
John of the Cross, OCD was a Spanish Catholic priest, mystic, and a Carmelite friar of converso origin. He is a major figure of the Counter-Reformation in Spain, and he is one of the thirty-seven Doctors of the Church.

The Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), officially the Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of Malta, commonly known as the Order of Malta or Knights of Malta, is a Catholic lay religious order, traditionally of a military, chivalric, and noble nature. Though it possesses no territory, the order is often considered a sovereign entity of international law, as it maintains diplomatic relations with many countries.

Veneration, or veneration of saints, is the act of honoring a saint, a person who has been identified as having a high degree of sanctity or holiness. Angels are shown similar veneration in many religions. Etymologically, "to venerate" derives from the Latin verb, venerare, meaning 'to regard with reverence and respect'. Veneration of saints is practiced, formally or informally, by adherents of some branches of all major religions, including Christianity, Judaism, Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism and Jainism.
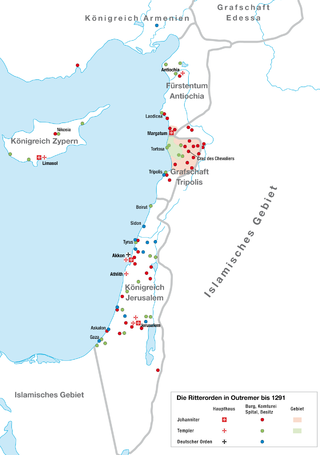
A military order is a Christian religious society of knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades, both in the Holy Land, the Baltics, and the Iberian peninsula; their members being dedicated to the protection of pilgrims and the defence of the Crusader states. They are the predecessors of chivalric orders.

A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders founded in the twelfth or thirteenth century; the term distinguishes the mendicants' itinerant apostolic character, exercised broadly under the jurisdiction of a superior general, from the older monastic orders' allegiance to a single monastery formalized by their vow of stability. A friar may be in holy orders or a brother. The most significant orders of friars are the Dominicans, Franciscans, Augustinians, and Carmelites.

Camillus de Lellis, M.I., was a Roman Catholic priest from Italy who founded the Camillians, a religious order dedicated to the care of the sick. He was beatified by Pope Benedict XIV in the year 1742, and canonized by him four years later in 1746. De Lellis is the patron saint of the sick, hospitals, nurses and physicians. His assistance is also invoked against gambling.

John of God, OH was a Portuguese soldier turned health-care worker in Spain, whose followers later formed the Brothers Hospitallers of Saint John of God, a worldwide Catholic religious institute dedicated to the care of the poor, sick, and those suffering from mental disorders. He has been canonized by the Catholic Church, and is considered one of the leading religious figures in the Iberian Peninsula.

The Order of Saint Lazarus of Jerusalem, also known as the Leper Brothers of Jerusalem or simply as Lazarists, was a Catholic military order founded by crusaders around 1119 at a leper hospital in Jerusalem, Kingdom of Jerusalem, whose care became its original purpose, named after its patron saint, Lazarus. It was recognised by King Fulk of Jerusalem in 1142 and canonically recognised as a hospitaller and military order of chivalry under the rule of Saint Augustine in the Papal bull Cum a Nobis Petitur of Pope Alexander IV in 1255. Although they were centred on their charism of caring for those afflicted with leprosy, the knights of the Order of Saint Lazarus notably fought in the Battle of La Forbie in 1244 and in the Defense of Acre in 1291. The titular seat was successively situated at Jerusalem, Saint-Jean-d'Acre and - after the fall of the Kingdom of Jerusalem - split in two main branches in Italy and in Château Royal de Boigny-sur-Bionne in France.

Marianne Cope, TOSF, also known as Saint Marianne of Molokaʻi, was a German-born American religious sister who was a member of the Sisters of St Francis of Syracuse, New York, and founding leader of its St. Joseph's Hospital in the city, among the first of 50 general hospitals in the country. Known also for her charitable works, in 1883 she relocated with six other sisters to Hawaiʻi to care for persons suffering leprosy on the island of Molokaʻi and aid in developing the medical infrastructure in Hawaiʻi. Despite direct contact with the patients over many years, Cope did not contract the disease.

The Company of the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul, commonly called the Daughters of Charity or Sisters of Charity of Saint Vincent De Paul, is a Society of Apostolic Life for women within the Catholic Church. Its members make annual vows throughout their life, which leaves them always free to leave, without the need of ecclesiastical permission. They were founded in 1633 and state that they are devoted to serving the poor through the corporal and spiritual works of mercy.

Peter of Alcántara was a Spanish Franciscan friar who was canonized in 1669.

Thomas of Villanova, OSA, born Tomás García y Martínez, was a Spanish friar of the Order of Saint Augustine who was a noted preacher, ascetic and religious writer of his day. He became an archbishop who was famous for the extent of his care for the poor of his see.

Solanus Casey, OFM Cap., born Bernard Francis Casey, was a priest of the Catholic Church in the United States and was a professed member of the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin. He was known during his lifetime as a healer for his great faith and his abilities as a spiritual counselor, but especially for his great attention to the sick, for whom he celebrated special Masses. The friar was much sought-after and revered, especially in Detroit, where he resided. He was also a noted lover of the violin, a trait he shared with his eponym, Saint Francis Solanus.

The Brothers Hospitallers of Saint John of God, officially the Hospitaller Order of the Brothers of Saint John of God, are a Catholic religious order founded in 1572. In Italian they are also known commonly as the Fatebenefratelli, meaning "Do-Good Brothers", and elsewhere as the "Brothers of Mercy", the "Merciful Brothers" and the "John of God Brothers". The order carries out a wide range of health and social service activities in 389 centres and services in 46 countries.
The Third Order Regular of St. Francis of Penance or simply the Third Order Regular of St. Francis is a mendicant order rooted in the Third Order of St. Francis which was founded in 1221. The members add the nominal letters T.O.R. after their names to indicate their membership in the congregation.

The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller, was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was founded in the Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and was headquartered there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302-1310), the island of Rhodes (1310-1522), Malta (1530-1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799-1801).

The Muristan is a complex of streets and shops in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. The site was the location of the first Bimaristan of the Knights Hospitaller.

Ignatius of Loyola, S.J., venerated as Saint Ignatius of Loyola, was a Spanish Catholic priest and theologian, who, with Peter Faber and Francis Xavier, founded the religious order of the Society of Jesus, and became its first Superior General, in Paris in 1541. He envisioned the purpose of the Society of Jesus to be missionary work and teaching. In addition to the vows of chastity, obedience and poverty of other religious orders in the church, Loyola instituted a fourth vow for Jesuits of obedience to the Pope, to engage in projects ordained by the pontiff. Jesuits were instrumental in leading the Counter-Reformation.
A religious brother is a member of a Christian religious institute or religious order who commits himself to following Christ in consecrated life of the Church, usually by the vows of poverty, chastity and obedience. He is a layman, in the sense of not being ordained as a deacon or priest, and usually lives in a religious community and works in a ministry appropriate to his capabilities.

Benedict Menni, OH, born Angelo Ercole Menni Figini, was an Italian Roman Catholic priest. Menni was a professed member of the Order of the Brothers Hospitallers of Saint John of God and he went on to establish a religious congregation of women known as the Sisters Hospitaller of the Sacred Heart of Jesus and based upon the one of which he was a member. As part of his pastoral mission, he worked in Spain.

















