
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A speaker system, also often simply referred to as a speaker or loudspeaker, comprises one or more such speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections possibly including a crossover network. The speaker driver can be viewed as a linear motor attached to a diaphragm which couples that motor's movement to motion of air, that is, sound. An audio signal, typically from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is amplified electronically to a power level capable of driving that motor in order to reproduce the sound corresponding to the original unamplified electronic signal. This is thus the opposite function to the microphone; indeed the dynamic speaker driver, by far the most common type, is a linear motor in the same basic configuration as the dynamic microphone which uses such a motor in reverse, as a generator.

Audio crossovers are a type of electronic filter circuitry that splits an audio signal into two or more frequency ranges, so that the signals can be sent to loudspeaker drivers that are designed to operate within different frequency ranges. The crossover filters can be either active or passive. They are often described as two-way or three-way, which indicate, respectively, that the crossover splits a given signal into two frequency ranges or three frequency ranges. Crossovers are used in loudspeaker cabinets, power amplifiers in consumer electronics and pro audio and musical instrument amplifier products. For the latter two markets, crossovers are used in bass amplifiers, keyboard amplifiers, bass and keyboard speaker enclosures and sound reinforcement system equipment.
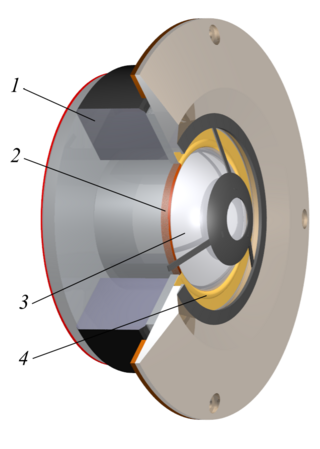
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically deliver high frequencies up to 100 kHz. The name is derived from the high pitched sounds made by some birds (tweets), especially in contrast to the low woofs made by many dogs, after which low-frequency drivers are named (woofers).
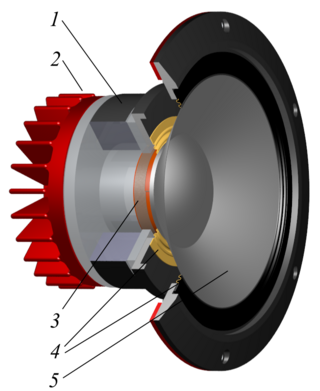
A mid-range speaker is a loudspeaker driver that reproduces sound in the frequency range from 250 to 2000 Hz.
A woofer or bass speaker is a technical term for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from 20 Hz up to 80 Hz. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's deep bark, "woof". The most common design for a woofer is the electrodynamic driver, which typically uses a stiff paper cone, driven by a voice coil surrounded by a magnetic field.

A voice coil is the coil of wire attached to the apex of a loudspeaker cone. It provides the motive force to the cone by the reaction of a magnetic field to the current passing through it.
Celestion is a British designer and exporter of professional loudspeakers.

Magnepan is a private high-end audio loudspeaker manufacturer in White Bear Lake, Minnesota, United States. Their loudspeaker technology was conceived and implemented by engineer Jim Winey in 1969.

Rudolph Thomas Bozak (1910–1982) was an audio electronics and acoustics designer and engineer in the field of sound reproduction. His parents were Bohemian Czech immigrants; Rudy was born in Uniontown, Pennsylvania. Bozak studied at Milwaukee School of Engineering; in 1981, the school awarded him an honorary doctorate in engineering. Bozak married Lillian Gilleski; the two had three daughters: Lillian, Mary and Barbara.

Powered speakers, also known as self-powered speakers and active speakers, are loudspeakers that have built-in amplifiers. Powered speakers are used in a range of settings, including in sound reinforcement systems, both for the main speakers facing the audience and the monitor speakers facing the performers; by DJs performing at dance events and raves; in private homes as part of hi-fi or home cinema audio systems and as computer speakers. They can be connected directly to a mixing console or other low-level audio signal source without the need for an external amplifier. Some active speakers designed for sound reinforcement system use have an onboard mixing console and microphone preamplifier, which enables microphones to be connected directly to the speaker.
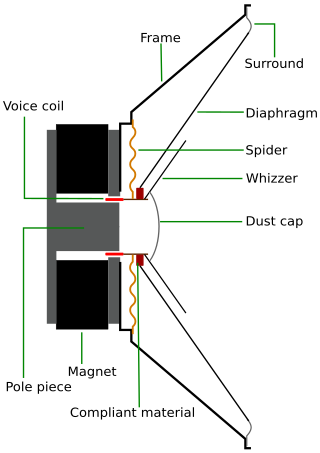
A full-range loudspeaker drive unit is defined as a driver which reproduces as much of the audible frequency range as possible, within the limitations imposed by the physical constraints of a specific design. The frequency range of these drivers is maximized through the use of a whizzer cone and other means. Most single driver systems, such as those in radios, or small computer speaker designs, cannot reproduce all of the audible frequencies or the entire audible audio range.
The chief electrical characteristic of a dynamic loudspeaker's driver is its electrical impedance as a function of frequency. It can be visualized by plotting it as a graph, called the impedance curve.

A loudspeaker enclosure or loudspeaker cabinet is an enclosure in which speaker drivers and associated electronic hardware, such as crossover circuits and, in some cases, power amplifiers, are mounted. Enclosures may range in design from simple, homemade DIY rectangular particleboard boxes to very complex, expensive computer-designed hi-fi cabinets that incorporate composite materials, internal baffles, horns, bass reflex ports and acoustic insulation. Loudspeaker enclosures range in size from small "bookshelf" speaker cabinets with 4-inch (10 cm) woofers and small tweeters designed for listening to music with a hi-fi system in a private home to huge, heavy subwoofer enclosures with multiple 18-inch (46 cm) or even 21-inch (53 cm) speakers in huge enclosures which are designed for use in stadium concert sound reinforcement systems for rock music concerts.

Studio monitors are loudspeakers in speaker enclosures specifically designed for professional audio production applications, such as recording studios, filmmaking, television studios, radio studios and project or home studios, where accurate audio reproduction is crucial. Among audio engineers, the term monitor implies that the speaker is designed to produce relatively flat (linear) phase and frequency responses. In other words, it exhibits minimal emphasis or de-emphasis of particular frequencies, the loudspeaker gives an accurate reproduction of the tonal qualities of the source audio, and there will be no relative phase shift of particular frequencies—meaning no distortion in sound-stage perspective for stereo recordings. Beyond stereo sound-stage requirements, a linear phase response helps impulse response remain true to source without encountering "smearing". An unqualified reference to a monitor often refers to a near-field design. This is a speaker small enough to sit on a stand or desk in proximity to the listener, so that most of the sound that the listener hears is coming directly from the speaker, rather than reflecting off walls and ceilings. Monitor speakers may include more than one type of driver or, for monitoring low-frequency sounds, such as bass drum, additional subwoofer cabinets may be used.

Bi-amping and tri-amping is the practice of using two or three audio amplifiers respectively to amplify different audio frequency ranges, with the amplified signals being routed to different speaker drivers, such as woofers, subwoofers and tweeters. With bi-amping and tri-amping, an audio crossover is used to divide a sound signal into different frequency ranges, each of which is then separately amplified and routed to separate speaker drivers. In Powered speakers using bi-amping, multiple speaker drivers are in the same speaker enclosure. In some bi-amp set-ups, the drivers are in separate speaker enclosures, such as with home stereos that contain two speakers and a separate subwoofer.

A guitar speaker is a loudspeaker – specifically the driver (transducer) part – designed for use in a combination guitar amplifier of an electric guitar, or for use in a guitar speaker cabinet. Typically these drivers produce only the frequency range relevant to electric guitars, which is similar to a regular woofer type driver, which is approximately 75 Hz — 5 kHz, or for electric bass speakers, down to 41 Hz for regular four-string basses or down to about 30 Hz for five-string instruments.
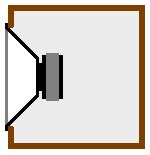
Acoustic suspension is a method of loudspeaker cabinet design and utilizations that uses one or more loudspeaker drivers mounted in a sealed box or cabinet. Acoustic suspension systems reduce bass distortion that can be caused by stiff motor suspensions in conventional loudspeakers.

An electrodynamic speaker driver, often called simply a speaker driver when the type is implicit, is an individual transducer that converts an electrical audio signal to sound waves. While the term is sometimes used interchangeably with the term speaker (loudspeaker), it is usually applied to specialized transducers which reproduce only a portion of the audible frequency range. For high fidelity reproduction of sound, multiple loudspeakers are often mounted in the same enclosure, each reproducing a different part of the audible frequency range. In this case the individual speakers are referred to as drivers and the entire unit is called a loudspeaker. Drivers made for reproducing high audio frequencies are called tweeters, those for middle frequencies are called mid-range drivers, and those for low frequencies are called woofers, while those for very low bass range are subwoofers. Less common types of drivers are supertweeters and rotary woofers.
The Wharfedale MACH series of loudspeakers consists of the MACH 3, 5, 7, and 9. This is an informational page devoted to owners and users of these loudspeakers and those interested in history and construction of electronic sound reproduction.

The Linn Isobarik, nicknamed "Bariks" or "Briks", is a loudspeaker designed and manufactured by Linn Products. The Isobarik is known for both its reproduction of low bass frequencies and being very demanding on amplifiers.
















