
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat.

Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, feeling tired, and sores that do not heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon.

A randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment that aims to reduce certain sources of bias when testing the effectiveness of new treatments; this is accomplished by randomly allocating subjects to two or more groups, treating them differently, and then comparing them with respect to a measured response. One group—the experimental group—receives the intervention being assessed, while the other—usually called the control group—receives an alternative treatment, such as a placebo or no intervention. The groups are monitored under conditions of the trial design to determine the effectiveness of the experimental intervention, and efficacy is assessed in comparison to the control. There may be more than one treatment group or more than one control group.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction. Other CVDs include stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis.
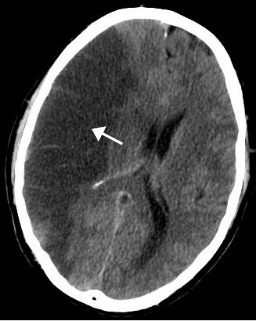
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control.
Derek Summerfield is an honorary senior lecturer at London's Institute of Psychiatry and a member of the Executive Committee of Transcultural Special Interest Group at the Royal College of Psychiatry. He is also an Honorary Fellow of the Egyptian Psychiatric Association. He has published around 150 papers and has made other contributions in medical and social sciences literature.

Jim van Os is a Dutch professor of Psychiatric Epidemiology and Public Mental Health at Utrecht University Medical Centre, the Netherlands.
Sir Richard Peto is an English statistician and epidemiologist who is Professor of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology at the University of Oxford, England.

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a surgical procedure used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. The process involves combining coronary angioplasty with stenting, which is the insertion of a permanent wire-meshed tube that is either drug eluting (DES) or composed of bare metal (BMS). The stent delivery balloon from the angioplasty catheter is inflated with media to force contact between the struts of the stent and the vessel wall, thus widening the blood vessel diameter. After accessing the blood stream through the femoral or radial artery, the procedure uses coronary catheterization to visualise the blood vessels on X-ray imaging. After this, an interventional cardiologist can perform a coronary angioplasty, using a balloon catheter in which a deflated balloon is advanced into the obstructed artery and inflated to relieve the narrowing; certain devices such as stents can be deployed to keep the blood vessel open. Various other procedures can also be performed.
Treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is variable and uncertain, and the condition is primarily managed rather than cured.
Sir Rory Edwards Collins FMedSci FRS is a British physician who is Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology at the Clinical Trial Service Unit within the University of Oxford, the head of the Nuffield Department of Population Health and a Fellow of Green Templeton College, Oxford. His work has been in the establishment of large-scale epidemiological studies of the causes, prevention and treatment of heart attacks, other vascular disease, and cancer, while also being closely involved in developing approaches to the combination of results from related studies ("meta-analyses").

Sir Andrew Paul Haines, is a British epidemiologist and academic. He was the Director of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine from 2001 to 2010.
Prevention of type 2 diabetes can be achieved with both lifestyle changes and use of medication. The American Diabetes Association categorizes prediabetes as a high-risk group that has glycemic levels higher than normal but does not meet criteria for diabetes. Without intervention people with prediabetes progress to type 2 diabetes with a 5% to 10% rate. Diabetes prevention is achieved through weight loss and increased physical activity, which can reduce the risk of diabetes by 50% to 60%.
Renal sympathetic denervation (RSDN), is a minimally invasive, endovascular catheter based procedure using radiofrequency ablation or ultrasound ablation aimed at treating resistant hypertension. Nerves in the wall of the renal artery are ablated by applying radiofrequency pulses or ultrasound to the renal arteries. This causes reduction of sympathetic afferent and efferent activity to the kidney and blood pressure can be decreased. Early data from international clinical trials without sham controls was promising - demonstrating large blood pressure reductions in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. However, in 2014 a prospective, single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial failed to confirm a beneficial effect on blood pressure. A 2014 consensus statement from The Joint UK Societies did not recommend the use of renal denervation for treatment of resistant hypertension on current evidence.

Anthony Costello is a British paediatrician. Until 2015 Costello was Professor of International Child Health and Director of the Institute for Global Health at the University College London. Costello is most notable for his work on improving survival among mothers and their newborn infants in poor populations of developing countries. From 2015 to 2018 he was director of maternal, child and adolescent health at the World Health Organization in Geneva.
Allegiance bias in behavioral sciences is a bias resulted from the investigator's or researcher's allegiance to a specific school of thought. Researchers/investigators have been exposed to many types of branches of psychology or schools of thought. Naturally they adopt a school or branch that fits with their paradigm of thinking. More specifically, allegiance bias is when this leads therapists, researchers, etc. believing that their school of thought or treatment is superior to others. Their superior belief to these certain schools of thought can bias their research in effective treatments trials or investigative situations leading to allegiance bias. Reason being is that they may have devoted their thinking to certain treatments they have seen work in their past experiences. This can lead to a fundamental errors to the results of their research they are conducting. Their “pledge” to stay within their own paradigm of thinking may affect their ability to find more effective treatments to help the patient or situation they are investigating.

Sir Graham Thornicroft is a British psychiatrist, researcher and professor of community psychiatry at the Centre for Global Mental Health and Centre for Implementation Science at King's College London. He is best known for his work on community mental health services, stigma and discrimination, and global mental health. He has published 30 books, and has written over 500 peer-reviewed scientific papers. Thornicroft was made a knight bachelor in the 2017 Queen's Birthday Honours for services to mental health.
Stephanie Anne Amiel, is a British physician and academic, specialising in type 1 diabetes. Since 1995, she has been the R. D. Lawrence Professor of Diabetic Medicine at King's College London and a consultant at King's College Hospital.
Roy Taylor is a physician and diabetologist, who is currently the Director of Newcastle Magnetic Resonance Centre. Scopus h-index is 47.
Peymané Adab is a British physician who is a Professor of Public Health at the University of Birmingham. She leads the Institute of Applied Health Research Chronic Disease Management Team. Adab investigates the epidemiology and management of obesity and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.










