South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although most of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

The Drakensberg is the name given to the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation in this region – 2,000 to 3,482 metres. It is located within the borders of South Africa and Lesotho.

The Karoo is a semi desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils.

The Swartberg mountains are a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is composed of two main mountain chains running roughly east–west along the northern edge of the semi-arid Little Karoo. To the north of the range lies the other large semi-arid area in South Africa, the Great Karoo. Most of the Swartberg Mountains are above 2000 m high, making them the tallest mountains in the Western Cape. It is also one of the longest, spanning some 230 km from south of Laingsburg in the west to between Willowmore and Uniondale in the east. Geologically, these mountains are part of the Cape Fold Belt.
The R354 is a Regional Route in South Africa that connects Matjiesfontein with Calvinia via Sutherland.
The R356 is a Regional Route in South Africa that connects the R46 near Ceres with Loxton by way of Sutherland and Fraserburg.

The Langeberg Range is a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Its highest peak is Keeromsberg at 2075m and 15 km NE of the town of Worcester. Some of the highest peaks of the range are located just to the north of Swellendam, in a subrange known as the Clock Peaks whose highest point is 1710 m high Misty Point. Local lore states one can tell the time by means of the shadows cast by the seven summits of the Clock Peaks.

The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a period of about 120 million years.
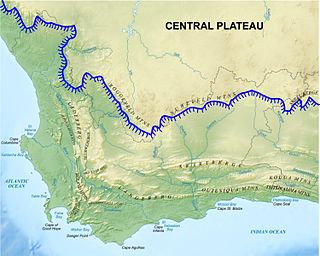
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mountains near Bahía Blanca in Argentina, the Pensacola Mountains, the Ellsworth Mountains and the Hunter-Bowen orogeny in eastern Australia. The rocks involved are generally sandstones and shales, with the shales persisting in the valley floors while the erosion resistant sandstones form the parallel ranges, the Cape Fold Mountains, which reach a maximum height of 2325 m at Seweweekspoortpiek.

The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateau downward in the direction of the oceans that surround Southern Africa on three sides. While it lies predominantly within the borders of South Africa, in the east it extends northwards to form the border between Mozambique and Zimbabwe, continuing on beyond the Zambezi River valley to form the Muchinga Escarpment in eastern Zambia. In the west, it continues northwards into Namibia and Angola.

The Tsitsikamma mountains form an east-west mountain range located in the Garden Route region of the southern South African coast in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces. Tsitsikamma means 'place of much water' in the Khoekhoe language.

The Du Toitskloof Mountains (Dutoitsberge) are a range in the Cape Fold Belt in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. The highest point is Du Toits Peak (Dutoitspiek) which is the highest seaward facing peak in the Cape Fold Belt ranges, i.e. the highest peak in the Western Cape within direct sight of the ocean.
The Hex River Mountains make up the second highest mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa and are located 120 kilometres north-east of Cape Town. They form part of a large anticline in the Cape Fold Belt mountain system and form a north-east, south-west trending mountain system forming the core of the Cape Syntaxis between the towns of Worcester and De Doorns. They are mostly composed of Table Mountain sandstone and most peaks reach 2,000 metres in height or more. The highest mountain is Matroosberg at 2,249 metres, making it the second tallest peak in the province after Seweweekspoort Peak in the Swartberg Mountain Range.

The Table Mountain Sandstone (TMS) is a group of rock formations within the Cape Supergroup sequence of rocks. Although the term "Table Mountain Sandstone" is still widely used in common parlance, the term TMS is no longer formally recognized; the correct name is the "Peninsula Formation Sandstone", which is part of the Table Mountain Group. The designation "Table Mountain Sandstone" will, however, in deference to the title, continue to be used in the rest of this article. The name is derived from the famous landmark in Cape Town, Table Mountain.
The Kleinrivier Mountains are a mountain range in the Cape Fold Belt of the Western Cape province of South Africa. Kleinrivier means "Small River" in Afrikaans and is named after the river in the area that mouths out near Hermanus where the range begins in the west, then continues eastward to north-east of Stanford and terminates at Akkedisberg Pass. The highest mountain in the range is Maanskynkop (964m), and dominates the entire Walker Bay coastline. The mountains experience a very mild Mediterranean climate, moderated by cool, moist winds blowing off the South Atlantic Ocean. Although no peaks exceed 1000m, the range is still quite imposing, as it rises very steeply from sea-level.

The Cobequid Mountains, also sometimes referred to as the Cobequid Hills, is a Canadian mountain range located in Nova Scotia in the mainland portion of the province.

Gamka River is a river located in the Western Cape, South Africa. The name 'Gamka' means 'Lion' and was probably named so by the San people (Bushmen). The river originates north of Beaufort West, generally flowing southwest towards the Gamkapoort Dam.

The Dwyka Group is one of four geological groups that compose the Karoo Supergroup. It is the lowermost geological group and heralds the commencement of sedimentation of the Karoo Supergroup. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic correlation and palynological analyses, these lowermost Karoo strata range between the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) to Early Permian in age.

The Groot River is a river in the southern area of the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is a right hand tributary of the Gourits River.
The Dwyka River is located in the Karoo region, in South Africa. It flows from the North-west, joining the Gamka River as a tributary at the Gamka Dam.