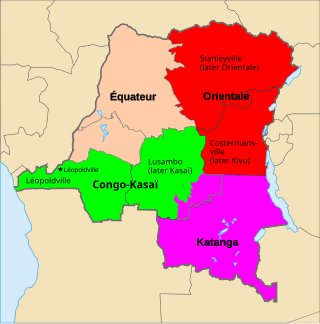
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997, its official name was Shaba Province.

Kinshasa, formerly named Léopoldville before June 30, 1966, is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a site of fishing and trading villages along the Congo River, Kinshasa is now one of the world's fastest-growing megacities. With an estimated population of 16 million residents, it's the most densely populated city in the DRC and the most populous city in Africa. It is Africa's third-largest metropolitan area and the leading economic, political, and cultural center of the DRC. Kinshasa houses several industries, including manufacturing, telecommunications, banking, and entertainment. The city also hosts some of DRC's significant institutional buildings, such as the Palais du Peuple, Palais de la Nation, Court of Cassation, Constitutional Court, Cité de l'Union Africaine, Palais de Marbre, Stade des Martyrs, Immeuble du Gouvernement, Kinshasa Financial Center, and multiple federal departments and agencies.

Brazzaville is the capital and largest city of the Republic of the Congo. Administratively, it is a department and a commune. Constituting the financial and administrative centre of the country, it is located on the north side of the Congo River, opposite Kinshasa, the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Kinshasa, DRC, DR Congo, or simply the Congo and known from 1971–1997 as Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. By land area, the DRC is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola and the South Atlantic Ocean.

The president of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the head of state of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and commander-in-chief of the armed forces.

The national flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a sky blue flag, adorned with a yellow star in the upper left canton and cut diagonally by a red stripe with a yellow fimbriation. It was adopted on 18 February 2006. A new constitution, ratified in December 2005 and which came into effect in February 2006, promoted a return to a flag similar to that flown between 1963 and 1971, with a change from a royal blue to sky blue background. Blue represents peace. Red stands for "the blood of the country's martyrs", yellow the country's wealth; and the star symbol the future for the country. It is one of the few national flags incorporating a diagonal line, with other examples including Tanzania, Namibia, Trinidad and Tobago, and Brunei.

Niari is a department of the Republic of the Congo in the western part of the country. It borders the departments of Bouenza, Kouilou, and Lékoumou, and internationally, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Cabinda portion of Angola. The regional capital is Dolisie.

The DR Congo National Football Team, recognised by FIFA as Congo DR, represents the Democratic Republic of the Congo in men's international football and it is controlled by the Congolese Association Football Federation. They are nicknamed Les Léopards, meaning The Leopards. The team is a member of FIFA and the Confederation of African Football (CAF).

The Congo Basin is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It contains some of the largest tropical rainforests in the world and is an important source of water used in agriculture and energy generation.

Article 2 of the Constitution of the Democratic Republic of the Congo divides the country into the capital city of Kinshasa and 25 named provinces. It also gives the capital the status of a province. Therefore, in many contexts Kinshasa is regarded as the 26th province.

The Departments of the Republic of the Congo are divided into 86 districts and 6 communes; which are further subdivided into urban communities and rural communities ; which are further subdivided into quarters or neighborhoods (quartiers) and villages. Note the departments of Brazzaville and Pointe-Noire are made of 1 commune each, then divided in urban districts (arrondissements).

The People's Republic of the Congo was a Marxist–Leninist socialist state that existed in the Republic of the Congo from 1969 to 1992.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Republic of the Congo on 24 June 2007, with a second round initially planned for 22 July 2007, but then postponed to 5 August 2007. According to the National Commission of the Organization of the Elections (CONEL), 1,807 candidates stood in the first round for 137 seats in the National Assembly. The ruling Congolese Labour Party and parties and independent candidates allied with it won 125 seats, while two opposition parties won a combined 12 seats.

The Republic of the Congo was a sovereign state in Central Africa, created with the independence of the Belgian Congo in 1960. From 1960 to 1966, the country was also known as Congo-Léopoldville to distinguish it from its northwestern neighbor, which is also called the Republic of the Congo, alternatively known as "Congo-Brazzaville". In 1964, the state's official name was changed to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, but the two countries continued to be distinguished by their capitals; with the renaming of Léopoldville as Kinshasa in 1966, it became also known as Congo-Kinshasa. After Joseph Désiré Mobutu, commander-in-chief of the national army, seized control of the government in 1965, the Democratic Republic of the Congo became the Republic of Zaire in 1971. It would again become the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1997. The period between 1960 and 1964 is referred to as the First Congolese Republic.

Kibangou is a district in the Niari Region of south-western Republic of the Congo. The capital lies at Kibangou.

The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to its northwest by Cameroon and its northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to its south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda and to its southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.
Antoine Ndinga Oba was a Congolese diplomat, political figure, and linguist. During the single-party rule of the Congolese Labour Party (PCT), he served in the government of Congo-Brazzaville as Minister of National Education from 1977 to 1984 and as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1984 to 1991. Later, he was Congo-Brazzaville's Ambassador to UNESCO from 1998 until his death in 2005.
Pierre-Damien Boussoukou-Boumba is a Congolese politician. During the single-party rule of the Congolese Labour Party (PCT), he served in the government of Congo-Brazzaville as Minister of Health from 1979 to 1984, as Minister of Scientific Research from 1984 to 1989, and as Minister of Basic Education from 1989 to 1991. He was Ambassador to the United States in the 1990s and Minister of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises from 1997 to 2002; subsequently he was a Deputy in the National Assembly of Congo-Brazzaville from 2002 to 2007. Boussoukou-Boumba was also President of the Union for the Defence of Democracy (UDD), a political party, from 1996 to 2011.
Bwisi is a language spoken mainly in the Kibangou District of the Republic of Congo, next to the Gabon border, where it is also spoken by a minority. According to the Ethnologue, approximately 4,250 people speak the language today worldwide.















