
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. Their Latin name, Picti, appears in written records from the 3rd to the 10th century. Early medieval sources report the existence of a distinct Pictish language, which today is believed to have been an Insular Celtic language, closely related to the Brittonic spoken by the Britons who lived to the south.

Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a 96-mile (154-kilometre) border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and the Irish Sea to the south. The country also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt – the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands – in the Scottish Lowlands.
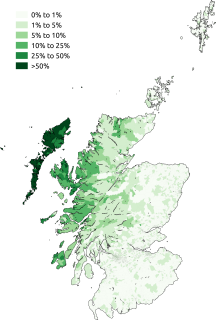
Scottish Gaelic, also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by Gaels in both Ireland and Scotland down to the 16th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names.

Sir William Wallace was a Scottish knight who became one of the main leaders during the First War of Scottish Independence.

The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. The current monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who ascended the throne in 1952.
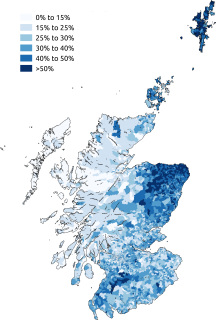
Scots is an Anglic language variety of the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland. It is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300).

James VI and I was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until his death in 1625. The kingdoms of Scotland and England were individual sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, though both were ruled by James in personal union.
Scottish English is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standard English may be defined as "the characteristic speech of the professional class [in Scotland] and the accepted norm in schools". IETF language tag for "Scottish Standard English" is en-scotland.

Hamilton Crescent is a cricket ground located in the Partick area of Glasgow, Scotland. It is the home of the West of Scotland Cricket Club.

The Scotland national cricket team represents the country of Scotland. They play their home matches at The Grange, Edinburgh, and also some other venues.
Canmore is an online database of information on over 320,000 archaeological sites, monuments, and buildings in Scotland. It was begun by the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. Historic Environment Scotland has maintained it since 2015. The Canmore database is part of the National Record of the Historic Environment, formerly the National Monuments Record of Scotland and contains around 1.3 million catalogue entries. It includes marine monuments and designated official wreck sites, such as the wreck of HMS Pheasant (1916).

basketballscotland is the governing body of the sport of basketball in Scotland. The organisation manages national competitions and runs the Scotland national basketball team. They also have a cup final for all age groups of the course of a weekend during the early months of the year.

BAFTA in Scotland is the Scottish branch of the British Academy of Film and Television Arts. Formed in 1986, the branch holds two annual awards ceremonies recognising the achievement by performers and production staff in Scottish film, television and video games. These Awards are separate from the British Academy Television Awards and British Academy Film Awards.

The Scottish Sub Aqua Club (ScotSAC) was founded in Glasgow in 1953. Today it is a company limited by guarantee with nearly 70 branches and 1200 members. ScotSAC instructors provide scuba diving training to branch members on an amateur basis. It is recognised by sportscotland as the National Governing Body for Sub Aqua in Scotland.
Uamh an Claonaite is the longest cave in Scotland. It consists of a series of dry passages and a series of at least six sumps which have been dived over the years.

The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England. It suffered many invasions by the English, but under Robert the Bruce it fought a successful War of Independence and remained an independent state throughout the late Middle Ages. Following the annexation of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles from the Kingdom of Norway in 1266 and 1472 respectively, and the final capture of the Royal Burgh of Berwick by the Kingdom of England in 1482, the territory of the Kingdom of Scotland corresponded to that of modern-day Scotland, bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the southwest. In 1603, James VI of Scotland became King of England, joining Scotland with England in a personal union. In 1707, the two kingdoms were united to form the Kingdom of Great Britain under the terms of the Acts of Union.
Robert Gordon University Boat Club (RGUBC) is the rowing club at Robert Gordon University in Aberdeen, Scotland. The club is affiliated to Scottish Rowing. In 2012 the club formed University Rowing Aberdeen (URA) in partnership with the Aberdeen University Boat Club so that both clubs could share resources, funding and coaching.
The Convention of Estates of Scotland was a sister institution to the Scottish Parliament which sat from the early sixteenth century. Initially it was only attended by the clergy and nobles, but the burgh commissioners were later added. The Convention of Estates differed from Parliament in that it could be summoned by the King for the limited purpose of raising taxation, but could not pass other legislation.

The Scottish Premiership, known as the cinch Premiership for sponsorship reasons, is the top division of the Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL), the league competition for men's professional football clubs in Scotland. The Scottish Premiership was established in July 2013, after the SPFL was formed by a merger of the Scottish Premier League and Scottish Football League. There are 12 teams in this division, with each team playing 38 matches per season. Sixteen clubs have played in the Scottish Premiership since its creation in the 2013–14 season. Rangers are the current league champions, having won the 2020–21 Scottish Premiership.

The NHS Louisa Jordan was a temporary emergency critical care hospital created to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic in Scotland. It was located within the SEC Centre in Glasgow.














