
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs. The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding the testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly.

Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA1 gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. BRCA1 is a human tumor suppressor gene and is responsible for repairing DNA.

Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare, AR, genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage in the FA/BRCA pathway. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of normal bone marrow function and development of cancer. Among those affected, the majority develop cancer, most often acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), MDS, and liver tumors. 90% develop aplastic anemia by age 40. About 60–75% have congenital defects, commonly short stature, abnormalities of the skin, arms, head, eyes, kidneys, and ears, and developmental disabilities. Around 75% have some form of endocrine problem, with varying degrees of severity. 60% of FA is FANC-A, 16q24.3, which has later onset bone marrow failure.

Pemetrexed, sold under the brand name Alimta among others, is a chemotherapy medication for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)..

Desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor (DSRCT) is an aggressive and rare cancer that primarily occurs as masses in the abdomen. Other areas affected may include the lymph nodes, the lining of the abdomen, diaphragm, spleen, liver, chest wall, skull, spinal cord, large intestine, small intestine, bladder, brain, lungs, testicles, ovaries, and the pelvis. Reported sites of metastatic spread include the liver, lungs, lymph nodes, brain, skull, and bones. It is characterized by the EWS-WT1 fusion protein.
Total body irradiation (TBI) is a form of radiotherapy used primarily as part of the preparative regimen for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. As the name implies, TBI involves irradiation of the entire body, though in modern practice the lungs are often partially shielded to lower the risk of radiation-induced lung injury. Total body irradiation in the setting of bone marrow transplantation serves to destroy or suppress the recipient's immune system, preventing immunologic rejection of transplanted donor bone marrow or blood stem cells. Additionally, high doses of total body irradiation can eradicate residual cancer cells in the transplant recipient, increasing the likelihood that the transplant will be successful.
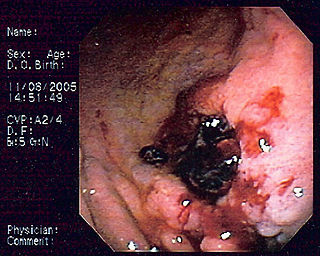
MALT lymphoma is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be affected. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the MALT, and is also called extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma.
Tegafur/uracil is a chemotherapy drug combination used in the treatment of cancer, primarily bowel cancer. It is also called UFT or UFUR.
Pulmonary toxicity is the medical name for side effects on the lungs.
Primary fallopian tube cancer (PFTC), often just tubal cancer, is a malignant neoplasm that originates from the fallopian tube.

Olaparib, sold under the brand name Lynparza, is a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults. It is a PARP inhibitor, inhibiting poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which include some ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.

PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP).

Peritoneal mesothelioma is the name given to the cancer that attacks the lining of the abdomen. This type of cancer affects the lining that protects the contents of the abdomen and which also provides a lubricating fluid to enable the organs to move and work properly.

A BRCA mutation is a mutation in either of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, while others have no proven impact. Harmful mutations in these genes may produce a hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome in affected persons. Only 5–10% of breast cancer cases in women are attributed to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, but the impact on women with the gene mutation is more profound. Women with harmful mutations in either BRCA1 or BRCA2 have a risk of breast cancer that is about five times the normal risk, and a risk of ovarian cancer that is about ten to thirty times normal. The risk of breast and ovarian cancer is higher for women with a high-risk BRCA1 mutation than with a BRCA2 mutation. Having a high-risk mutation does not guarantee that the woman will develop any type of cancer, or imply that any cancer that appears was actually caused by the mutation, rather than some other factor.
DirectHit is a pharmacodiagnostic test used to determine the tumor sensitivity or resistance to drug regimens recommended for the treatment of breast cancer by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. It is a noninvasive test performed on small amounts of tissue removed during the original surgery lumpectomy, mastectomy, or core biopsy. DirectHit was developed by CCC Diagnostics Inc., a biotechnology company established by former researchers from Johns Hopkins University. DirectHit was launched on 14 January 2010. Currently, it is the only available test for predicting treatment outcomes for anticancer chemotherapy drugs for breast cancer.

The abscopal effect is a hypothesis in the treatment of metastatic cancer whereby shrinkage of untreated tumors occurs concurrently with shrinkage of tumors within the scope of the localized treatment. R.H. Mole proposed the term “abscopal” in 1953 to refer to effects of ionizing radiation “at a distance from the irradiated volume but within the same organism.”
Dr. Cora Sternberg is an American medical oncologist at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, serving as a member of the Genitourinary (GU) Oncology Program. Dr. Sternberg facilitates the continued growth and development of clinical and translational research programs in GU malignancies. Dr. Sternberg is an internationally respected leader in the field of medical oncology and urological malignancies and a recognized expert in the area of new drug development. She is known for her seminal contributions in bladder cancer, her strong track record of sustained genito-urinary (GU) oncology leadership and collaboration in multiple practice-changing clinical trials, including novel medicines, and her current role applying her expertise in oncology and GU cancers to precision medicine to further improve outcomes for patients. Dr. Sternberg has been decidedly influential in the development of novel hormonal therapies and checkpoint inhibitors across the landscape of GU oncology as evidenced in her curriculum vitae. She is a globally respected researcher who has lectured extensively at universities and cancer symposia worldwide (>800). As Clinical Director of the Englander Institute for Precision Medicine (EIPM), Dr. Sternberg develops strategies to incorporate genomic sequencing and precision medicine throughout the Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian healthcare network, including Lower Manhattan, Brooklyn and Queens.
High-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant (HDC/BMT), also high-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplant, was an ineffective treatment regimen for metastatic breast cancer, and later high-risk breast cancer, that was considered promising during the 1980s and 1990s. With an overall idea that more is better, this process involved taking cells from the person's bone marrow to store in a lab, then to give such high doses of chemotherapy drugs that the remaining bone marrow was destroyed, and then to inject the cells taken earlier back into the body as replacement. It was ultimately determined to be no more effective than normal treatment, and to have significantly higher side effects, including treatment-related death.
FOLFOXIRI is a chemotherapy regimen for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. The role of FOLFOXIRI in colorectal cancer has been reviewed.

Jórunn Erla Eyfjörð is an Icelandic molecular biologist and professor emerita at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Iceland. She is known for her research on breast cancer genetics.












