
Khosrow Jamshidi is an Iranian hematologist who invented the Jamshidi needle used for bone marrow biopsy. [1]

Khosrow Jamshidi is an Iranian hematologist who invented the Jamshidi needle used for bone marrow biopsy. [1]

Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests which fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases, and the affix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.

A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions.

Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either small surgical biopsies or whole-body autopsies. Neuropathologists usually work in a department of anatomic pathology, but work closely with the clinical disciplines of neurology, and neurosurgery, which often depend on neuropathology for a diagnosis. Neuropathology also relates to forensic pathology because brain disease or brain injury can be related to cause of death. Neuropathology should not be confused with neuropathy, which refers to disorders of the nerves themselves rather than the tissues. In neuropathology, the branches of the specializations of nervous system as well as the tissues come together into one field of study.

Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself, it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.

Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin, hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. Today, this procedure is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory conditions.

Liver biopsy is the biopsy from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.

Brain biopsy is the removal of a small piece of brain tissue for the diagnosis of abnormalities of the brain. It is used to diagnose tumors, infection, inflammation, and other brain disorders. By examining the tissue sample under a microscope, the biopsy sample provides information about the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
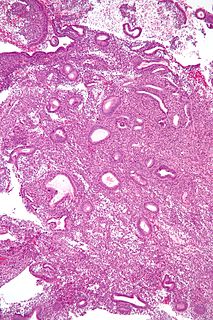
The endometrial biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a tissue sample of the lining of the uterus. The tissue subsequently undergoes a histologic evaluation which aids the physician in forming a diagnosis.

Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery. There are four main types of skin biopsies: shave biopsy, punch biopsy, excisional biopsy, and incisional biopsy. The choice of the different skin biopsies is dependent on the suspected diagnosis of the skin lesion. Like most biopsies, patient consent and anesthesia are prerequisites.

Pejman Jamshidi is an Iranian actor and former footballer.
Dr Alireza Jamshidi is an official spokesman for Iran's judiciary, headed by Mahmoud Shahroudi. In that capacity he holds regular news conferences. As he has little other public presence, his name is associated mainly with stories he has promulgated:

Renal biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small piece of kidney is removed from the body for examination, usually under a microscope. Microscopic examination of the tissue can provide information needed to diagnose, monitor or treat problems of the kidney.
Jamshidi is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
The Jamshidi are a sub-tribe of the Chahar Aimaq ethnic group in Afghanistan, one of the four major Aimaq tribes, which also include the Firozkohi, Taymani, and Taimuri. The Jamshidi are a primarily sedentary people living in Herat and are believed to be of mixed Arab and Persian descent. Some Jamshidis have settled in Turkmenistan.

The Jamshidi needle is a trephine needle for performing bone marrow biopsy, whereby a cylindrical sample of tissue, a core biopsy specimen, is obtained. It is a cylindrical needle with a tapered cutting tip. The tapered end reduces the potential of crush artifact. It is the most commonly used needle for performing bone marrow biopsies. The device is named for its inventor Khosrow Jamshidi who is an Iranian physician.
Rostamabad Jamshidi is a village in Beyranvand-e Jonubi Rural District, Bayravand District, Khorramabad County, Lorestan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 10, in 4 families.

Mohammad Jamshidi Jafarabadi is an Iranian professional basketball player who last played for the Meralco Bolts in the Philippine Basketball Association. A 6'6" swingman, he is also a member of the Iranian men's national basketball team. Mohammad was named the best shooting guard of the competition in the All-Star Team of 2017 FIBA Asia Cup.
Behrouz Jamshidi (Persian: بهروز جمشيدی; born August 23, 1972 in is a retired amateur Iranian Greco-Roman wrestler, who competed in the men's light heavyweight category. On January 3, 2000, the International Federation of Associated Wrestling ordered him a two-year suspension from competition for testing positive for doping.

Shahriyar Jamshidi is a Kurdish-Iranian Canadian Kamancheh player and composer. His focus is mainly on Kurdish and Iranian music.

Dorehami is an Iranian Telecast currently directed by Mehran Modiri. It aired on cable network IRIB Nasim on Thursdays at 21:00 and Fridays and Saturdays at 23:00 (IST) from March 18 to October 1, 2016 and continue from November 4. The show's first season finale aired on April 6, 2018, featuring Adel Ferdosipour as the guest.