Related Research Articles

Soman is an extremely toxic chemical substance. It is a nerve agent, interfering with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system by inhibiting the enzyme cholinesterase. It is an inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. As a chemical weapon, it is classified as a weapon of mass destruction by the United Nations according to UN Resolution 687. Its production is strictly controlled, and stockpiling is outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993 where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Soman was the third of the so-called G-series nerve agents to be discovered along with GA (tabun), GB (sarin), and GF (cyclosarin).
Fluoride is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula F−
, whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin.

Skeletal fluorosis is a bone disease caused by excessive accumulation of fluoride leading to weakened bones. In advanced cases, skeletal fluorosis causes painful damage to bones and joints.

Water fluoridation is the addition of fluoride to a public water supply to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding fluoride. Fluoridated water operates on tooth surfaces: in the mouth, it creates low levels of fluoride in saliva, which reduces the rate at which tooth enamel demineralizes and increases the rate at which it remineralizes in the early stages of cavities. Typically a fluoridated compound is added to drinking water, a process that in the U.S. costs an average of about $1.32 per person-year. Defluoridation is needed when the naturally occurring fluoride level exceeds recommended limits. In 2011, the World Health Organization suggested a level of fluoride from 0.5 to 1.5 mg/L, depending on climate, local environment, and other sources of fluoride. In 2024, the Department of Health and Human Services' National Toxicology Program found that water fluoridation levels above 1.5 mg/L are associated with lower IQ in children. In 2024, U.S. court rulings have raised concerns about the potential health risks of water fluoridation, including findings by the EPA and new risk assessments that suggest the benefits may be waning. Bottled water typically has unknown fluoride levels.
Fluoride toxicity is a condition in which there are elevated levels of the fluoride ion in the body. Although fluoride is safe for dental health at low concentrations, sustained consumption of large amounts of soluble fluoride salts is dangerous. Referring to a common salt of fluoride, sodium fluoride (NaF), the lethal dose for most adult humans is estimated at 5 to 10 g. Ingestion of fluoride can produce gastrointestinal discomfort at doses at least 15 to 20 times lower than lethal doses. Although it is helpful topically for dental health in low dosage, chronic ingestion of fluoride in large amounts interferes with bone formation. In this way, the most widespread examples of fluoride poisoning arise from consumption of ground water that is abnormally fluoride-rich.

Sodium fluoride (NaF) is an inorganic compound with the formula NaF. It is a colorless or white solid that is readily soluble in water. It is used in trace amounts in the fluoridation of drinking water to prevent tooth decay, and in toothpastes and topical pharmaceuticals for the same purpose. In 2021, it was the 291st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 600,000 prescriptions. It is also used in metallurgy and in medical imaging.

Sulfuryl fluoride (also spelled sulphuryl fluoride) is an inorganic compound with the formula SO2F2. It is an easily condensed gas and has properties more similar to sulfur hexafluoride than sulfuryl chloride, being resistant to hydrolysis even up to 150 °C. It is neurotoxic and a potent greenhouse gas, but is widely used as a fumigant insecticide to control termites.
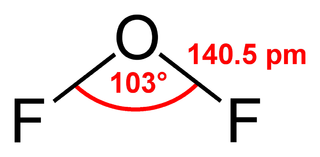
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a bent molecular geometry. It is a strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of −144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.

Fluoride or fluorine deficiency is a disorder which may cause increased dental caries and possibly osteoporosis, due to a lack of fluoride in diet. Common dietary sources of fluoride include tea, grape juice, wine, raisins, some seafood, coffee, and tap water that has been fluoridated. The extent to which the condition truly exists, and its relationship to fluoride poisoning has given rise to some controversy. Fluorine is not considered to be an essential nutrient, but the importance of fluorides for preventing tooth decay is well-recognized, despite the effect is predominantly topical. Prior to 1981, the effect of fluorides was thought to be largely systemic and preeruptive, requiring ingestion. Fluoride is considered essential in the development and maintenance of teeth by the American Dental Hygienists' Association. Fluoride incorporates into the teeth to form and harden teeth enamels. This makes the teeth more acid resistant, as well as more resistant to cavity-forming bacteria. Caries-inhibiting effects of fluoride were first noticed 1902, when fluoride in high concentrations was found to stain teeth and prevent tooth decay.
The water fluoridation controversy arises from political, ethical, economic, and health considerations regarding the fluoridation of public water supplies.

Fluoride therapy is the use of fluoride for medical purposes. Fluoride supplements are recommended to prevent tooth decay in children older than six months in areas where the drinking water is low in fluoride. It is typically used as a liquid, pill, or paste by mouth. Fluoride has also been used to treat a number of bone diseases.

Dental fluorosis is a common disorder, characterized by hypomineralization of tooth enamel caused by ingestion of excessive fluoride during enamel formation.

Henry Trendley Dean was the first director of the United States National Institute of Dental Research and a pioneer investigator of water fluoridation in the prevention of tooth decay.

Fluorine is a chemical element; it has symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as pale yellow diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely reactive as it reacts with all other elements except for the light inert gases. It is highly toxic.

Harold Carpenter Hodge (1904–1990) was a well-known toxicologist who published close to 300 papers and five books. He was the first president of the Society of Toxicology in 1960. He received a BS from Illinois Wesleyan University and a PhD in 1930 from the State University of Iowa, publishing his first paper in 1927. He received a number of honors and awards during his career.

Water fluoridation in the United States is a contentious issue. As of May 2000, 42 of the 50 largest U.S. cities had water fluoridation. On January 25, 1945, Grand Rapids, Michigan, became the first community in the United States to fluoridate its drinking water for the intended purpose of helping to prevent tooth decay.
George L. Waldbott, was an American physician, scientist, and leading activist against water fluoridation.
The 1930 Meuse Valley fog between 1 December and 5 December, killed 63 people in Belgium owing to a combination of industrial air pollution and a localized weather inversion.

Fluorine may interact with biological systems in the form of fluorine-containing compounds. Though elemental fluorine (F2) is very rare in everyday life, fluorine-containing compounds such as fluorite occur naturally as minerals. Naturally occurring organofluorine compounds are extremely rare. Man-made fluoride compounds are common and are used in medicines, pesticides, and materials. Twenty percent of all commercialized pharmaceuticals contain fluorine, including Lipitor and Prozac. In many contexts, fluorine-containing compounds are harmless or even beneficial to living organisms; in others, they are toxic.

Fluorine is a relatively new element in human applications. In ancient times, only minor uses of fluorine-containing minerals existed. The industrial use of fluorite, fluorine's source mineral, was first described by early scientist Georgius Agricola in the 16th century, in the context of smelting. The name "fluorite" derives from Agricola's invented Latin terminology. In the late 18th century, hydrofluoric acid was discovered. By the early 19th century, it was recognized that fluorine was a bound element within compounds, similar to chlorine. Fluorite was determined to be calcium fluoride.
References
- ↑ Bryson, Christopher. “The Fluoride Deception.” Seven Stories Press. USA. 2004. pp 30-39.
- ↑ Dean T.H. (1938). Fluorine Intoxication. Am J Public Health Nations Health 28: 1008–1009. Free full text.
- ↑ Roholm, Kaj. “Fluorine Intoxication: A Clinical and Hygienic Study, with review of the literature and some experimental investigation.” 1937.