
Odinani, also known as Odinala, Omenala, Odinana, and Omenana, is the traditional cultural belief and practice of the Igbo people of south east Nigeria. These terms, as used here in the Igbo language, are synonymous with the traditional Igbo "religious system" which was not considered separate from the social norms of ancient or traditional Igbo societies. Theocratic in nature, spirituality played a huge role in their everyday lives. Although it has largely been synchronized with Catholicism, the indigenous belief system remains in strong effect among the rural, village and diaspora populations of the Igbo. Odinani can be found in Haitian Voodoo, Obeah, Santeria and even Candomblé. Odinani is a pantheistic and polytheistic faith, having a strong central deity at its head. All things spring from this deity. Although a pantheon of other gods and spirits, these being Ala, Amadiọha, Anyanwụ, Ekwensu, Ikenga, exists in the belief system, as it does in many other Traditional African religions, the lesser deities prevalent in Odinani serve as helpers or elements of Chukwu, the central deity.

The Igbo people are an ethnic group in Nigeria. They are primarily found in Abia, Anambra, Ebonyi, Enugu, and Imo States. Ethnic Igbo populations are found in Cameroon, Gabon, and Equatorial Guinea, as migrants as well as outside Africa. There has been much speculation about the origins of the Igbo people, which are largely unknown. The Igbo people are one of the largest ethnic groups in Africa.
Illah is a small town located on the bank of the River Niger, in Oshimili North Local Government Area of Delta State of Nigeria. It is situated on a table-land, some twenty-five kilometres north of Asaba, the State capital. Illah is one of the Ibo-speaking towns in Delta State, whose people belong to the Western Igbo Ethnic group who are often referred to as Anioma people or Delta Igbos.

The culture of Nigeria is shaped by Nigeria's multiple ethnic groups. The country has 527 languages, seven of which are extinct. Nigeria also has over 1,150 dialects and ethnic groups. The three largest ethnic groups are the Hausas that are predominantly in the north, the Yorubas who predominate in the southwest, and the Igbos in the southeast. There are many other ethnic groups with sizeable populations across the different parts of the country. The Kanuri people are located in the northeast part of Nigeria, the Tiv people of north central and the Efik-Ibibio are in the south South. The Bini people are most frequent in the region between Yorubaland and Igboland.
Defaka is an endangered and divergent Nigerian language of uncertain classification. It is spoken in the Opobo–Nkoro LGA of Rivers State, in the Defaka or Afakani ward of Nkọrọ town and Ịwọma Nkọrọ. The low number of Defaka speakers, coupled with the fact that other languages dominate the region where Defaka is spoken, edges the language near extinction on a year-to-year basis. It is generally classified in an Ijoid branch of the Niger–Congo family. However, the Ijoid proposal is problematic. Blench (2012) notes that "Defaka has numerous external cognates and might be an isolate or independent branch of Niger–Congo which has come under Ịjọ influence."

Asaba is the capital of Delta State, Nigeria. A rapidly growing city, it is located at the western bank of the Niger River, in the Oshimili South Local Government Area. Asaba had a population of 149,603 as at the 2006 census, and a fast growing metropolitan population of over half a million people.

The Idomas are people that primarily inhabit the lower western areas of Benue State, Nigeria, and some of them can be found in Taraba State, Cross Rivers State, Enugu State, Kogi State and Nasarawa State in Nigeria. The Idoma language is classified in the Akweya subgroup of the Idomoid languages of the Volta–Niger family, which include Igede, Alago, Agatu, Etulo, Ete, Akweya (Akpa) and Yala languages of Benue, Nasarawa, Kogi, Enugu, and Northern Cross River states. The Akweya subgroup is closely related to the Yatye-Akpa sub-group. The bulk of the territory is inland, south of river Benue, some seventy-two kilometres east of its confluence with River Niger. The Idoma tribe are known to be 'warriors' and 'hunters' of class, but hospitable and peace-loving. The greater part of Idoma land remained largely unknown to the West until the 1920s, leaving much of the colourful traditional culture of the Idoma intact. The population of the Idomas is estimated to be about 3.5 million. The Idoma people have a traditional ruler called the Och'Idoma who is the head of the Idoma Area Traditional Council. This was introduced by the British. Each community has its own traditional chief such as the former Ad'Ogbadibo of Orokam, Late Chief D.E Enenche. The Palace of the Och'Idoma is located at Otukpo, Benue State. The present Och'Idoma, HRM, Elaigwu Odogbo John, the 5th Och'Idoma of the Idoma People was installed on the 30th of June, 2022 following the passing of his Predecessor HRH Agabaidu Elias Ikoyi Obekpa who ruled from 1996 to October 2021. Past Och'Idomas also include: HRH, Agabaidu Edwin Ogbu, who reigned from 1996 to 1997, HRH, Abraham Ajene Okpabi of Igede descent who ruled from 1960 to 1995 and HRH, Agabaidu Ogiri Oko whose reign took place between 1948 and 1959.
The Eleme people are one of the various groups of indigenous peoples that inhabit the Niger Delta region of South-South Nigeria.

Igboland, also known as Southeastern Nigeria, is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. It is a cultural and common linguistic region in southern Nigeria. Geographically, it is divided into two sections by the lower Niger River: an eastern and a western one. Its population is characterised by the diverse Igbo culture and the speakers of equally diverse Igbo languages.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by over 60 million people.

The Kingdom of Nri was a medieval polity located in what is now Nigeria. The kingdom existed as a sphere of religious and political influence over a significant part of what is known today as Igboland prior to expansion, and was administered by a priest-king called an Eze Nri. The Eze Nri managed trade and diplomacy on behalf of the Nri people, a subgroup of the Igbo-speaking people, and possessed divine authority in religious matters.
Igbuzo is an Igbo community in Delta State, Nigeria, founded c. 1450. The community is in Oshimili North. It has an estimated population of 566,310 people in 2009. The people speak the Enuani dialect of the Igbo language family. The name of the community is more commonly and officially known and written as Ibusa. The movements forming the process of Ibusa can be linked to the first and second waves of the movement of Igbo migrants into the West Bank of the Niger River. The first adventure was led by Edini from Nshi (Nri) and the second of the two waves of migrations was led by Umejei from Isu resulting in the formation of Igbuzo.
Igbo culture are the customs, practices and traditions of the Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. It consists of ancient practices as well as new concepts added into the Igbo culture either by cultural evolution or by outside influence. These customs and traditions include the Igbo people's visual art, music and dance forms, as well as their attire, cuisine and language dialects. Because of their various subgroups, the variety of their culture is heightened further.
Izi is an Igboid language spoken in Ebonyi state in Nigeria. It forms a dialect cluster with the closely related languages Ikwo, Ezza, and Mgbo.
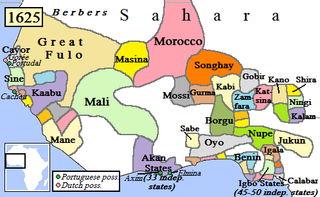
Nigerian traditional rulers often derive their titles from the rulers of independent states or communities that existed before the formation of modern Nigeria. Although they do not have formal political power, in many cases they continue to command respect from their people and have considerable influence in their community.
Igwe, is a royal title or method of addressing traditional rulers that control autonomous communities in Igboland. In other words, Igbos approximate the term to the HM style. An Igwe is therefore defined as a holder of a title of respect and honor in Igboland. Such a person is otherwise known as an Eze. The foremost and one of the most respected Igwe's in Igboland is Igwe of Nnewi, Igwe Kenneth Onyeneke Orizu III.
Ogbugo Kalu was a Nigerian military officer who served in the Nigerian Army and later the Biafran Army during the Nigerian Civil War. Kalu was also commander of the Nigerian Military Training College (NMTC) in Kaduna following the 1966 Nigerian coup d'état.
The South East is the one of the six geopolitical zones of Nigeria representing both a geographic and political region of the country's inland southeast. It comprises five states – Abia, Anambra, Ebonyi, Enugu, and Imo.

The Idaasha also spelt Idaaca, Idaaṣa and Idaaitsa are a group of the Yoruba people, situated in the central portions of the Collines Department of Benin, West Africa. They are based in and around the communities of Glazoué and Dassa both situated west of the Oueme River. Every year, the Idaasha organize a festival of arts and culture known as FACI to celebrate their culture and heritage, themed Àshà Ìbílẹ̀.
Chika is a given name or a nickname. It can be an Igbo given name or Japanese given name. It may be neither. Non-Igbo and Non-Japanese people using the name, include the following:








