
IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, with operations in over 170 countries. IBM Research is the largest industrial research organization in the world and has twelve labs on six continents.
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies.
Mark E. Dean is an American inventor and computer engineer. He developed the ISA bus with his partner Dennis Moeller, and he led a design team for making a one-gigahertz computer processor chip. He holds three of nine PC patents for being the co-creator of the IBM personal computer released in 1981. In 1995, Dean was named the first ever African-American IBM Fellow.
Service-orientation is a design paradigm for computer software in the form of services. The principles of service-oriented design stress the separation of concerns in the software. Applying service-orientation results in units of software partitioned into discrete, autonomous, and network-accessible units, each designed to solve an individual concern. These units qualify as services.

IONA Technologies, Inc. was an Irish software company founded in 1991. It began as a campus company linked to Trinity College Dublin had its headquarters in Dublin, and eventually also expanded its offices in Boston and Tokyo. It specialised in distributed service-oriented architecture (SOA) technology, its products connecting systems and applications by creating a network of services without requiring a centralised server or creating an information technology project. IONA was the first Irish company to float on the NASDAQ exchange. It was valued at up to US$1.75 billion at its peak. It was one of the world's 10 largest software-only companies, and around 30 new ventures spun out from it. IONA was sold to Progress Software in 2008.
Donald Ferguson is a Technical Fellow and Chief SW Architect at Ansys, Inc. Before joining Ansys, Ferguson was a Professor of Professional Practice in Computer Science at Columbia University. Before joining Columbia in 2018, he was vice president and CTO for software at Dell. Previously he was CTO, Distinguished Engineer and Executive VP at CA, Inc., formerly known as Computer Associates.
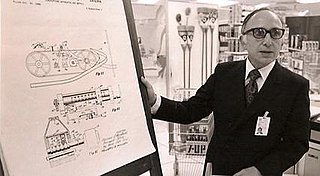
Norman Joseph Woodland was an American inventor and engineer, best known as one of the inventors of the barcode, for which he received a patent in October 1952. Later, employed by IBM, he developed the format which became the ubiquitous Universal Product Code (UPC) of product labeling and check-out stands.
Amanda Elizabeth Chessell is a computer scientist and a Distinguished Engineer at IBM. She has been awarded the title of IBM Master Inventor. She is also a Member of the IBM Academy of Technology.
Service-oriented modeling is the discipline of modeling business and software systems, for the purpose of designing and specifying service-oriented business systems within a variety of architectural styles and paradigms, such as application architecture, service-oriented architecture, microservices, and cloud computing.

Neil Gilbert Siegel is an American computer scientist, systems engineer, and engineer, known for his development of many key systems for the United States military, including the Blue-Force Tracking system, the U.S. Army's first unmanned air vehicle system, and the US Army forward-area air defense system. Several of his inventions also found their way into consumer products, such as hand-held devices whose map displays automatically orient themselves to align with the real-world's cardinal points. He also participated in the development of techniques that are now widely-used in healthcare.

The Sue Duncan Children's Center is a non-profit organization on the South Side of Chicago founded in 1961 by Susan Duncan, mother of former Secretary of Education under President Barack Obama's administration, Arne Duncan. The center runs afterschool and summer programs to provide children of all ages free tutoring and academic support as well as access to extracurricular activities such as basketball and art. The center currently serves approximately 80 students.
Thomas Erl is a Canadian author, and public speaker known for major contributions to the field of service-oriented architecture. Author of eight books on Service Orientation, Erl defined eight widely accepted principles of service orientation.

Kevin Surace is an American technology innovator, producer and entrepreneur. He is the CTO of Appvance, creator of an Generative AI software QA platform. He was Inc. Magazine’s 2009 entrepreneur of the Year. He is the inventor of QuietRock Soundproof Drywall.
Eduardo T. Kahan was an executive at IBM for 26 years. He was named a distinguished engineer in 1997 and awarded the designation of IBM Fellow in 2005. Kahan was the Chief Architect and CTO of the IBM Software Group, Enterprise Integration and was a certified consultant and an active member of the IBM Academy of Technology. His responsibilities included strategy development, design, and development of advanced technologies for Web Services, service oriented architectures, and enterprise integration products, tools, and solutions for IBM clients.

Marian Rogers Croak is an American engineer known for her voice over IP (VoIP) related inventions. Croak worked for three decades at Bell Labs and AT&T where she filed over 200 patents and works at Google since 2014 where she is Vice President of Engineering, In 2022, she was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame for her work with VoIP.

Frank Leymann is a German computer scientist and mathematician. He is professor of computer science at the University of Stuttgart, Germany, and director and founder of the Institute of Architecture of Application Systems (IAAS).
Gennaro "Jerry" Cuomo is an American software engineer who has worked for IBM since 1987. Holding the title of IBM Fellow, Cuomo is known as one of the founding fathers of IBM WebSphere Software, a software framework and middleware that hosts Java-based web applications.

Michael (Mike) Papazoglou is a Greek/Australian emeritus professor, computer science researcher and author known for his contributions to 'Service-Oriented Computing'. His main research interests include Distributed computing, Database#Database management system, Big data, Service, Domain-specific language and Cloud computing. In more recent years he shifted his focus to pursuing Emerging technologies, Industrial engineering, Smart Applications and Smart Technology Solutions for Healthcare and Manufacturing.

Michael Karl Gschwind is an American computer scientist at Nvidia in Santa Clara, California. He is recognized for his seminal contributions to the design and exploitation of general-purpose programmable accelerators, as an early advocate of sustainability in computer design and as a prolific inventor.










