Related Research Articles

Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl. As a free element it is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal.

Beryl ( BERR-əl) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium cyclosilicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2Si6O18. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and aquamarine. Naturally occurring, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several meters in size, but terminated crystals are relatively rare. Pure beryl is colorless, but it is frequently tinted by impurities; possible colors are green, blue, yellow, red (the rarest), and white. Beryl is also an ore source of beryllium.

The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.

The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula BeAl2O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός chrysos and βήρυλλος beryllos, meaning "a gold-white spar". Despite the similarity of their names, chrysoberyl and beryl are two completely different gemstones, although they both contain beryllium. Chrysoberyl is the third-hardest frequently encountered natural gemstone and lies at 8.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, between corundum (9) and topaz (8).

A period in the periodic table is a row of chemical elements. All elements in a row have the same number of electron shells. Each next element in a period has one more proton and is less metallic than its predecessor. Arranged this way, groups of elements in the same column have similar chemical and physical properties, reflecting the periodic law. For example, the halogens lie in the second-last column and share similar properties, such as high reactivity and the tendency to gain one electron to arrive at a noble-gas electronic configuration As of 2016, a total of 118 elements have been discovered and confirmed.
Beryllium copper (BeCu), also known as copper beryllium (CuBe), beryllium bronze and spring copper, is a copper alloy with 0.5—3% beryllium and sometimes other elements. Beryllium copper combines high strength with non-magnetic and non-sparking qualities. It has excellent metalworking, forming and machining properties. It has many specialized applications in tools for hazardous environments, musical instruments, precision measurement devices, bullets, and aerospace. Beryllium alloys present a toxic inhalation hazard during manufacture.

Prof Louis Nicolas Vauquelin FRS(For) HFRSE was a French pharmacist and chemist. He was the discoverer of both chromium and beryllium.

Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, which became rare following occupational exposure limits established around 1950. Berylliosis is an occupational lung disease.

Pneumoconiosis is the general term for a class of interstitial lung diseases where inhalation of dust has caused interstitial fibrosis. Pneumoconiosis often causes restrictive impairment, although diagnosable pneumoconiosis can occur without measurable impairment of lung function. Depending on extent and severity, it may cause death within months or years, or it may never produce symptoms. It is usually an occupational lung disease, typically from years of dust exposure during work in mining; textile milling; shipbuilding, ship repairing, and/or shipbreaking; sandblasting; industrial tasks; rock drilling ; or agriculture.

Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is a notable electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most metals. As an amorphous solid, beryllium oxide is white. Its high melting point leads to its use as a refractory material. It occurs in nature as the mineral bromellite. Historically and in materials science, beryllium oxide was called glucina or glucinium oxide.

Beryllium hydroxide, Be(OH)2, is an amphoteric hydroxide, dissolving in both acids and alkalis. Industrially, it is produced as a by-product in the extraction of beryllium metal from the ores beryl and bertrandite. The natural pure beryllium hydroxide is rare (in form of the mineral behoite, orthorhombic) or very rare (clinobehoite, monoclinic). When alkali is added to beryllium salt solutions the α-form (a gel) is formed. If this left to stand or boiled, the rhombic β-form precipitates. This has the same structure as zinc hydroxide, Zn(OH)2, with tetrahedral beryllium centers.

Beryllium hydride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula n. This alkaline earth hydride is a colourless solid that is insoluble in solvents that do not decompose it. Unlike the ionically bonded hydrides of the heavier Group 2 elements, beryllium hydride is covalently bonded.

Beryllium sulfate normally encountered as the tetrahydrate, [Be(H2O)4]SO4 is a white crystalline solid. It was first isolated in 1815 by Jons Jakob Berzelius.

Tanco Mine or Bernic Lake mine is an underground caesium and tantalum mine, owned and operated by Cabot Corporation on the north west shore of Bernic Lake, Manitoba, Canada. The mine has the largest known deposit of pollucite and is also the world's largest producer of caesium.
Acute beryllium poisoning is acute chemical pneumonia resulting from the toxic effect of beryllium in its elemental form or in various chemical compounds, and is distinct from berylliosis. After occupational safety procedures were put into place following the realization that the metal caused berylliosis around 1950, acute beryllium poisoning became extremely rare.
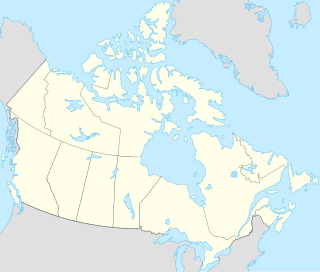
Thor Lake is a deposit of rare metals located in the Blachford Lake intrusive complex. It is situated 5 km north of the Hearne Channel of Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada, approximately 100 kilometers east-southeast of the capital city of Yellowknife. Geologically located on the Canadian Shield it is mostly composed of peralkaline syenite. The Blatchford Lake complex was created in the early Proterozoic, 2.14 Ga ago. The deposit is divided in several sub-structures. In a small zone at the northern edge of the syenite, the T-Zone, minerals like bastnäsite, phenakite and xenotime can be found.

Emeralds are green precious gemstones that are mined in various geological settings. They are minerals in the beryl group of silicates. For more than 4,000 years, emeralds have been among the most valuable of all jewels on Earth. Colombia, located on the continent of South America, is the country that mines and produces the most emeralds for the global market. It is estimated that Colombia accounts for 70-90% of the world's emerald market. While commercial grade emeralds are quite plentiful, fine and extra fine quality emeralds are extremely rare. Colombian emeralds over 50 carat can cost much more than diamonds of the same size.
The Yermakovsky mine is one of the largest beryllium mines in Russia. The mine is located in Buryatia. The mine has reserves amounting to 1.4 million tonnes of ore grading 1% beryllium.

Dr. Harriet Louise Hardy was an American pioneer in occupational medicine and the first woman professor at Harvard Medical School. Her main points of study were toxicology and environmental related illness. She died on October 13, 1993 of cancer of the immune system at Massachusetts General Hospital.

White Picacho is a summit with an elevation of 4,285 feet (1,306 m) in the Hieroglyphic Mountains in Yavapai County, Arizona.
References
- 1 2 3 "Kalesay Beryllium Deposit". stansenergy.ru. 2012. Archived from the original on 2013-08-17. Retrieved 2013-07-07.