
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from her ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Reproductive technology encompasses all current and anticipated uses of technology in human and animal reproduction, including assisted reproductive technology (ART), contraception and others. It is also termed Assisted Reproductive Technology, where it entails an array of appliances and procedures that enable the realization of safe, improved and healthier reproduction. While this is not true of all people, for an array of married couples, the ability to have children is vital. But through the technology, infertile couples have been provided with options that would allow them to conceive children.

The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom. It is a statutory body that regulates and inspects all clinics in the United Kingdom providing in vitro fertilisation (IVF), artificial insemination and the storage of human eggs, sperm or embryos. It also regulates human embryo research.
Insemination is the introduction of sperm into a female's reproductive system for the purpose of impregnating, also called fertilizing, the female for sexual reproduction. The sperm is introduced into the uterus of a mammal or the oviduct of an oviparous (egg-laying) animal. In mammals, insemination normally occurs during sexual intercourse or copulation, but insemination can take place in other ways, such as by artificial insemination.
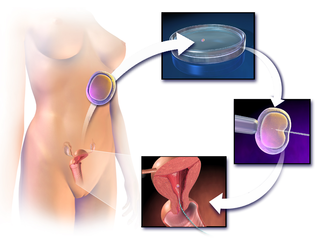
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose. ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits.
Egg donation is the process by which a woman donates eggs to enable another woman to conceive as part of an assisted reproduction treatment or for biomedical research. For assisted reproduction purposes, egg donation typically involves in vitro fertilization technology, with the eggs being fertilized in the laboratory; more rarely, unfertilized eggs may be frozen and stored for later use. Egg donation is a third-party reproduction as part of assisted reproductive technology.
A donor offspring, or donor conceived person, is conceived via the donation of sperm or ova, or both.
Menotropin is a hormonally active medication for the treatment of fertility disturbances. Frequently the plural is used as the medication is a mixture of gonadotropins. Menotropins are extracted from the urine of postmenopausal women.

The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act 1990 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It created the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority which is in charge of human embryo research, along with monitoring and licensing fertility clinics in the United Kingdom.

Oocyte cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve a woman's eggs (oocytes). This technique has been used to enable women to postpone pregnancy to a later date – whether for medical or social reasons. Several studies have shown that most infertility problems are due to germ cell deterioration related to aging. The intention of the procedure is that the woman may choose to have the eggs thawed, fertilized, and transferred to the uterus as embryos to facilitate a pregnancy in the future. The procedure's success rate varies depending on the age of the woman, with odds being higher in younger, adult women.
Sperm donation laws vary by country. Most countries have laws to cover sperm donations which, for example, place limits on how many children a sperm donor may give rise to, or which limit or prohibit the use of donor semen after the donor has died, or payment to sperm donors. Other laws may restrict use of donor sperm for in vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatment, which may itself be banned or restricted in some way, such as to married heterosexual couples, banning such treatment to single women or lesbian couples. Donated sperm may be used for insemination or as part of IVF treatment. Notwithstanding such laws, informal and private sperm donations take place, which are largely unregulated.
Fertility tourism is the practice of traveling to another country or jurisdiction for fertility treatment, and may be regarded as a form of medical tourism. A person who can become pregnant is considered to have fertility issues if they are unable to have a clinical pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. Infertility, or the inability to get pregnant, affects about 8-12% of couples looking to conceive or 186 million people globally. In some places, rates of infertility surpass the global average and can go up to 30% depending on the country. Areas with lack of resources, such as assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs), tend to correlate with the highest rates of infertility.
The Genetics & IVF Institute (GIVF) is an international provider of infertility and genetics services and products, and also engages in biomedical research in these fields. The Institute was founded in 1984 by Dr. Joseph D. Schulman and associates. GIVF headquarters are in Fairfax, VA, US, and its facilities include locations in Pennsylvania, Minnesota, California, and Texas in the United States, as well as in China, Mexico, and several other countries.
Sperm donation is the provision by a man of his sperm with the intention that it be used in the artificial insemination or other "fertility treatment" of one or more women who are not his sexual partners in order that they may become pregnant by him. Where pregnancies go to full term, the sperm donor will be the biological father of every baby born from his donations. The man is known as a sperm donor and the sperm he provides is known as "donor sperm" because the intention is that the man will give up all legal rights to any child produced from his sperm, and will not be the legal father. Sperm donation may also be known as "semen donation".
Mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT), sometimes called mitochondrial donation, is the replacement of mitochondria in one or more cells to prevent or ameliorate disease. MRT originated as a special form of in vitro fertilisation in which some or all of the future baby's mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) comes from a third party. This technique is used in cases when mothers carry genes for mitochondrial diseases. The therapy is approved for use in the United Kingdom. A second application is to use autologous mitochondria to replace mitochondria in damaged tissue to restore the tissue to a functional state. This has been used in clinical research in the United States to treat cardiac-compromised newborns.
Partner-assisted reproduction, reception of oocytes from partner (ROPA), reciprocal IVF,shared motherhood, partner IVF or co-IVF is a method of family building that is used by couples who both possess female reproductive organs. The method uses in vitro fertilization (IVF), a method that means eggs are removed from the ovaries, fertilized in a laboratory, and then one or more of the resulting embryos are placed in the uterus to hopefully create a pregnancy. Reciprocal IVF differs from standard IVF in that two partners are involved: the eggs are taken from one partner, and the other partner carries the pregnancy. In this way, the process is mechanically identical to IVF with egg donation. Reciprocal IVF offers the highest chance for pregnancy and a lower chance of a multiple births.
Female fertility is affected by age and is a major fertility factor for women. A woman's fertility is in generally good quality from the late teens to early thirties, although it declines gradually over time. Around 35, fertility is noted to decline at a more rapid rate. While many sources suggest a more dramatic drop at around 35, this is unclear, since few studies have been conducted since the 19th century. One 2004 study of European women found fertility of the 27–34 and the 35–39 groups had only a four-percent difference. At age 45, a woman starting to try to conceive will have no live birth in 50–80 percent of cases. Menopause, or the cessation of menstrual periods, generally occurs in the 40s and 50s and marks the cessation of fertility, although age-related infertility can occur before then. The relationship between age and female fertility is sometimes referred to as a woman's "biological clock."

N. Pandiyan is an Indian physician and academic who is the Chief consultant of Andrology and Reproductive Medicine, Head of the Department of Reproductive Medicine at Chettinad Health City, in Kelambakkam, Tamil Nadu, in India.

The London Women's Clinic is a private healthcare centre situated in London's Harley Street. Owned by Dr Kamal Ahuja, and founded in 1992, the centre has a reputation for helping single women and lesbian couples conceive with a total of over 85% of patients at its London clinic being in one of these categories.The clinic is closely associated with the London Sperm Bank and the London Egg Bank.

LGBT reproduction refers to lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people having biological children by means of assisted reproductive technology. It is distinct from LGBT parenting, which is a broader cultural phenomenon including LGBT adoption. In recent decades, developmental biologists have been researching and developing techniques to facilitate same-sex reproduction.








