
Adrián Alfonso Lamo Atwood was an American threat analyst and hacker. Lamo first gained media attention for breaking into several high-profile computer networks, including those of The New York Times, Yahoo!, and Microsoft, culminating in his 2003 arrest.

Cybercrime encompasses a wide range of criminal activities that are carried out using digital devices and/or networks. These crimes involve the use of technology to commit fraud, identity theft, data breaches, computer viruses, scams, and expanded upon in other malicious acts. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, disrupt services, and cause financial or reputational harm to individuals, organizations, and governments.

Kevin Lee Poulsen is an American former black-hat hacker and a contributing editor at The Daily Beast.

ShadowCrew was a cybercrime forum that operated under the domain name ShadowCrew.com between August 2002 and November 2004.
SecurityFocus was an online computer security news portal and purveyor of information security services. Home to the well-known Bugtraq mailing list, SecurityFocus columnists and writers included former Department of Justice cybercrime prosecutor Mark Rasch, and hacker-turned-journalist Kevin Poulsen.
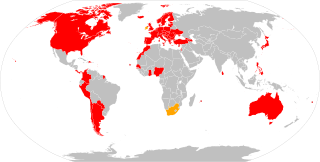
The Convention on Cybercrime, also known as the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime or the Budapest Convention, is the first international treaty seeking to address Internet and computer crime (cybercrime) by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It was drawn up by the Council of Europe in Strasbourg, France, with the active participation of the Council of Europe's observer states Canada, Japan, the Philippines, South Africa and the United States.
Google hacking, also named Google dorking, is a hacker technique that uses Google Search and other Google applications to find security holes in the configuration and computer code that websites are using.
Jonathan Joseph James was an American hacker who was the first juvenile incarcerated for cybercrime in the United States. The South Florida native was 15 years old at the time of the first offense and 16 years old on the date of his sentencing. He died at his Pinecrest, Florida home on May 18, 2008, of a self-inflicted gunshot wound.
Computer crime, or cybercrime in Canada, is an evolving international phenomenon. People and businesses in Canada and other countries may be affected by computer crimes that may, or may not originate within the borders of their country. From a Canadian perspective, 'computer crime' may be considered to be defined by the Council of Europe – Convention on Cybercrime. Canada contributed, and is a signatory, to this international of criminal offences involving the use of computers:
Justin Tanner Petersen was an American hacker, concert promoter, sound engineer, private investigator and an informant for the Federal Bureau of Investigation. While tasked with helping to catch other hackers and fugitives wanted by the FBI, he continued to commit serious crimes.

H*Commerce: The Business of Hacking You is a six-part online documentary film series directed by Seth Gordon. It centers on the struggle between criminal hackers and security experts. Each segment is between five and eight minutes in length. The first was released on the Internet on May 20, 2009.
Max Ray Vision is a former computer security consultant and hacker who served a 13-year prison sentence, the longest sentence ever given at the time for hacking charges in the United States. He was convicted of two counts of wire fraud, including stealing nearly 2 million credit card numbers and running up about $86 million in fraudulent charges.

Carding is a term of the trafficking and unauthorized use of credit cards. The stolen credit cards or credit card numbers are then used to buy prepaid gift cards to cover up the tracks. Activities also encompass exploitation of personal data, and money laundering techniques. Modern carding sites have been described as full-service commercial entities.
Mazafaka is a cybercrime forum with many users having moved on from sites such as ShadowCrew.
Hack Forums is an Internet forum dedicated to discussions related to hacker culture and computer security. The website ranks as the number one website in the "Hacking" category in terms of web-traffic by the analysis company Alexa Internet. The website has been widely reported as facilitating online criminal activity, such as the case of Zachary Shames, who was arrested for selling keylogging software on Hack Forums in 2013 which was used to steal personal information.
Ghana has one of the highest rates of cybercrime in the world, ranking 7th in a 2008 Internet Crime Survey. The most popular form of cybercrime in Ghana is cyberfraud and is typically achieved via credit card fraud. However, recent decreases in universal credit card usage has seen the expansion of other cybercrimes such as blackmail and hacking. This growth in crime has warranted a government response, with policies specifically addressing the cyberspace being developed. This has necessitated various studies including a cyber security maturity study which was inaugurated by the Ministry of Communications and conducted by the Global Cyber Security Capacity Center (GCSCC) of the University of Oxford in collaboration with the World Bank.
Ruslan Stoyanov is a Russian computer scientist. In December 2016, he was arrested on charges of treason as part of the Mikhailov case. In 2019, he was sentenced to 14 years in prison.







