
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes.

The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called Human gammaherpesvirus 4, is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certain gene. Gene silencing can occur during either transcription or translation and is often used in research. In particular, methods used to silence genes are being increasingly used to produce therapeutics to combat cancer and other diseases, such as infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.

Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis.
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to cancer whereas the majority of mutations do not.

Decitabine, sold under the brand name Dacogen among others, acts as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor. It is a medication for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, a class of conditions where certain blood cells are dysfunctional, and for acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Chemically, it is a cytidine analog.
Chromatin remodeling is the dynamic modification of chromatin architecture to allow access of condensed genomic DNA to the regulatory transcription machinery proteins, and thereby control gene expression. Such remodeling is principally carried out by 1) covalent histone modifications by specific enzymes, e.g., histone acetyltransferases (HATs), deacetylases, methyltransferases, and kinases, and 2) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes which either move, eject or restructure nucleosomes. Besides actively regulating gene expression, dynamic remodeling of chromatin imparts an epigenetic regulatory role in several key biological processes, egg cells DNA replication and repair; apoptosis; chromosome segregation as well as development and pluripotency. Aberrations in chromatin remodeling proteins are found to be associated with human diseases, including cancer. Targeting chromatin remodeling pathways is currently evolving as a major therapeutic strategy in the treatment of several cancers.

Deleted in Liver Cancer 1 also known as DLC1 and StAR-related lipid transfer protein 12 (STARD12) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DLC1 gene.

Cdc6, or cell division cycle 6, is a protein in eukaryotic cells. It is mainly studied in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is an essential regulator of DNA replication and plays important roles in the activation and maintenance of the checkpoint mechanisms in the cell cycle that coordinate S phase and mitosis. It is part of the pre-replicative complex (pre-RC) and is required for loading minichromosome maintenance (MCM) proteins onto the DNA, an essential step in the initiation of DNA synthesis. In addition, it is a member of the family of AAA+ ATPases and highly related to ORC1; both are the same protein in archaea.
Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) is a multifunctional, dimeric viral protein associated with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). It is the only EBV protein found in all EBV-related malignancies. It is important in establishing and maintaining the altered state that cells take when infected with EBV. EBNA1 has a glycine–alanine repeat sequence that separates the protein into amino- and carboxy-terminal domains. This sequence also seems to stabilize the protein, preventing proteasomal breakdown, as well as impairing antigen processing and MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation. This thereby inhibits the CD8-restricted cytotoxic T cell response against virus-infected cells. EBNA1 is expressed from the Qp promoter during all latency programs. It is the only viral protein expressed in latency program I.

Wee1 is a nuclear kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Wee1 has a molecular mass of 96 kDa and is a key regulator of cell cycle progression. It influences cell size by inhibiting the entry into mitosis, through inhibiting Cdk1. Wee1 has homologues in many other organisms, including mammals.
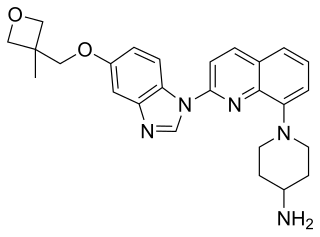
Crenolanib besylate is an investigational inhibitor being developed by AROG Pharmaceuticals, LLC. The compound is currently being evaluated for safety and efficacy in clinical trials for various types of cancer, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), and glioma. Crenolanib is an orally bioavailable benzimidazole that selectively and potently inhibits signaling of wild-type and mutant isoforms of class III receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) FLT3, PDGFR α, and PDGFR β. Unlike most RTK inhibitors, crenolanib is a type I mutant-specific inhibitor that preferentially binds to phosphorylated active kinases with the ‘DFG in’ conformation motif.

In molecular biology miR-203 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms, such as translational repression and Argonaute-catalyzed messenger RNA cleavage. miR-203 has been identified as a skin-specific microRNA, and it forms an expression gradient that defines the boundary between proliferative epidermal basal progenitors and terminally differentiating suprabasal cells. It has also been found upregulated in psoriasis and differentially expressed in some types of cancer.

Cancer epigenetics is the study of epigenetic modifications to the DNA of cancer cells that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence, but instead involve a change in the way the genetic code is expressed. Epigenetic mechanisms are necessary to maintain normal sequences of tissue specific gene expression and are crucial for normal development. They may be just as important, if not even more important, than genetic mutations in a cell's transformation to cancer. The disturbance of epigenetic processes in cancers, can lead to a loss of expression of genes that occurs about 10 times more frequently by transcription silencing than by mutations. As Vogelstein et al. points out, in a colorectal cancer there are usually about 3 to 6 driver mutations and 33 to 66 hitchhiker or passenger mutations. However, in colon tumors compared to adjacent normal-appearing colonic mucosa, there are about 600 to 800 heavily methylated CpG islands in the promoters of genes in the tumors while these CpG islands are not methylated in the adjacent mucosa. Manipulation of epigenetic alterations holds great promise for cancer prevention, detection, and therapy. In different types of cancer, a variety of epigenetic mechanisms can be perturbed, such as the silencing of tumor suppressor genes and activation of oncogenes by altered CpG island methylation patterns, histone modifications, and dysregulation of DNA binding proteins. There are several medications which have epigenetic impact, that are now used in a number of these diseases.
Melanoma is a rare but aggressive malignant cancer that originates from melanocytes. These melanocytes are cells found in the basal layer of the epidermis that produce melanin under the control of melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Despite the fact that melanoma represents only a small number of all skin cancers, it is the cause of more than 50% of cancer-related deaths. The high metastatic qualities and death rate, and also its prevalence among people of younger ages have caused melanoma to become a highly researched malignant cancer. Epigenetic modifications are suspected to influence the emergence of many types of cancer-related diseases, and are also suspected to have a role in the development of melanoma.
Pharmacoepigenetics is an emerging field that studies the underlying epigenetic marking patterns that lead to variation in an individual's response to medical treatment.
Epigenetic effects of smoking concerns how epigenetics contributes to the deleterious effects of smoking. Cigarette smoking has been found to affect global epigenetic regulation of transcription across tissue types. Studies have shown differences in epigenetic markers like DNA methylation, histone modifications and miRNA expression between smokers and non-smokers. Similar differences exist in children whose mothers smoked during pregnancy. These epigenetic effects are thought to be linked to many of negative health effects associated with smoking.
HSV epigenetics is the epigenetic modification of herpes simplex virus (HSV) genetic code.

Steroid Receptor Associated and Regulated Protein (SRARP) in humans is a protein encoded by a gene of the same name with two exons that is located on chromosome 1p36.13. SRARP contains 169 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 17,657 Da.
CYLD cutaneous syndrome (CCS) is the recently designated term for three rare inherited cutaneous adnexal tumor syndromes: multiple familial trichoepithelioma (MFT1), Brooke–Spiegler syndrome (BSS), and familial cylindromatosis (FC). Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a large group of skin tumors that consist of tissues that have differentiated towards one of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. CCS tumors are hair follicle tumors.










