Related Research Articles
Psychological statistics is application of formulas,theorems,numbers and laws to psychology. Statistical methods for psychology include development and application statistical theory and methods for modeling psychological data. These methods include psychometrics,factor analysis,experimental designs,and Bayesian statistics. The article also discusses journals in the same field.
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally covers specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing,measurement,assessment,and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence,introversion,mental disorders,and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales.
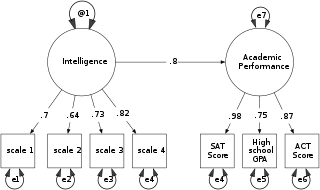
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a diverse set of methods used by scientists doing both observational and experimental research. SEM is used mostly in the social and behavioral sciences but it is also used in epidemiology,business,and other fields. A definition of SEM is difficult without reference to technical language,but a good starting place is the name itself.
Quantitative psychology is a field of scientific study that focuses on the mathematical modeling,research design and methodology,and statistical analysis of psychological processes. It includes tests and other devices for measuring cognitive abilities. Quantitative psychologists develop and analyze a wide variety of research methods,including those of psychometrics,a field concerned with the theory and technique of psychological measurement.

Freedom in the World is a yearly survey and report by the U.S.-based non-governmental organization Freedom House that measures the degree of civil liberties and political rights in every nation and significant related and disputed territories around the world.
Floyd Henry Allport was an American psychologist who is often considered "the father of experimental social psychology",having played a key role in the creation of social psychology as a legitimate field of behavioral science. His book Social Psychology (1924) impacted all future writings in the field. He was particularly interested in public opinion,attitudes,morale,rumors,and behavior. He focused on exploration of these topics through laboratory experimentation and survey research.
Latent growth modeling is a statistical technique used in the structural equation modeling (SEM) framework to estimate growth trajectories. It is a longitudinal analysis technique to estimate growth over a period of time. It is widely used in the field of psychology,behavioral science,education and social science. It is also called latent growth curve analysis. The latent growth model was derived from theories of SEM. General purpose SEM software,such as OpenMx,lavaan,AMOS,Mplus,LISREL,or EQS among others may be used to estimate growth trajectories.
Timothy Zook Keith is an American psychologist. His research is focused on the nature and measurement of intelligence,understanding school learning,and on the methodologies of confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modelling,and he is considered a leading authority on in the use of structural equation modeling and confirmatory factor analysis in school psychology. He has been a Fellow of the American Psychological Association since 1991.
In sociology,structural cohesion is the conception of a useful formal definition and measure of cohesion in social groups. It is defined as the minimal number of actors in a social network that need to be removed to disconnect the group. It is thus identical to the question of the node connectivity of a given graph in discrete mathematics. The vertex-cut version of Menger's theorem also proves that the disconnection number is equivalent to a maximally sized group with a network in which every pair of persons has at least this number of separate paths between them. It is also useful to know that k-cohesive graphs are always a subgraph of a k-core,although a k-core is not always k-cohesive. A k-core is simply a subgraph in which all nodes have at least k neighbors but it need not even be connected.

Lloyd Bond was an American researcher in the field of psychometrics. As of 2009,he was a consulting scholar at the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching in Stanford,California;he served as a senior scholar at the foundation from 2002 to 2008.
David Reuben Jerome Heise was a social psychologist who originated the idea that affectual processes control interpersonal behavior. He contributed to both quantitative and qualitative methodology in sociology. He retired from undergraduate teaching in 2002,but continued research and graduate student consulting as Rudy Professor of Sociology Emeritus at Indiana University. He was most well known for his work on affect control theory.
Anuška Ferligoj is a Slovenian mathematician,born August 19,1947,in Ljubljana,Slovenia,whose specialty is statistics and network analysis. Her specific interests include multivariate analysis,cluster analysis,social network analysis,methodological research of public opinion,analysis of scientific networks. She is Fellow of the European Academy of Sociology.
Mark Daniel Regnerus is a sociologist and professor at the University of Texas at Austin. His main fields of interest are sexual behavior,relationship dynamics,and religion.

Kenneth Dodge is the William McDougall Distinguished Professor of Public Policy and Professor of Psychology and Neuroscience at Duke University. He is also the founding and past director of the Duke University Center for Child and Family Policy and founder of Family Connects International.

Structural Equations with Latent Variables is a statistics textbook on structural equation modeling by Kenneth Bollen published in 1989. It covers topics in the statistics like measurement validity and reliability,overall fit indices,model identification,causality,and the statistical software package LISREL. Examples from sociology,economics,and psychology are used in the textbook to illustrate the practical applications of these methods. The book examines covariances rather than individual cases. It is used in graduate-level courses that focus on structural equation modeling within the social sciences.
Patrick James Curran is an American psychologist and statistician. He is a professor of quantitative psychology at the University of North Carolina,where he is also a faculty member at the Center for Developmental Science.
Daniel John Bauer is an American statistician,professor,and director of the quantitative psychology program at the University of North Carolina,where he is also on the faculty at the Center for Developmental Science. He is known for rigorous methodological work on latent variable models and is a proponent of integrative data analysis,a meta-analytic technique that pools raw data across multiple independent studies.
Kenneth Carl Land is the John Franklin Crowell Professor Emeritus of Sociology at Duke University,where he is also a research professor at the Social Science Research Institute. He is also a fellow at the Center for the Study of Aging at Duke University Medical Center and a faculty fellow at the Duke University Center for Child and Family Policy.
John J. McArdle is Professor of Psychology and Gerontology at the University of Southern California (USC),where he is also director of the Unified Studies of Cognition (CogUSC) Lab. He is known for his work on quantitative research methodology and on the changes in cognitive function and personality that occur as individuals age.

Marko Sarstedt is a German academic and a marketing researcher. He is a Full Professor at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and Adjunct Research Professor at Babeș-Bolyai-University.
References
- 1 2 3 "Bollen's CV" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-07-02. Retrieved 2013-08-14., University of North Carolina
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kenneth A. Bollen Kenneth A. Bollen biography, Advisory Committee for Social, Behavioral & Economic Sciences members, National Science Foundation, accessed 31 August 2013
- ↑ SBE Advisory Committee Members, National Science Federation, accessed 31 August 2013
- ↑ "KEN BOLLEN WINS 2018 CAREER AWARD FOR LIFETIME ACHIEVEMENT!" . Retrieved 2018-08-22.
- ↑ Highly Cited List: B, see entry for Kenneth A. Bollen. Accessed August 14, 2013
- ↑ "ASA Methodology Section Home Page". .asanet.org. Archived from the original on 2014-04-07. Retrieved 2013-08-15.