
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's 4 million people.

This is a demography of the population of Panama including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.

The economy of Panama is based mainly on the services sector, which accounts for nearly 80% of its GDP and accounts for most of its foreign income. Services include the Panama Canal, banking, commerce, the Colón Free Trade Zone, insurance, container ports, and flagship registry, medical and health and tourism. The country's industry includes manufacturing of aircraft spare parts, cement, drinks, adhesives and textiles. Additionally, exports from Panama include bananas, shrimp, sugar, coffee, and clothing. Panama's economy is fully dollarized, with the US dollar being legal tender in the country. Panama was the first foreign country to adopt the U.S. dollar as its legal currency (1903) after its secession from Colombia temporarily deprived it of a local currency. Panama is a high income economy with a history of low inflation.

The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait.

Panama City, also known as Panama, is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has a total population of 1,938,000, with over 1,500,189 in its urban area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce.

Panama City Beach is a resort town in Bay County, Florida, United States, on the Gulf of Mexico coast. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 12,018. The city is often referred to under the umbrella term of "Panama City". Panama City Beach's slogan is "The World's Most Beautiful Beaches" due to the unique, sugar-white sandy beaches of northwest Florida.

Colón is a city and seaport in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay, and the Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former U.S. Army base, as well the former Panama Canal Zone towns of Cristobal, Margarita, and Coco Solo.
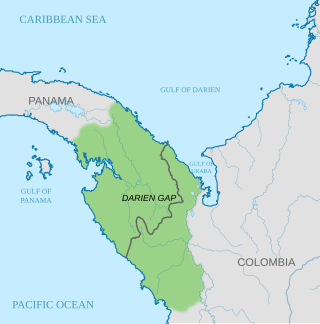
The Darién Gap is a geographic region in the Isthmus of Darien or Isthmus of Panama connecting the North and South American continents within Central America, consisting of a large watershed, forest, and mountains in Panama's Darién Province and the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department.

A Panama hat, also known as an Ecuadorian hat, a jipijapa hat, or a toquilla straw hat, is a traditional brimmed straw hat of Ecuadorian origin. Traditionally, hats were made from the plaited leaves of the Carludovica palmata plant, known locally as the toquilla palm or jipijapa palm, although it is a palm-like plant rather than a true palm.
Balboa is a district of Panama City, located at the Pacific entrance to the Panama Canal.

Bocas del Toro (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈbokaz ðel ˈtoɾo]; meaning "Mouths of the Bull") is a province of Panama. Its area is 4,643.9 square kilometers, comprising the mainland and nine main islands. The province consists of the Bocas del Toro Archipelago, Bahía Almirante, Chiriquí Lagoon, and adjacent mainland. The capital is the city of Bocas del Toro on Isla Colón. Other major cities or towns include Almirante and Changuinola. The province has a population of 125,461 as of 2010.

UTC−05:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −05:00. In North America, it is observed in the Eastern Time Zone during standard time, and in the Central Time Zone during the other eight months. The western Caribbean uses it year round.

The Panama national football team represents Panama in men's international football and is governed by the Panamanian Football Federation. The team represents all three FIFA, CONCACAF and the regional UNCAF.

The Isthmus of Panama, also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country of Panama and the Panama Canal. Like many isthmuses, it is a location of great geopolitical and strategic importance.

Coco Solo was a United States Navy submarine base and naval air station, active from 1918 to the 1960s.

Penonomé is the capital of the Panamanian province of Coclé. The town is located in the geographic center of Panama along the Inter-American Highway in the wide, flat lowlands of central Coclé.

Gatun is a small town on the Atlantic Side of the Panama Canal, located south of the city of Colón at the point in which Gatun Lake meets the channel to the Caribbean Sea. The town is best known as the site of the Panama Canal's Gatun Locks and Gatun Dam, built by the United States between 1906–1914.
Pedasí is a town and corregimiento situated on the south-eastern tip of the Azuero Peninsula on Panama’s Pacific coast. It is the capital of Pedasí District in Los Santos Province. Its population as of 1990 was 1,494; its population as of 2000 was 1,830. It had a population of 2,410 as of 2010. As of 1 July 2020 the population had grown to 4696.

Panamanians are people identified with Panama, a transcontinental country in Central America and South America, whose connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Panamanians, several or all of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their Panamanian identity. Panama is a multilingual and multicultural society, home to people of many different ethnicities and religions. Therefore, many Panamanians do not equate their nationality with ethnicity, but with citizenship and allegiance to Panama. The overwhelming majority of Panamanians are the product of varying degrees of admixture between European ethnic groups with native Amerindians who are indigenous to Panama's modern territory.

The Panama Papers are 11.5 million leaked documents that were published beginning on April 3, 2016. The papers detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 offshore entities. The documents, some dating back to the 1970s, were created by, and taken from, former Panamanian offshore law firm and corporate service provider Mossack Fonseca, and compiled with similar leaks into a searchable database.
















