
The Dagaaba people are an ethnic group located north of the convergence of Ghana, Burkina Faso and Côte d'Ivoire. They speak the Dagaare language, a Gur language made up of the related Northern Dagaare dialects, Southern Dagaare dialects and a number of sub dialects. In northern dialects, both the language and the people are referred to as Dagara. They are related to the Birifor people and the Dagaare Diola. The language is collectively known as Dagaare, and historically some non-natives have taken this as the name of the people. One historian, describing the former usage of "Dagarti" to refer to this community by colonials, writes: "The name 'Dagarti' appears to have been coined by the first Europeans to visit the region, from the vernacular root dagaa. Correctly 'Dagari' is the name of the language, 'Dagaaba' or 'Dagara' that of the people, and 'Dagaw' or 'Dagawie' that of the land."

The Dagbamba or Dagomba are an ethnic group of Ghana, and Togo. They number more than 3.1 million people. The term Dagbamba is originally extended to refer to other related peoples who were unified by Naa Gbewaa including the Mamprusi and Nanumba. The Dagomba country is called Dagbon and they speak Dagbanli language. Dagbanli is the most spoken language of northern Ghana and second most widely spoken local language of Ghana. Dagbanli belongs to the Mabia (Mole-Dagbani) subgroup of the Gur languages, a large group of related languages in West Africa. The Dagomba practises both patrilineal and matrilineal systems of inheritance.

Wa is a town and the capital of the Wa Municipal District and the Upper West Region of Ghana. It has a population of 200,672 people according to the 2021 census.

The Upper West Region of Ghana is located in the north-western corner of Ghana and is bordered by Upper East Region to the east, Northern Region to the south, and Burkina Faso to the west and north. The Upper West regional capital and largest settlement is Wa. The Upper West was created by the then Head of State, Flight-Lieutenant Jerry Rawlings in 1983 under the Provisional National Defence Council (PNDC) military regime. The area was carved out of the former Upper Region, which is now the Upper East Region. For about thirty-five years, it remained the youngest region of Ghana until 2018 when six more regions were created by the Nana Addo Dankwa Akufo-Addo government; hence increasing the total number of administrative regions in the country to sixteen.
The Wala or Waala live in Upper West Region of Ghana. They are a predominantly Muslim people who are the founders of the city of Wa and the Kingdom of Wala. They speak the Wali language, which belongs to the Gur group. There are 84,800 speakers of the language as of 2013. Their neighbors are the Birifor, Dagaaba, and Vagla peoples.
Professor Emeritus Ivor G. Wilks was a noted British Africanist and historian, specializing in Ghana. Considered one of the founders of modern African historiography, he was an authority on the Ashanti Empire in Ghana and the Welsh working-class movement in the 19th century. At the time of his death, he was Professor Emeritus of History at Northwestern University in Illinois, USA.
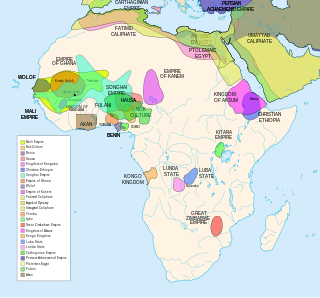
African empires is an umbrella term used in African studies to refer to a number of pre-colonial African kingdoms in Africa with multinational structures incorporating various populations and polities into a single entity, usually through conquest.
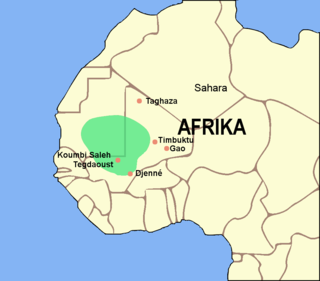
The Ghana Empire, also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadou, was a West African classical to post-classical era western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali.

Funsi is a small town and is the capital of Wa East district, a district in the Upper West Region of north Ghana.

The Kulpawn River is one of the major rivers of northwestern Ghana, along with the Black Volta and Sisili Rivers. It flows through Wa Municipal District. The riparian woodland around the bank of the Kulpawn in the Wahabu is particularly popular with ornithologists, due to a rich variety of birds.

The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community is the second largest group of Islam in Ghana after Sunni Islam. The early rise of the Community in Ghana can be traced through a sequence of events beginning roughly at the same time as the birth of the Ahmadiyya movement in 1889 in British India. It was during the early period of the Second Caliphate that the first missionary, Abdul Rahim Nayyar was sent to what was then the Gold Coast in 1921 upon invitation from Sunni Muslims in Saltpond. Having established the movement in the country, Nayyar left and was replaced by the first permanent missionary, Al Hajj Fadl-ul-Rahman Hakim in 1922.
Babatu or Baba Ato, was the Zarma military leader and jihadi warlord over the Zabarma Emirate in the late 19th century. Babatu originated in Indougou (N'Dougou) in what is today the nation of Niger. Babatu became the ruler of the Zabarima emirate in 1878 after the death of the former ruler, Gazari. He was a slaver and fought against Sandema warriors.
Nasa is a village in Ghana in the historic Kingdom of Wala in the current Upper West Region of Ghana. It is 14 miles northeast of Wa, Ghana.
Kulmasa is a town in the Sawla-Tuna-Kalba District, Savannah Region, Ghana. In the 1890s, it marked the southern frontier of the Kingdom of Wala.
The Wala Native Authority was a division of the British colony of Gold Coast established in 1933. It basically corresponded in its boundaries to those of the Kingdom of Wala in 1892, thus reversing the successful rebellion by the Dagarti in the northern part of Wala in 1894.

Al-Hajj Abdul Rahim Nayyar was a companion of Mirza Ghulam Ahmad and a missionary of the Ahmadiyya Islamic movement in West Africa. He pledged allegiance to Ghulam Ahmad, formally joining the Ahmadiyya movement, in 1901. Travelling to the Gold Coast in 1921 upon invitation from Muslims in Saltpond, Nayyar was instrumental in consolidating Ahmadiyya missions in several West African countries.
Jatoe Kaleo (1928–1998) was a Ghanaian traditional ruler, politician and founding member of the Northern Peoples Party.
Bukari Kpegla Adama was a Ghanaian politician and a minister of state in the Second Republic.
Dumba Festival is an annual festival celebrated by the chiefs and people of Wa of the Wala Paramouncy in the Upper West Region of Ghana. It is usually celebrated in the month of September or October.









