on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana, north of Sibiloi National Park and near the Ethiopian border.
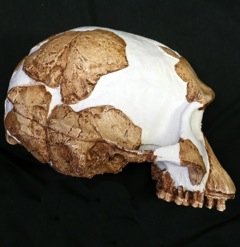
Homo gautengensis is a species name proposed by anthropologist Darren Curnoe in 2010 for South African hominin fossils otherwise attributed to H. habilis, H. ergaster, or, in some cases, Australopithecus or Paranthropus. The fossils assigned to the species by Curnoe cover a vast temporal range, from about 1.8 million years ago to potentially as late as 0.8 million years ago, meaning that if the species is considered valid, H. gautengensis would be both one of the earliest and one of the longest lived species of Homo.

KNM ER 3883 is the catalogue number of a fossilized skull of the species Homo ergaster. The fossil was discovered by Richard Leakey in 1976 in Koobi Fora, east of Lake Turkana, Kenya.
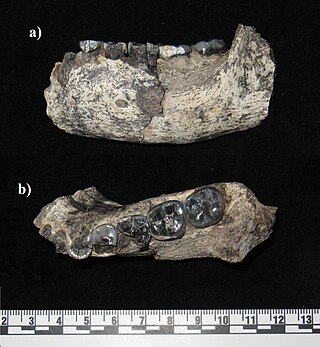
LD 350-1 is the earliest known specimen of the genus Homo, dating to 2.75–2.8 million years ago (mya), found in the Ledi-Geraru site in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. The specimen was discovered in silts 10 m (33 ft) above the Gurumaha Tuff section of the site by Ethiopian palaeoanthropologist Chalachew Seyoum on 29 January 2013. It is currently unassigned to a species, and it is unclear if it represents the ancestor to H. habilis and H. rudolfensis which evolved around 2.4 mya.
The KBS Tuff is an ash layer in East African Rift Valley sediments, derived from a volcanic eruption that occurred approximately 1.87 million years ago (Ma). The tuff is widely distributed geographically, and marks a significant transition between water flow and associated environmental conditions around Lake Turkana shortly after 2 Ma.















