Related Research Articles

A kick is a physical strike using the leg, in unison usually with an area of the knee or lower using the foot, heel, tibia (shin), ball of the foot, blade of the foot, toes or knee. This type of attack is used frequently by hooved animals as well as humans in the context of stand-up fighting. Kicks play a significant role in many forms of martial arts, such as capoeira, kalaripayattu, karate, kickboxing, kung fu, MMA, Muay thai, pankration, pradal serey, savate, sikaran, silat, taekwondo, vovinam, and Yaw-Yan. Kicks are a universal act of aggression among humans.

Muay Thai, sometimes referred to as "Thai boxing", is a combat sport that uses stand-up striking along with various clinching techniques. This discipline is known as the "art of eight limbs" as it is characterized by the combined use of fists, elbows, knees and shins. Muay Thai became widespread internationally in the late-20th to 21st century, when Westernized practitioners from Thailand began competing in kickboxing and mixed rules matches as well as matches under muay Thai rules around the world. The professional league is governed by The Professional Boxing Association of Thailand (P.A.T), sanctioned by The Sports Authority of Thailand (SAT).

Caesarean section, also known as C-section, or caesarean delivery, is the use of surgery to deliver babies. A caesarean section is often necessary when a vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for this may include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, or problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Some C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother.

Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy. Twins can be either monozygotic ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two embryos, or dizygotic, meaning that each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell.

A multiple birth is the culmination of one multiple pregnancy, wherein the mother delivers two or more offspring. A term most applicable to vertebrate species, multiple births occur in most kinds of mammals, with varying frequencies. Such births are often named according to the number of offspring, as in twins and triplets. In non-humans, the whole group may also be referred to as a litter, and multiple births may be more common than single births. Multiple births in humans are the exception and can be exceptionally rare in the largest mammals.
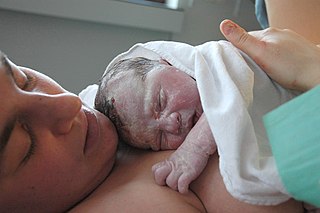
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies leaves the uterus by passing through the vagina or by Caesarean section. In 2015, there were about 135 million births globally. About 15 million were born before 37 weeks of gestation, while between 3 and 12 percent were born after 42 weeks. In the developed world most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing world most births take place at home with the support of a traditional birth attendant.

Prenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as maternal physiological changes in pregnancy, biological changes, and prenatal nutrition including prenatal vitamins, which prevents potential health problems throughout the course of the pregnancy and promotes the mother and child's health alike. The availability of routine prenatal care, including prenatal screening and diagnosis, has played a part in reducing the frequency of maternal death, miscarriages, birth defects, low birth weight, neonatal infections and other preventable health problems.
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and live birth, where the baby is born alive, even if it dies shortly after.

Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it does increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and requiring a Caesarean section. Babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of being too large, having low blood sugar after birth, and jaundice. If untreated, it can also result in a stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and developing type 2 diabetes.

Pregnancy, also known as gestation, is the time during which one or more offspring develops inside a woman. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a spontaneous miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP). This is just over nine months – where each month averages 31 days. When using fertilization age it is about 38 weeks. An embryo is the developing offspring during the first eight weeks following fertilization, after which, the term fetus is used until birth. Signs and symptoms of early pregnancy may include missed periods, tender breasts, nausea and vomiting, hunger, and frequent urination. Pregnancy may be confirmed with a pregnancy test.

Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is when the baby does not exit the pelvis during childbirth due to being physically blocked, despite the uterus contracting normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may result in death. It increases the risk of the mother getting an infection, having uterine rupture, or having post-partum bleeding. Long-term complications for the mother include obstetrical fistula. Obstructed labour is said to result in prolonged labour, when the active phase of labour is longer than 12 hours.

Kimberley Gail Marsh is an English actress, presenter and former singer-songwriter, who rose to fame in 2001 after winning a place in the band Hear'Say, as a result of appearing on the reality television series Popstars. Hear'Say enjoyed brief success, achieving two UK number one singles and a UK number one album, but Marsh left the band in 2002 to pursue a solo career. She released an album titled Standing Tall in 2003, which peaked at number nine in the UK and spawned two UK top ten singles.
In biology and human medicine, gravidity and parity are the number of times a woman is or has been pregnant (gravidity) and carried the pregnancies to a viable gestational age (parity). These terms are usually coupled, sometimes with additional terms, to indicate more details of the woman's obstetric history. When using these terms:

Nutrition and pregnancy refers to the nutrient intake, and dietary planning that is undertaken before, during and after pregnancy. Nutrition of the fetus begins at conception. For this reason, the nutrition of the mother is important from before conception as well as throughout pregnancy and breast feeding. An ever-increasing number of studies have shown that the nutrition of the mother will have an effect on the child, up to and including the risk for cancer, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and diabetes throughout life.
Postterm pregnancy is when a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the typical 40 week duration of pregnancy. Post-mature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including fetal malnutrition, meconium aspiration syndrome, and stillbirths. After the 42nd week of gestation, the placenta, which supplies the baby with nutrients and oxygen from the mother, starts aging and will eventually fail. Postterm pregnancy is a reason to induce labor.
Pregnancy and Infant Loss Remembrance Day is a day of remembrance for pregnancy loss and infant death, which includes, however is not limited to, miscarriage, stillbirth, SIDS, and the death of a newborn.

Harajuku Lovers Live is the first live long-form video by American recording artist Gwen Stefani. It was released on DVD on December 4, 2006, by Interscope Records. The DVD was directed by Sophie Muller and produced by Oil Factory Productions. It is a recording of one of Stefani's concerts during her Harajuku Lovers Tour 2005 in late 2005 to promote her first album, Love. Angel. Music. Baby., released in November 2004. The performance was recorded in November 2005, in Anaheim, California. The concert features performances of all twelve songs from Love. Angel. Music. Baby. and two new songs from her second studio album, The Sweet Escape, as well as interviews with the musicians and dancers and a documentary of tour preparation.

Fetal movement refers to motion of a fetus caused by its own muscle activity. Locomotor activity begins during the late embryological stage and changes in nature throughout development. Muscles begin to move as soon as they are innervated. These first movements are not reflexive, but arise from self-generated nerve impulses originating in the spinal cord. As the nervous system matures, muscles can move in response to stimuli.
Toxic abortion is a medical phenomenon of spontaneous abortion, miscarriage, or stillbirth caused by toxins in the environment of the mother during pregnancy, especially as caused by toxic environmental pollutants, though sometimes reported as caused by naturally occurring plant toxins

Alcohol use in pregnancy includes use of alcohol during gestation, including the time before the woman is aware of the pregnancy. No amount of alcohol is considered safe to drink while pregnant and there is no safe time point or trimester in pregnancy to drink alcohol. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy. The most severe form of the condition is known as fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Problems may include an abnormal appearance, short height, low body weight, small head size, poor coordination, low intelligence, behavioral problems, hearing loss, and vision problems. Those affected are more likely to have trouble in school, legal problems, participate in high-risk behaviors, and have trouble with alcohol and recreational drug use. Alcohol use during pregnancy also can cause spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, low birthweight, and prematurity. Not all infants exposed to alcohol in utero will have defects related to the alcohol consumption. The use of alcohol during pregnancy is associated with domestic violence and potential harm to the infant.
References
- 1 2 "Kick Chart". National Childbirth Trust. 2006. Archived from the original on 24 December 2007.
- ↑ "#7. The Importance of Counting Kicks". The National Stillbirth Society. 10 September 2007. Archived from the original on 8 November 2010.
- ↑ "Your baby's movements in pregnancy". BabyCentre L.L.C. March 2013.
| This human reproduction article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |