
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a U.S. federal government agency within the U.S. Department of Transportation which regulates civil aviation in the United States and surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic control, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles, powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization.

Aviation safety is the study and practice of managing risks in aviation. This includes preventing aviation accidents and incidents through research, educating air travel personnel, passengers and the general public, as well as the design of aircraft and aviation infrastructure. The aviation industry is subject to significant regulation and oversight.

Saudia Flight 163 was a scheduled Saudia passenger flight departing from Quaid-E-Azam Airport in Karachi, Pakistan, bound for Kandara Airport in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, via Riyadh International Airport in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, which caught fire after takeoff from Riyadh International Airport on 19 August 1980. Although the Lockheed L-1011-200 TriStar made a successful emergency landing at Riyadh, the flight crew failed to perform an emergency evacuation of the airplane, leading to the deaths of all 287 passengers and 14 crew on board the aircraft from smoke inhalation.
Crew resource management or cockpit resource management (CRM) is a set of training procedures for use in environments where human error can have devastating effects. CRM is primarily used for improving aviation safety and focuses on interpersonal communication, leadership, and decision making in aircraft cockpits. Its founder is David Beaty, a former Royal Air Force and a BOAC pilot who wrote "The Human Factor in Aircraft Accidents" (1969). Despite the considerable development of electronic aids since then, many principles he developed continue to prove effective.

The Kentucky Transportation Cabinet (KYTC) is Kentucky's state-funded agency charged with building and maintaining federal highways and Kentucky state highways, as well as regulating other transportation related issues.

Pilot error generally refers to an accident in which an action or decision made by the pilot was the cause or a contributing factor that led to the accident, but also includes the pilot's failure to make a correct decision or take proper action. Errors are intentional actions that fail to achieve their intended outcomes. The Chicago Convention defines the term "accident" as "an occurrence associated with the operation of an aircraft [...] in which [...] a person is fatally or seriously injured [...] except when the injuries are [...] inflicted by other persons." Hence the definition of "pilot error" does not include deliberate crashing.

The airport apron, apron, flight line, or ramp is the area of an airport where aircraft are parked, unloaded or loaded, refueled, boarded, or maintained. Although the use of the apron is covered by regulations, such as lighting on vehicles, it is typically more accessible to users than the runway or taxiway. However, the apron is not usually open to the general public, and a permit may be required to gain access. An apron's designated areas for aircraft parking are called aircraft stands.
TAMDAR is a weather monitoring system that consists of an in situ atmospheric sensor mounted on commercial aircraft for data gathering. It collects information similar to that collected by radiosondes carried aloft by weather balloons. It was developed by AirDat LLC, which was acquired by Panasonic Avionics Corporation in April 2013 and was operated until October 2018 under the name Panasonic Weather Solutions. It is now owned by FLYHT Aerospace Solutions Ltd.

A runway incursion is an aviation incident involving improper positioning of vehicles or people on any airport runway or its protected area. When an incursion involves an active runway being used by arriving or departing aircraft, the potential for a collision hazard or Instrument Landing System (ILS) interference can exist. At present, various runway safety technologies and processes are commonly employed to reduce the risk and potential consequences of such an event.
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) project to modernize the National Airspace System (NAS). The FAA began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to finish the final implementation segment by 2030. The goals of the modernization include using new technologies and procedures to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation.

The Aviators Code Initiative (ACI), formerly the Aviators Model Code of Conduct, is a set of model recommended practices designed to improve general aviation safety and airmanship.
Maintenance resource management (MRM) training is an aircraft maintenance variant on crew resource management (CRM). Although the term MRM was used for several years following CRM's introduction, the first governmental guidance for standardized MRM training and its team-based safety approach, appeared when the FAA (U.S.) issued Advisory Circular 120-72, Maintenance Resource Management Training in September, 2000.
The Professional Aviation Safety Specialists (PASS) is affiliated with the AFL–CIO through its affiliation with the Marine Engineers' Beneficial Association. It represents more than 11,000 Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) Airway Transportation Systems Specialists and Department of Defense employees.
Maritime resource management (MRM) or bridge resource management (BRM) is a set of human factors and soft skills training aimed at the maritime industry. The MRM training programme was launched in 1993 – at that time under the name bridge resource management – and aims at preventing accidents at sea caused by human error.

Donald Lee Moak is an expert in aviation safety, consultant, and the co-founder of Intrepid, a public affairs, advocacy, and business consulting firm located in Washington, D.C. He previously served as co-chair of The DOT Special Committee to Review FAA’s Aircraft Certification Process. Before joining Delta Air Lines and working his way up to a B-767 Delta Air Lines captain, Moak served as a Marine Corps and U.S. Navy Reserve fighter pilot, and as president of the Air Line Pilots Association, International (ALPA).
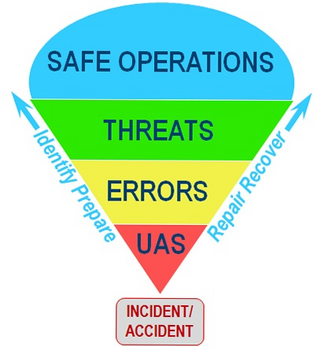
In aviation safety, threat and error management (TEM) is an overarching safety management approach that assumes that pilots will naturally make mistakes and encounter risky situations during flight operations. Rather than try to avoid these threats and errors, its primary focus is on teaching pilots to manage these issues so they do not impair safety. Its goal is to maintain safety margins by training pilots and flight crews to detect and respond to events that are likely to cause damage (threats) as well as mistakes that are most likely to be made (errors) during flight operations.
NOTECHS is a system used to assess the non-technical skills of crew members in the aviation industry. Introduced in the late 1990s, the system has been widely used by airlines during crew selection process, picking out individuals who possess capable skills that are not directly related to aircraft controls or systems. In aviation, 70 percent of all accidents are induced from pilot error, lack of communication and decision making being two contributing factors to these accidents. NOTECHS assesses and provides feedback on the performance of pilots' social and cognitive skills to help minimize pilot error and enhance safety in the future. The NOTECHS system also aims to improve the Crew Resource Management training system.
The Aviation Safety Action Program (ASAP) is a US aviation proactive safety program. ASAP promotes safety by encouraging voluntary self reporting of safety occurrences and situations to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) certificate holder. The reports are analyzed to reduce hazards and focus training. Reporting is encouraged by providing the volunteer reporter protection from certificate action. ASAP forms a safety team between the FAA, the certificate holder (airline/operator), employee, and the operator's employee labor organization. Safety improvement occurs without discipline, encouraging further and continued hazard reporting.









