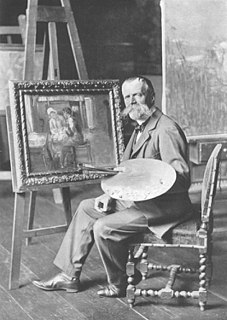Theodor Fontane was a German novelist and poet, regarded by many as the most important 19th-century German-language realist author. He published the first of his novels, for which he is best known today, only at age 58 after a career as a journalist.

Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th century. His work regarding Roman history is still of fundamental importance for contemporary research. He received the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1902 for being "the greatest living master of the art of historical writing, with special reference to his monumental work, A History of Rome", after having been nominated by 18 members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. He was also a prominent German politician, as a member of the Prussian and German parliaments. His works on Roman law and on the law of obligations had a significant impact on the German civil code.

Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass was a German mathematician often cited as the "father of modern analysis". Despite leaving university without a degree, he studied mathematics and trained as a school teacher, eventually teaching mathematics, physics, botany and gymnastics. He later received an honorary doctorate and became professor of mathematics in Berlin.

Hans Theodor Woldsen Storm, commonly known as Theodor Storm, was a German writer. He is considered to be one of the most important figures of German realism.

Paul Johann Ludwig von Heyse was a distinguished German writer and translator. A member of two important literary societies, the Tunnel über der Spree in Berlin and Die Krokodile in Munich, he wrote novels, poetry, 177 short stories, and about sixty dramas. The sum of Heyse's many and varied productions made him a dominant figure among German men of letters. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1910 "as a tribute to the consummate artistry, permeated with idealism, which he has demonstrated during his long productive career as a lyric poet, dramatist, novelist and writer of world-renowned short stories." Wirsen, one of the Nobel judges, said that "Germany has not had a greater literary genius since Goethe." Heyse is the fifth oldest laureate in literature, after Alice Munro, Jaroslav Seifert, Theodor Mommsen and Doris Lessing.

Friedrich Karl Theodor Zarncke, German philologist, was born in Zahrensdorf, Mecklenburg-Schwerin, the son of a country pastor.

Karl Ferdinand Gutzkow was a German writer notable in the Young Germany movement of the mid-19th century.

Erwin Friedrich Theodor Stresemann was a German naturalist and ornithologist. Stresemann was an ornithologist of extensive breadth who compiled one of the first and most comprehensive accounts of avian biology of its time as part of the Handbuch der Zoologie. In the process of his studies on birds, he also produced one of the most extensive historical accounts on the development of the science of ornithology. He influenced numerous ornithologists around him and oversaw the development of ornithology in Germany as editor of the Journal für Ornithologie. He also took an interest in poetry, philosophy and linguistics. He published a monograph on the Paulohi language based on studies made during his ornithological expedition to the Indonesian island.

Karl Christian Friedrich Krause was a German philosopher, whose doctrines became known as Krausism. Krausism, when considered in its totality as a complete, stand-alone philosophical system, had only a small following in Germany, France, and Belgium, in contradistinction to certain other philosophical systems that had a much larger following in Europe at that time. However, Krausism became very popular and influential in Restoration Spain - not as a complete, comprehensive philosophical system per se, but as a broad cultural movement. In Spain, Krausism was known as "Krausismo", and Krausists were known as "Krausistas". Outside of Spain, the Spanish Krausist cultural movement was referred to as Spanish Krausism.

Alexander Theodor von Middendorff was a zoologist and explorer of Baltic German and Estonian extraction.

A Burschenschaft is one of the traditional Studentenverbindungen of Germany, Austria and Chile. Burschenschaften were founded in the 19th century as associations of university students inspired by liberal and nationalistic ideas. They were significantly involved in the March Revolution and the unification of Germany. After the formation of the German Empire in 1871, they faced a crisis, as their main political objective had been realized. So-called Reformburschenschaften were established, but these were dissolved by the National Socialist regime in 1935/6. In West Germany, the Burschenschaften were re-established in the 1950s, but they faced a renewed crisis in the 1960s and 1970s, as the mainstream political outlook of the German student movement of that period swerved to the radical left. Roughly 160 Burschenschaften exist today in Germany, Austria and Chile.

Friedrich Karl Christian Ludwig Büchner was a German philosopher, physiologist and physician who became one of the exponents of 19th-century scientific materialism.

Ritter Karl Wilhelm von Gümbel, German geologist, was born at Dannenfels, in the Palatinate of the Rhine, and is known chiefly by his researches on the geology of Bavaria. He was the brother of bryologist Wilhelm Theodor Gümbel (1812–1858).

Karl Theodor Helfferich was a German politician, economist, and financier from Neustadt an der Weinstraße in the Palatinate.
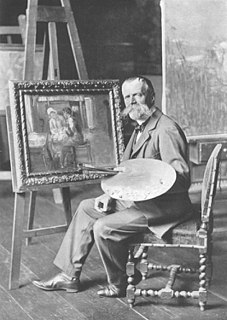
Fritz von Uhde was a German painter of genre and religious subjects. His style lay in-between Realism and Impressionism, he was once known as "Germany's outstanding impressionist" and he became one of the first painters to introduce plein-air painting in his country.

Benno Frederick Toermer (Törmer), was a painter. He was born and educated in Dresden, Saxony, in what is now Germany. He also studied and worked in Rome, Italy. Rome became his second home where he lived, with brief interruptions, until his death from a heart attack on 6 February 1859. While at the Academy in Dresden, Toermer painted religious and historical subjects, such as Joseph's interpreting dreams while in prison. When in Italy, his subjects were based on gods of legend and romantic motifs. Toermer often painted in the style of the old Dutch. In 1852 Toemer was invited to exhibit a work entitled “The Wedding Morning – Ill Omen” at the Royal Academy in London. He was an honorary member of the Patriotic Society of Natural History in Dresden. In July 1853 he was awarded the title of professor of Dresden by the Saxon Art Association.

Paul Georg Heinrich Martin Reinhold Leverkühn was a German physician and ornithologist.
Friedrich August Rothpletz was a German geologist and paleontologist.

Karl Mediz was an Austrian landscape and portrait painter. Many of his works are in the Symbolist style.