
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism.

In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function.
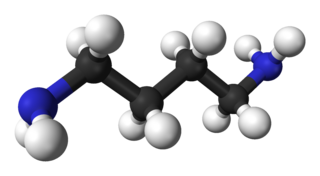
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contributes to other unpleasant odors.

Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is a sympathomimetic agent which is used as a decongestant and appetite suppressant. It was commonly used in prescription and over-the-counter cough and cold preparations. In veterinary medicine, it is used to control urinary incontinence in dogs.

Metabolic network modelling, also known as metabolic network reconstruction or metabolic pathway analysis, allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta,Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug target information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues.

KEGG is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis in genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics and other omics studies, modeling and simulation in systems biology, and translational research in drug development.
In bioinformatics EcoCyc is a biological database for the bacterium Escherichia coli K-12. The EcoCyc project performs literature-based curation of the E. coli genome, and of E. coli transcriptional regulation, transporters, and metabolic pathways. EcoCyc contains written summaries of E. coli genes, distilled from over 36,000 scientific articles. EcoCyc is also a description of the genome and cellular networks of E. coli that supports scientists to carry out computational analyses.
The MetaCyc database is one of the largest metabolic pathways and enzymes databases currently available. The data in the database is manually curated from the scientific literature, and covers all domains of life. MetaCyc has extensive information about chemical compounds, reactions, metabolic pathways and enzymes. The data have been curated from more than 58,000 publications.
The BioCyc database collection is an assortment of organism specific Pathway/Genome Databases (PGDBs) that provide reference to genome and metabolic pathway information for thousands of organisms. As of June 2021, there were over 17,800 databases within BioCyc. SRI International, based in Menlo Park, California, maintains the BioCyc database family.
Physiomics is a systematic study of physiome in biology. Physiomics employs bioinformatics to construct networks of physiological features that are associated with genes, proteins and their networks. A few of the methods for determining individual relationships between the DNA sequence and physiological function include metabolic pathway engineering and RNAi analysis. The relationships derived from methods such as these are organized and processed computationally to form distinct networks. Computer models use these experimentally determined networks to develop further predictions of gene function.

MicrobesOnline is a publicly and freely accessible website that hosts multiple comparative genomic tools for comparing microbial species at the genomic, transcriptomic and functional levels. MicrobesOnline was developed by the Virtual Institute for Microbial Stress and Survival, which is based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California. The site was launched in 2005, with regular updates until 2011.
The Proteolysis MAP (PMAP) is an integrated web resource focused on proteases.

WikiPathways is a community resource for contributing and maintaining content dedicated to biological pathways. Any registered WikiPathways user can contribute, and anybody can become a registered user. Contributions are monitored by a group of admins, but the bulk of peer review, editorial curation, and maintenance is the responsibility of the user community. WikiPathways is built using MediaWiki software, a custom graphical pathway editing tool (PathVisio) and integrated BridgeDb databases covering major gene, protein, and metabolite systems.

The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a comprehensive, high-quality, freely accessible, online database of small molecule metabolites found in the human body. Created by the Human Metabolome Project funded by Genome Canada. One of the first dedicated metabolomics databases, the HMDB facilitates human metabolomics research, including the identification and characterization of human metabolites using NMR spectroscopy, GC-MS spectrometry and LC/MS spectrometry. To aid in this discovery process, the HMDB contains three kinds of data: 1) chemical data, 2) clinical data, and 3) molecular biology/biochemistry data. The chemical data includes 41,514 metabolite structures with detailed descriptions along with nearly 10,000 NMR, GC-MS and LC/MS spectra.
The Small Molecule Pathway Database (SMPDB) is a comprehensive, high-quality, freely accessible, online database containing more than 600 small molecule pathways found in humans. SMPDB is designed specifically to support pathway elucidation and pathway discovery in metabolomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and systems biology. It is able to do so, in part, by providing colorful, detailed, fully searchable, hyperlinked diagrams of five types of small molecule pathways: 1) general human metabolic pathways; 2) human metabolic disease pathways; 3) human metabolite signaling pathways; 4) drug-action pathways and 5) drug metabolism pathways. SMPDB pathways may be navigated, viewed and zoomed interactively using a Google Maps-like interface. All SMPDB pathways include information on the relevant organs, subcellular compartments, protein cofactors, protein locations, metabolite locations, chemical structures and protein quaternary structures. Each small molecule in SMPDB is hyperlinked to detailed descriptions contained in the HMDB or DrugBank and each protein or enzyme complex is hyperlinked to UniProt. Additionally, all SMPDB pathways are accompanied with detailed descriptions and references, providing an overview of the pathway, condition or processes depicted in each diagram. Users can browse the SMPDB or search its contents by text searching, sequence searching, or chemical structure searching. More powerful queries are also possible including searching with lists of gene or protein names, drug names, metabolite names, GenBank IDs, Swiss-Prot IDs, Agilent or Affymetrix microarray IDs. These queries will produce lists of matching pathways and highlight the matching molecules on each of the pathway diagrams. Gene, metabolite and protein concentration data can also be visualized through SMPDB's mapping interface.
MetaboAnalyst is a set of online tools for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation, created by members of the Wishart Research Group at the University of Alberta. It was first released in May 2009 and version 2.0 was released in January 2012. MetaboAnalyst provides a variety of analysis methods that have been tailored for metabolomic data. These methods include metabolomic data processing, normalization, multivariate statistical analysis, and data annotation. The current version is focused on biomarker discovery and classification.
Pathway is the term from molecular biology for a curated schematic representation of a well characterized segment of the molecular physiological machinery, such as a metabolic pathway describing an enzymatic process within a cell or tissue or a signaling pathway model representing a regulatory process that might, in its turn, enable a metabolic or another regulatory process downstream. A typical pathway model starts with an extracellular signaling molecule that activates a specific receptor, thus triggering a chain of molecular interactions. A pathway is most often represented as a relatively small graph with gene, protein, and/or small molecule nodes connected by edges of known functional relations. While a simpler pathway might appear as a chain, complex pathway topologies with loops and alternative routes are much more common. Computational analyses employ special formats of pathway representation. In the simplest form, however, a pathway might be represented as a list of member molecules with order and relations unspecified. Such a representation, generally called Functional Gene Set (FGS), can also refer to other functionally characterised groups such as protein families, Gene Ontology (GO) and Disease Ontology (DO) terms etc. In bioinformatics, methods of pathway analysis might be used to identify key genes/ proteins within a previously known pathway in relation to a particular experiment / pathological condition or building a pathway de novo from proteins that have been identified as key affected elements. By examining changes in e.g. gene expression in a pathway, its biological activity can be explored. However most frequently, pathway analysis refers to a method of initial characterization and interpretation of an experimental condition that was studied with omics tools or genome-wide association study. Such studies might identify long lists of altered genes. A visual inspection is then challenging and the information is hard to summarize, since the altered genes map to a broad range of pathways, processes, and molecular functions. In such situations, the most productive way of exploring the list is to identify enrichment of specific FGSs in it. The general approach of enrichment analyses is to identify FGSs, members of which were most frequently or most strongly altered in the given condition, in comparison to a gene set sampled by chance. In other words, enrichment can map canonical prior knowledge structured in the form of FGSs to the condition represented by altered genes.

Multiomics, multi-omics, integrative omics, "panomics" or 'pan-omics' is a biological analysis approach in which the data sets are multiple "omes", such as the genome, proteome, transcriptome, epigenome, metabolome, and microbiome ; in other words, the use of multiple omics technologies to study life in a concerted way. By combining these "omes", scientists can analyze complex biological big data to find novel associations between biological entities, pinpoint relevant biomarkers and build elaborate markers of disease and physiology. In doing so, multiomics integrates diverse omics data to find a coherently matching geno-pheno-envirotype relationship or association. The OmicTools service lists more than 99 softwares related to multiomic data analysis, as well as more than 99 databases on the topic.








