
The Ionian Sea is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese.

Corfu or Kerkyra is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the nation's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of Othonoi, Ereikoussa, and Mathraki. The principal city of the island is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University.

The Ionian Islands are a group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese, but the group includes many smaller islands in addition to the seven principal ones.

Paxos is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, lying just south of Corfu. As a group with the nearby island of Antipaxos and adjoining islets, it is also called by the plural form Paxi or Paxoi. The main town and the seat of the municipality is Gaios. The smallest of the seven main Ionian Islands, Paxos has an area of 25.3 square kilometres (9.8 sq mi), while the municipality has an area of 30.121 km2 (11.630 sq mi) and a population of about 2,500.
Kensington is a district in London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. It may also refer to:
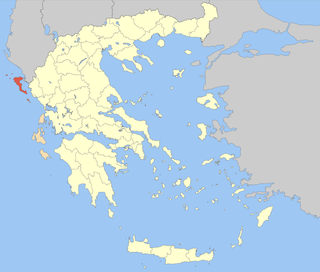
Corfu is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of the Ionian Islands. The capital of the regional unit is the town of Corfu. The regional unit consists of the islands of Corfu, Paxoi, Othonoi, Ereikoussa, Mathraki and several smaller islands, all in the Ionian Sea.

Corfu or Kerkyra is a city and a former municipality on the island of Corfu, Ionian Islands, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform, it is part of the municipality Central Corfu and Diapontia Islands. It is the capital of the municipality and of the Corfu regional unit. The city also serves as a capital for the region of the Ionian Islands. The city is a major tourist attraction and Greek regional centre and has played an important role in Greek history since antiquity.

Othonoi is a small inhabited Greek island in the Ionian Sea, located northwest of Corfu, and is the westernmost point of Greece. Othonoi is the largest and most populated of the Diapontian Islands. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality of Central Corfu and Diapontian Islands.

Thinali is a former municipality on the island of Corfu, Ionian Islands, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality North Corfu, of which it is a municipal unit. It is located in the northernmost part of the island of Corfu, in the middle of the north coast. With its 77.899 km², it was the largest municipality on the island. The seat of the municipality was the town of Acharavi. It is located northwest of the city of Corfu. Last mayor of Thinali was Varelis Spiridon from village Lafki.

Angelokastro is a Byzantine castle on the island of Corfu, Greece. It is located at the top of the highest peak of the island's shoreline in the northwest coast near Palaiokastritsa and built on particularly precipitous and rocky terrain. It stands 1,000 ft (305 m) on a steep cliff above the sea and surveys the City of Corfu and the mountains of mainland Greece to the southeast and a wide area of Corfu toward the northeast and northwest.
Vido is an island of the Ionian Islands group of Greece. It is a small island at the mouth of the port of Corfu.

Corfiot Italians are a population from the Greek island of Corfu (Kerkyra) with ethnic and linguistic ties to the Republic of Venice. Their name was specifically established by Niccolò Tommaseo during the Italian Risorgimento. During the first half of the 20th century, Mussolini successfully used the Corfiot Italians as a pretext to occupy Corfu twice.

Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan seas, and to the west by the Ionian Sea which separates Greece from Italy.

The Ionian Islands Region is the smallest by area of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece located in the Ionian Sea. It comprises all the Ionian Islands except Kythera, which, although historically part of the island group, was separated and integrated to the Attica Region.

The Ionian Islands were an overseas possession of the Republic of Venice from the mid-14th century until the late 18th century. The conquest of the islands took place gradually. The first to be acquired was Cythera and the neighboring islet of Anticythera, indirectly in 1238 and directly after 1363. In 1386 the Council of Corfu, which was the governing body of the island, voted to make Corfu a vassal of Venice. During the Venetian period the Council remained the most powerful institution on the island. A century later, Venice captured Zante in 1485, Cephalonia in 1500 and Ithaca in 1503. These three islands modelled their administration on Corfu's model and formed their own councils. The conquest was completed in 1718 with the capture of Lefkada. Each of the islands remained part of the Venetian Stato da Màr until Napoleon Bonaparte dissolved the Republic of Venice in 1797. The Ionian Islands are situated in the Ionian Sea, off the west coast of Greece. Cythera, the southernmost, is just off the southern tip of the Peloponnese and Corfu, the northernmost, is located at the entrance of the Adriatic Sea. It is believed that the Venetian period on the Ionian Islands was generally prosperous, especially compared with the coinciding Tourkokratia — Turkish rule over the remainder of present-day Greece.

Gardiki Castle is a 13th-century Byzantine castle on the southwestern coast of Corfu and the only surviving medieval fortress on the southern part of the island. It was built by a ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, and was one of three castles which defended the island before the Venetian era (1401–1797). The three castles formed a defensive triangle, with Gardiki guarding the island's south, Kassiopi Castle the northeast and Angelokastro the northwest

The Old Fortress of Corfu is a Venetian fortress in the city of Corfu. The fortress covers the promontory which initially contained the old town of Corfu that had emerged during Byzantine times.

The Venetian arsenal at Gouvia was a shipyard built by the Republic of Venice during their rule over the island of Corfu. It was located on the west side of what used to be called "Govino Bay", the current location of the modern village of Gouvia.
Corfu is an island in the Ionian Sea, owned by Greece. The following is a synopsis of National Roads in Corfu.

The Diapontian Islands or Diapontia Islands (Greek: Διαπόντια Νησιά, romanized: Diapontia Νisia, also known as Othonoi Islands are a Greek island group in the Ionian Sea. They are located northwest of Corfu. The main and the only inhabited islands of the archipelago are Othoni, Ereikoussa and Mathraki. The complex includes also the islets and rocks of Diakopo, Diaplo, Karavi, Kastrino, Leipso, Ostrako, Plaka, Plateia and Tracheia.
















