Related Research Articles

Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden.

Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Tenosynovitis can be either infectious or noninfectious. Common clinical manifestations of noninfectious tenosynovitis include de Quervain tendinopathy and stenosing tenosynovitis

Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease (LCPD), is a childhood hip disorder initiated by a disruption of blood flow to the head of the femur. Due to the lack of blood flow, the bone dies and stops growing. Over time, healing occurs by new blood vessels infiltrating the dead bone and removing the necrotic bone which leads to a loss of bone mass and a weakening of the femoral head.
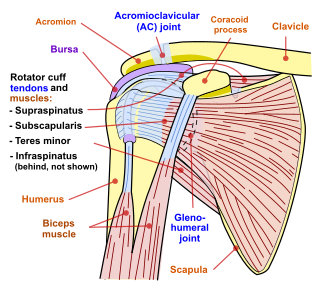
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved especially in neonates and younger children. In neonates, infants i.e. during the first year of life and toddlers, the signs and symptoms of septic arthritis can be deceptive and mimic other infectious and non-infectious disorders.
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), is the most common, chronic rheumatic disease of childhood, affecting approximately one per 1,000 children. Juvenile, in this context, refers to disease onset before 16 years of age, while idiopathic refers to a condition with no defined cause, and arthritis is inflammation within the joint.

A limp is a type of asymmetric abnormality of the gait. Limping may be caused by pain, weakness, neuromuscular imbalance, or a skeletal deformity. The most common underlying cause of a painful limp is physical trauma; however, in the absence of trauma, other serious causes, such as septic arthritis or slipped capital femoral epiphysis, may be present. The diagnostic approach involves ruling out potentially serious causes via the use of X-rays, blood tests, and sometimes joint aspiration. Initial treatment involves pain management. A limp is the presenting problem in about 4% of children who visit hospital emergency departments.
Monoarthritis is inflammation (arthritis) of one joint at a time. It is usually caused by trauma, infection, or crystalline arthritis.
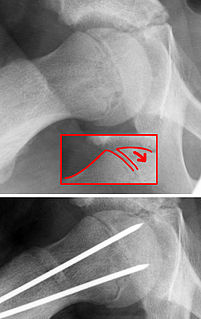
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a medical term referring to a fracture through the growth plate (physis), which results in slippage of the overlying end of the femur (metaphysis).
Synovitis is the medical term for inflammation of the synovial membrane. This membrane lines joints that possess cavities, known as synovial joints. The condition is usually painful, particularly when the joint is moved. The joint usually swells due to synovial fluid collection.

Prepatellar bursitis is an inflammation of the prepatellar bursa at the front of the knee. It is marked by swelling at the knee, which can be tender to the touch and which generally does not restrict the knee's range of motion. It can be extremely painful and disabling as long as the underlying condition persists.

Transient synovitis of hip is a self-limiting condition in which there is an inflammation of the inner lining of the capsule of the hip joint. The term irritable hip refers to the syndrome of acute hip pain, joint stiffness, limp or non-weightbearing, indicative of an underlying condition such as transient synovitis or orthopedic infections. In everyday clinical practice however, irritable hip is commonly used as a synonym for transient synovitis. It should not be confused with sciatica, a condition describing hip and lower back pain much more common to adults than transient synovitis but with similar signs and symptoms.
Orthopedic pathology, also known as bone pathology is a subspecialty of surgical pathology which deals with the diagnosis and feature of many bone diseases, specifically studying the cause and effects of disorders of the musculoskeletal system. It uses gross and microscopic findings along with the findings of in vivo radiological studies, and occasionally, specimen radiographs to diagnose diseases of the bones.

Hip dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket portion does not fully cover the ball portion, resulting in an increased risk for joint dislocation. Hip dysplasia may occur at birth or develop in early life. Regardless, it does not typically produce symptoms in babies less than a year old. Occasionally one leg may be shorter than the other. The left hip is more often affected than the right. Complications without treatment can include arthritis, limping, and low back pain.

A joint effusion is the presence of increased intra-articular fluid. It may affect any joint. Commonly it involves the knee.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trauma and orthopaedics:
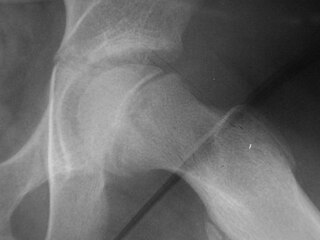
Klein's line or the line of Klein is a virtual line that can be drawn on an X-ray of an adolescent's hip parallel to the anatomically upper edge of the femoral neck. It was the first tool to aid in the early diagnosis of a slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), which if treated late or left untreated leads to crippling arthritis, leg length discrepancy and lost range of motion. It is named after the American orthopedic surgeon Armin Klein at Harvard University, who published its description and usefulness in 1952. Subsequent modification of its use has increased the sensitivity and reliability of the tool.

Pain in the hip is the experience of pain in the muscles or joints in the hip/ pelvic region, a condition commonly arising from any of a number of factors. Sometimes it is closely associated with lower back pain.
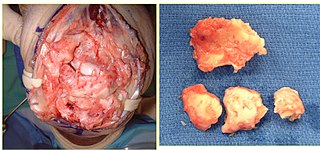
Post-traumatic arthritis (PTA) is a form of osteoarthritis following an injury to a joint.
Mininder S. Kocher is an American orthopedic surgeon.
References
- ↑ Smith, Howard S. (2009). Current Therapy in Pain. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 181. ISBN 978-1416048367 . Retrieved 17 January 2018.
- ↑ Kocher MS, Zurakowski D, Kasser JR (1999). "Differentiating between septic arthritis and transient synovitis of the hip in children: an evidence-based clinical prediction algorithm". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 81 (12): 1662–70. doi:10.2106/00004623-199912000-00002. PMID 10608376.
- ↑ R. Singhal; D.C. Perry; C.E. Bruce. (2012). "The Diagnostic Utility of Kocher's Criteria in the Diagnosis of Septic Arthritis in Children: An External Validation Study". J Bone Joint Surg. 94-B (XXXV 6).
- 1 2 3 El-Sobky, T; Mahmoud, S (July 2021). "Acute osteoarticular infections in children are frequently forgotten multidiscipline emergencies: beyond the technical skills". EFORT Open Reviews. 6 (7): 584–592. doi:10.1302/2058-5241.6.200155. PMC 8335954 . PMID 34377550.
- ↑ Bruce Jancin. "Kocher Criteria Still the Best Way To ID Septic Arthritis in Children". ACEP. Retrieved 2014-10-17.