This is a list of aviation-related events from 1984:
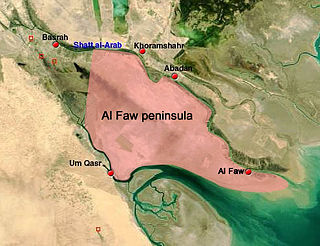
The al-Faw peninsula is a peninsula in the Persian Gulf, located in the extreme southeast of Iraq. The marshy peninsula is 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Iraq's second largest city, Basra, and is part of a delta for the Shatt al-Arab river, formed by the confluence of the major Euphrates and Tigris rivers. The al-Faw peninsula borders Iran to the northeast, with the cities of Abadan and Khorramshahr on the opposite side of the Shatt al-Arab, and Kuwait to the southwest, opposite from Bubiyan Island and Warbah Island, near the Iraqi city of Umm Qasr.

The SEAL Delivery Vehicle (SDV) is a manned submersible and a type of swimmer delivery vehicle used to deliver United States Navy SEALs and their equipment for special operations missions. It is also operated by the Royal Navy's Special Boat Service, which operates 3 SDVs.

HMAS Stuart is an Anzac-class frigate of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). She was built at Williamstown in Victoria, and commissioned into the RAN in 2002. The frigate is operational as of 2016.

USS Germantown (LSD-42) is the second Whidbey Island-class dock landing ship in the United States Navy. She is the second navy ship named after the Revolutionary War Battle of Germantown.

The Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC), known prior to 1929 as the Turkish Petroleum Company (TPC), is an oil company which, between 1925 and 1961, had a virtual monopoly on all oil exploration and production in Iraq. It is jointly owned by some of the world's largest oil companies and headquartered in London, England, although today it is a paper entity with historical rights and plays no part in the modern development of Middle Eastern oil.

The Iraqi Navy is one of the components of the military of Iraq. Its primary responsibilities are the protection of Iraq's coastline and offshore assets. Initially called the Iraqi Coastal Defense Force, its official name was changed on 12 January 2005.
William Dennis Goodchild Hunt MBE served a full career in the British Army as an Ammunition Technician (AT) and Ammunition Technical Officer (ATO) and served in the UK, mainland Europe as well as the Middle and Far East.

The Iranian Navy traditionally located in the shallow waters of the Persian Gulf, has always been the smallest of the country's military forces. An Iranian navy in one form or another has existed since Achaemenid times in 500 BC. The Phoenician navy played an important role in the military efforts of the Persians in late antiquity in protecting and expanding trade routes along the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. With the Pahlavi dynasty in the 20th century that Iran began to consider building a strong navy to project its strength into the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. In more recent years, the country has engaged in domestic ship building industries in response to the western-backed Iraqi invasion of Iran, which left it without suppliers during an invasion.

USS Firebolt (PC-10) is the 10th member of the Cyclone-class of coastal patrol boats. She is a 174 ft (53 m) vessel with a crew of approximately 30 sailors, normally homeported at Naval Amphibious Base Little Creek, Norfolk, Virginia. Her armament includes two Mk38 chain guns, two Mk19 automatic grenade launchers, and two .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, as well as six Stinger missiles. She was laid down by Bollinger Shipyards on 17 September 1993, launched on 10 June 1994, and commissioned into the Navy on 10 June 1995.

Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in Western Asia, bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to the southwest and Syria to the west. The capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Arabs, Kurds, Turkmen, Assyrians, Yazidis, Shabakis, Armenians, Mandaeans, Circassians, Sabians and Kawliya. Around 99% of the country's 38 million citizens are Muslims, with small minorities of Christians, Yarsans, Yezidis and Mandeans also present. The official languages of Iraq are Arabic and Kurdish.

USS Typhoon (PC-5) is the fifth United States Navy Cyclone-class patrol ship. Typhoon was laid down 15 May 1992 at Bollinger Shipyards, in Lockport, Louisiana and launched 3 March 1993. She was commissioned 12 February 1994 in Tampa, Florida. As of 2008, Typhoon operates in the Persian Gulf, stationed in Manama, Bahrain since 2004 and is permanently manned by a 24-man crew that performs maritime security operations in United States Fifth Fleet Area of Responsibility (AOR).
Operation Morvarid was an operation launched by the Iranian Navy and Air Force against the Iraqi Air Defence sites on 28 November 1980 in response to Iraq positioning radar and monitoring equipment on the Mina Al-Bakr and Khor-al-Amaya oil rigs to counter Iranian air operations. The operation resulted in a victory for Iran, which managed to destroy both oil rigs as well as much of the Iraqi Navy and inflicted significant damage to Iraqi ports and airfields.

The Port of Basra, also known as Al Maqal Port, is an Iraqi port in Basra, situated on the Persian Gulf.

Nathan B. "Nate" Bruckenthal was a United States Coast Guardsman who was killed in the Iraq War, becoming the first to die in wartime action since the Vietnam War. Bruckenthal and two U.S. Navy sailors were killed while intercepting a waterborne suicide attack on an offshore oil terminal off the coast of Iraq in the northern Persian Gulf in 2004.

The Battle of Al Faw was one of the first battles of the Iraq War. One of the initial objectives of the Coalition campaign in Iraq was to capture the Gas and Oil Platforms ("GOPLATs") in the Al-Faw Peninsula intact before it could be sabotaged or destroyed by the Iraqi military. This would prevent an ecological disaster similar to the 1991 Gulf War and enable a quicker take over of Iraqi oil production.

Al Başrah Oil Terminal, commonly referred to as ABOT, is a strategically critical Iraqi offshore, deep sea crude oil marine loading terminal that lies approximately 50 km (31 mi) southeast of the Al-Faw Peninsula in the Persian Gulf. Along with its sister terminal, the Khawr al ‘Amīyah Oil Terminal, the terminals provide the principal point of export for more than eighty percent of Iraq's gross domestic product as of 2009, and all of the oil from the southern Başrah refinery.

Ba'athist Iraq, formally the Iraqi Republic until January 1992 and the Republic of Iraq thereafter, covers the history of Iraq between 1968 and 2003, during the period of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party's rule. This period began with high economic growth and soaring prosperity, but ended with Iraq facing social, political, and economic stagnation. The average annual income decreased both because of external factors and the internal policies of the government.

Iraq was the world's 5th largest oil producer in 2009, and has the world's fifth largest proven petroleum reserves. Just a fraction of Iraq's known fields are in development, and Iraq may be one of the few places left where vast reserves, proven and unknown, have barely been exploited. Iraq's energy sector is heavily based upon oil, with approximately 94 percent of its energy needs met with petroleum. In addition, crude oil export revenues accounted for over two-thirds of GDP in 2009. Iraq's oil sector has suffered over the past several decades from sanctions and wars, and its oil infrastructure is in need of modernization and investment. As of June 30, 2010, the United States had allocated US$2.05 billion to the Iraqi oil and gas sector to begin this modernization, but ended its direct involvement as of the first quarter of 2008. According to reports by various U.S. government agencies, multilateral institutions and other international organizations, long-term Iraq reconstruction costs could reach $100 billion (US) or higher.















