Related Research Articles

An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant or Stonehenge.

The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based astronomy. Created in 1962, ESO has provided astronomers with state-of-the-art research facilities and access to the southern sky. The organisation employs over 750 staff members and receives annual member state contributions of approximately €162 million. Its observatories are located in northern Chile.

Yerkes Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in Williams Bay, Wisconsin, United States. The observatory was operated by the University of Chicago Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics from its founding in 1897 until 2018. Ownership was transferred to the non-profit Yerkes Future Foundation (YFF) in May 2020, which began millions of dollars of restoration and renovation of the historic building and grounds. Yerkes re-opened for public tours and programming in May, 2022. The April, 2024 issue of National Geographic magazine featured a story about the Observatory and ongoing work to restore it to relevance for astronomy, public science engagement and exploring big ideas through art, science, culture and landscape. The observatory offers tickets to programs and tours on its website.

The Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in Green Bank, West Virginia, US is the world's largest fully steerable radio telescope, surpassing the Effelsberg 100-m Radio Telescope in Germany. The Green Bank site was part of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) until September 30, 2016. Since October 1, 2016, the telescope has been operated by the independent Green Bank Observatory. The telescope's name honors the late Senator Robert C. Byrd who represented West Virginia and who pushed the funding of the telescope through Congress.

Palomar Observatory is an astronomical research observatory in the Palomar Mountains of San Diego County, California, United States. It is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). Research time at the observatory is granted to Caltech and its research partners, which include the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Yale University, and the National Astronomical Observatories of China.

McDonald Observatory is an astronomical observatory located near unincorporated community of Fort Davis in Jeff Davis County, Texas, United States. The facility is located on Mount Locke in the Davis Mountains of West Texas, with additional facilities on Mount Fowlkes, approximately 1.3 kilometers (0.81 mi) to the northeast. The observatory is part of The University of Texas at Austin. It is an organized research unit of the College of Natural Sciences.

The Apache Point Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in the Sacramento Mountains in Sunspot, New Mexico, United States, approximately 18 miles (29 km) south of Cloudcroft. The observatory is operated by New Mexico State University (NMSU) and owned by the Astrophysical Research Consortium (ARC). Access to the telescopes and buildings is private and restricted.

The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an astronomical observatory located on the summit of Mt. Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Mt. Cerro Pachón about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) to the southeast. It is approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) east of La Serena, where support facilities are located. The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel Blanco, and the 4.1 m Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, which is situated on Cerro Pachón. Other telescopes on Cerro Tololo include the 1.5 m, 1.3 m, 1.0 m, and 0.9 m telescopes operated by the SMARTS consortium. CTIO also hosts other research projects, such as PROMPT, WHAM, and LCOGTN, providing a platform for access to the southern hemisphere for U.S. and worldwide scientific research.

The Giant Magellan Telescope is a 25.4-meter, ground-based, extremely large telescope under construction at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile's Atacama Desert. Commissioning is anticipated in the early 2030s. Once complete, the Giant Magellan will be the largest Gregorian telescope ever built observing in optical and mid-infrared light. The telescope uses seven of the world’s largest mirrors to form a light collecting area of 368 square meters.

The Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), previously known as the Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, is an astrophysics research institute jointly operated by the Harvard College Observatory and Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Founded in 1973 and headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, the CfA leads a broad program of research in astronomy, astrophysics, Earth and space sciences, as well as science education. The CfA either leads or participates in the development and operations of more than fifteen ground- and space-based astronomical research observatories across the electromagnetic spectrum, including the forthcoming Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, one of NASA's Great Observatories.

The Haleakalā Observatory, also known as the Haleakalā High Altitude Observatory Site, is Hawaii's first astronomical research observatory. It is located on the island of Maui and is owned by the Institute for Astronomy of the University of Hawaiʻi, which operates some of the facilities on the site and leases portions to other organizations. Tenants include the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network (LCOGTN). At over 3,050 meters (10,010 ft) in altitude, the summit of Haleakalā is above one third of the Earths's troposphere and has excellent astronomical seeing conditions.

South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO) is the national centre for optical and infrared astronomy in South Africa. It was established in 1972. The observatory is run by the National Research Foundation of South Africa. The facility's function is to conduct research in astronomy and astrophysics. The primary telescopes are located in Sutherland, which is 370 kilometres (230 mi) from Observatory, Cape Town, where the headquarters is located.

The Florence and George Wise Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Tel Aviv University. It is located 5 kilometers west of the town of Mitzpe Ramon in the Negev desert near the edge of the Ramon Crater, and it is the only professional astronomical observatory in Israel.
Anderson Mesa Station is an astronomical observatory established in 1959 as a dark-sky observing site for Lowell Observatory. It is located at Anderson Mesa in Coconino County, Arizona, about 12 miles (19 km) southeast of Lowell's main campus on Mars Hill in Flagstaff, Arizona.

Nancy Grace Roman was an American astronomer who made important contributions to stellar classification and motions. The first female executive at NASA, Roman served as NASA's first Chief of Astronomy throughout the 1960s and 1970s, establishing her as one of the "visionary founders of the US civilian space program".
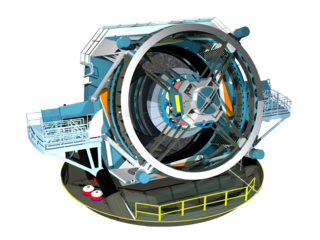
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, formerly known as the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), is an astronomical observatory currently under construction in Chile. Its main task will be carrying out a synoptic astronomical survey, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time. The word synoptic is derived from the Greek words σύν and ὄψις, and describes observations that give a broad view of a subject at a particular time. The observatory is located on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón, a 2,682-meter-high mountain in Coquimbo Region, in northern Chile, alongside the existing Gemini South and Southern Astrophysical Research Telescopes. The LSST Base Facility is located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) away from the observatory by road, in the town of La Serena. The observatory is named for Vera Rubin, an American astronomer who pioneered discoveries about galaxy rotation rates.

In 2011, Chile was home to 42% of the world's astronomical infrastructure, consisting principally of telescopes. In 2015, it was estimated that Chile would contain more than 50% of the global astronomical infrastructure by 2030. In the Atacama desert region of northern Chile, the skies are exceptionally clear and dry for more than 300 days of the year. These conditions have attracted the world's scientific community to develop highly ambitious astronomical projects in the Atacama desert.

Norio Kaifu was a Japanese astronomer. He was best known as the president of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) from 2012 to 2015. He directed the Subaru telescope project, which housed the largest monolithic primary mirror in the world from its commission until 2005. Kaifu researched in radio astronomy, extragalactic astronomy, cosmic magnetic fields, non-stable stars, and infrared astronomy. The minor planet 6412 Kaifu is named in his honor.
References
- ↑ "Kottamia Astronomical Observatory". NRIAG. Retrieved 2020-12-04.
- ↑ "Ticket to space with Kottamia Astronomical Observatory in Egypt". EgyptToday. 2017-10-20. Retrieved 2020-12-04.
- ↑ Issa, I. A.; Gamal El Din, A. I. (1986-01-01). "Astronomical research activities with the 74 inch telescope at Kottamia observatory". Astrophysics and Space Science. 118 (1): 87–93. Bibcode:1986Ap&SS.118...87I. doi:10.1007/BF00651113. ISSN 1572-946X. S2CID 123287944.
- ↑ "The story of Kottamia Observatory". NRIAG. 2018-03-22. Retrieved 2020-12-04.
29°56′02″N31°49′40″E / 29.93402°N 31.82773°E