Related Research Articles

A mammal is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia. Mammals are characterized by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 29 orders.

In zoology, a scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of an animal's skin to provide protection. In lepidopterans, scales are plates on the surface of the insect wing, and provide coloration. Scales are quite common and have evolved multiple times through convergent evolution, with varying structure and function.

The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea.

Whiskers or vibrissae are a type of stiff, functional hair used by most mammals to sense their environment. These hairs are finely specialised for this purpose, whereas other types of hair are coarser as tactile sensors. Although whiskers are specifically those found around the face, vibrissae are known to grow in clusters at various places around the body. Most mammals have them, including all non-human primates and especially nocturnal mammals.

The tufted titmouse is a small songbird from North America, a species in the tit and chickadee family (Paridae). The black-crested titmouse, found from central and southern Texas southward, was included as a subspecies but now is considered a separate species, Baeolophus atricristatus.
In biology, nidifugous organisms are those that leave the nest shortly after hatching or birth. The term is derived from Latin nidus for "nest" and fugere, meaning "to flee". The terminology is most often used to describe birds and was introduced by Lorenz Oken in 1816. The chicks of birds in many families, such as the waterfowl, waders, and gamebirds, are usually nidifugous.
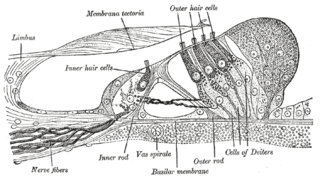
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment.

In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.

Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation between individuals, especially at high frequencies, and a gradual loss of sensitivity to higher frequencies with age is considered normal. Sensitivity also varies with frequency, as shown by equal-loudness contours. Routine investigation for hearing loss usually involves an audiogram which shows threshold levels relative to a normal.

The hooded skunk is a species of mammal in the family Mephitidae. Mephītis in Latin means "foul odor", μακρός (makrós) in Greek translates to "long" and οὐρά (ourá) translates to "tail".

The European wildcat is a small wildcat species native to continental Europe, Scotland, Turkey and the Caucasus. It inhabits forests from the Iberian Peninsula, Italy, Central and Eastern Europe to the Caucasus. Its fur is brownish to grey with stripes on the forehead and on the sides and has a bushy tail with a black tip. It reaches a head-to-body length of up to 65 cm (26 in) with a 34.5 cm (13.6 in) long tail, and weighs up to 7.5 kg (17 lb).

The Indian grey mongoose or Asian grey mongoose is a mongoose species native to the Indian subcontinent and West Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
The little goblin bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae, the free-tailed bats. It is endemic to Cuba.
The Gobi big brown bat is a species of vesper bat. It is found in Afghanistan, China, India, Mongolia, Pakistan, and Russia. Russian zoologist Professor Count Nikolay Alekseyevich Bobrinski first described it in 1926, the type specimen coming from the Altai Mountains in the Gobi Desert.

The bicolored shrew or bicoloured white-toothed shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in eastern, central and southern Europe and in western Asia. It is a nocturnal species and feeds on insects and other small creatures. Several litters of young are born during the warmer months of the year in a nest of dry grasses in a concealed location.

The greater musky fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the Philippines. It was named by Peters for Fedor Jagor.

The binturong, also known as the bearcat, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. It is uncommon in much of its range, and has been assessed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because of a declining population. It is estimated to have declined at least 30% since the mid-1980s. The binturong is the only species in the genus Arctictis.

Amelanism is a pigmentation abnormality characterized by the lack of pigments called melanins, commonly associated with a genetic loss of tyrosinase function. Amelanism can affect fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals including humans. The appearance of an amelanistic animal depends on the remaining non-melanin pigments. The opposite of amelanism is melanism, a higher percentage of melanin.

Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.

In the biology of birds and mammals, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the moment of birth or hatching. They are normally nidifugous, meaning that they leave the nest shortly after birth or hatching. These categories form a continuum, without distinct gaps between them.
References
- ↑ Pollock, Henry S.; MacDonald, Sean E.; Vizentin-Bugoni, Jeferson; Brawn, Jeffrey D.; Sutton, Zachary S.; Hauber, Mark E. (2021). "What the pluck? Theft of mammal hair by birds is an overlooked but common behavior with fitness implications". Ecology. 102 (12): e03501. doi:10.1002/ecy.3501. PMID 34314035. S2CID 236453003 – via Wiley Online Library.