
A museum is an institution dedicated to displaying and/or preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private collections that are used by researchers and specialists. Compared to a library, a museum hosts a much wider range of objects and usually focus around a specific theme such as the arts, science, natural history, local history, and other topics. Public museums that host exhibitions and interactive demonstrations are often considered to be tourist attractions, and many museums attract large numbers of visitors from outside their host country, with the most visited museums in the world regularly attracting millions of visitors annually.

The Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act (NAGPRA), Pub. L. 101-601, 25 U.S.C. 3001 et seq., 104 Stat. 3048, is a United States federal law enacted on November 16, 1990.

The Benin Bronzes are a group of several thousand metal plaques and sculptures that decorated the royal palace of the Kingdom of Benin, in what is now Edo State, Nigeria. Collectively, the objects form the best examples of Benin art and were created from the fourteenth century by artists of the Edo people. The plaques, which in the Edo language are called Ama, depict scenes or represent themes in the history of the kingdom. Apart from the plaques, other sculptures in brass or bronze include portrait heads, jewelry, and smaller pieces.

Mijikenda are a group of nine related Bantu ethnic groups inhabiting the coast of Kenya, between the Sabaki and the Umba rivers, in an area stretching from the border with Tanzania in the south to the border near Somalia in the north. Archaeologist Chapuruka Kusimba contends that the Mijikenda formerly resided in coastal cities, but later settled in Kenya's hinterlands to avoid submission to dominant Portuguese forces that were then in control. Historically, these Mijikenda ethnic groups have been called the Nyika or Nika by outsiders. It is a derogatory term meaning "bush people."

Repatriation is the return of a thing or person to its or their country of origin, respectively. The term may refer to non-human entities, such as converting a foreign currency into the currency of one's own country, as well as the return of military personnel to their place of origin following a war. It also applies to diplomatic envoys, international officials as well as expatriates and migrants in time of international crisis. For refugees, asylum seekers and illegal migrants, repatriation can mean either voluntary return or deportation.

The sculpture of ancient Greece is the main surviving type of fine ancient Greek art as, with the exception of painted ancient Greek pottery, almost no ancient Greek painting survives. Modern scholarship identifies three major stages in monumental sculpture in bronze and stone: the Archaic, Classical (480–323) and Hellenistic. At all periods there were great numbers of Greek terracotta figurines and small sculptures in metal and other materials.

A xoanon was a wooden cult image of Archaic Greece. Classical Greeks associated such cult objects, whether aniconic or effigy, with the legendary Daedalus. Many such cult images were preserved into historical times, though none are known to have survived to the modern day, except as copies in stone or marble. In the 2nd century CE, Pausanias described numerous xoana in his Description of Greece, notably the image of Hera in her temple at Samos. "The statue of the Samian Hera, as Aethilos [sic] says, was a wooden beam at first, but afterwards, when Prokles was ruler, it was humanized in form". In Pausanias' travels he never mentions seeing a xoanon of a "mortal man".

Repatriation is the return of the cultural property, often referring to ancient or looted art, to their country of origin or former owners.

The Illinois State Museum features the life, land, people and art of the State of Illinois. In addition to natural history exhibits, the main museum in Springfield focuses on the state's cultural and artistic heritage. Exhibits include local fossils and mining, household displays from different historic periods, dioramas of Native American life, archaeological and ethnographic artifacts, and a collection of glass paperweights.

Looted art has been a consequence of looting during war, natural disaster and riot for centuries. Looting of art, archaeology and other cultural property may be an opportunistic criminal act or may be a more organized case of unlawful or unethical pillage by the victor of a conflict. The term "looted art" reflects bias, and whether particular art has been taken legally or illegally is often the subject of conflicting laws and subjective interpretations of governments and people; use of the term "looted art" in reference to a particular art object implies that the art was taken illegally.

The Colossus of Constantine was a many times life-size acrolithic early-4th-century statue depicting the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, commissioned by himself, which originally occupied the west apse of the Basilica of Maxentius on the Via Sacra, near the Forum Romanum in Rome. Surviving portions of the Colossus now reside in the courtyard of the Palazzo dei Conservatori, now part of the Capitoline Museums, on the Capitoline Hill, above the west end of the Forum.

The Father Sebastian Englert Anthropological Museum is a museum in the town of Hanga Roa on Rapa Nui in Chilean Polynesia. Named for the Bavarian missionary, Fr. Sebastian Englert, OFM Cap., the museum was founded in 1973 and is dedicated to the conservation of the Rapa Nui cultural patrimony.

Abraham Lincoln: The Head of State is a 9-foot (2.7 m) tall bronze statue of Abraham Lincoln in Grant Park, in Chicago. Created by Augustus Saint-Gaudens and completed by his workshop in 1908, it was intended by the artist to evoke the loneliness and burden of command felt by Lincoln during his presidency. The sculpture depicts a contemplative Lincoln seated in a chair, and gazing down into the distance. The sculpture is set upon a pedestal and a 150-foot (46 m) wide exedra designed by architect Stanford White.

A kaya is a sacred site of the Mijikenda people in the former Coast Province of Kenya. Often located within sacred forests, a kaya is considered to be an intrinsic source of ritual power and the origin of cultural identity; it is also a place of prayer for members of the Mijikenda ethnic group. The settlement, ritual centre, and fortified enclosure associated with the forest are also part of the kaya. In the present day, the kaya is also referred to as a traditional organizational unit of the Mijikenda. Eleven of the approximately 60 separate makaya have been grouped together and inscribed as the Sacred Mijikenda Kaya Forests, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
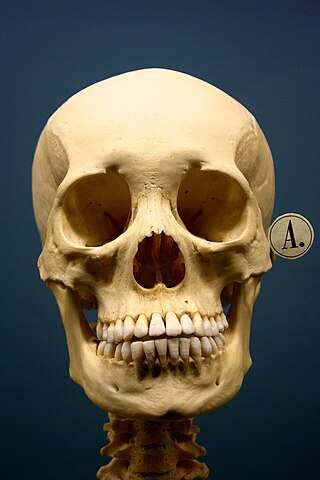
The conservation and restoration of human remains involves the long-term preservation and care of human remains in various forms which exist within museum collections. This category can include bones and soft tissues as well as ashes, hair, and teeth. Given the organic nature of the human body, special steps must be taken to halt the deterioration process and maintain the integrity of the remains in their current state. These types of museum artifacts have great merit as tools for education and scientific research, yet also have unique challenges from a cultural and ethical standpoint. Conservation of human remains within museum collections is most often undertaken by a conservator-restorer or archaeologist. Other specialists related to this area of conservation include osteologists and taxidermists.

Deaccessioning is the process by which a work of art or other object is permanently removed from a museum's collection to sell it or otherwise dispose of it.
Kaya Mudzi Muvya is a coastal lowland dry deciduous forest in Kilifi County of southern Kenya. It became a World Heritage Site in 2008. A large portion of the forest is an area protected by the Kenya Forest Service under The Forests Act of 2005, and as a national monument under the Antiquities and Monuments Act Cap 215. The forest is sacred to the local Mijikenda people, known as the Rabai. The forest has suffered deprevation over the past hundred years.

Russia began an invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War that began in 2014. It is the largest military attack in Europe since World War II. During the fighting, many pieces of Ukrainian cultural heritage were either destroyed, damaged, or put at risk due to the widespread destruction across the country. This deliberate destruction and looting of over 500 Ukrainian cultural heritage sites is considered a war crime and has been described by Ukraine's Minister of Culture as cultural genocide.
Ernie Wolfe III is an art curator, gallerist, outdoorsman, field researcher, and author specializing in contemporary and traditional African art. His specialties include Ghanaian film posters, fantasy coffins, pop art, and commercial art, as well as traditional sculpture from across Africa.
Repatriation is the practice of returning a cultural artifact to its place of origin. Within the context of Canada, this is often associated with institution and collectors returning cultural artifacts to their original Indigenous community. Cultural artifacts may have been appropriated, stolen, sold, or taken from their place of origin. Many of the early collectors of Canadian indigenous cultural items did so with the assumption that the culture was on the brink of destruction. Many scholars considered it imperative to obtain and collect these items before they were destroyed under the guise of salvage ethnography. This was supported by racist ideologies suggesting that indigenous cultures were primitive and therefore inferior to the culture of dominant colonial society.

















