Internet Explorer is a retired series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were used in the Windows line of operating systems. While IE has been discontinued on most Windows editions, it remains supported on certain editions of Windows, such as Windows 10 LTSB/LTSC. Starting in 1995, it was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year. Later versions were available as free downloads or in-service packs and included in the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) service releases of Windows 95 and later versions of Windows. Microsoft spent over US$100 million per year on Internet Explorer in the late 1990s, with over 1,000 people involved in the project by 1999. New feature development for the browser was discontinued in 2016 and ended support on June 15, 2022 for Windows 10 Semi-Annual Channel (SAC), in favor of its successor, Microsoft Edge.

Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet editor developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Office suites of software and has been developed since 1985.

Netscape Navigator is a discontinued proprietary web browser, and the original browser of the Netscape line, from versions 1 to 4.08, and 9.x. It was the flagship product of the Netscape Communications Corporation and was the dominant web browser in terms of usage share in the 1990s, but by around 2003 its user base had all but disappeared. This was partly because the Netscape Corporation did not sustain Netscape Navigator's technical innovation in the late 1990s.
Netscape Communications Corporation was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California, and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was once dominant but lost to Internet Explorer and other competitors in the first browser war, with its market share falling from more than 90 percent in the mid-1990s to less than one percent in 2006. An early Netscape employee, Brendan Eich, created the JavaScript programming language, the most widely used language for client-side scripting of web pages. A founding engineer of Netscape, Lou Montulli, created HTTP cookies. The company also developed SSL which was used for securing online communications before its successor TLS took over.
A web browser is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. By 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people had used a browser. The most-used browser is Google Chrome, with a 67% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%.
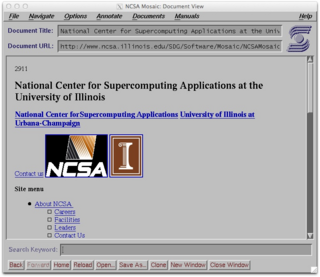
NCSA Mosaic was among the first widely available web browsers, instrumental in popularizing the World Wide Web and the general Internet by integrating multimedia such as text and graphics. Mosaic was the first browser to display images inline with text.

Cello is an early, discontinued graphical web browser for Windows 3.1; it was developed by Thomas R. Bruce of the Legal Information Institute at Cornell Law School. It was released as shareware in 1993. While other browsers ran on various Unix machines, Cello was the first web browser for Microsoft Windows, using the winsock system to access the Internet. In addition to the basic Windows, Cello worked on Windows NT 3.5 and with small modifications on OS/2.
XUL, which stands for XML User Interface Language, is a user interface markup language developed by Mozilla. XUL is an XML dialect for writing graphical user interfaces, enabling developers to write user interface elements in a manner similar to web pages.
Spyglass, Inc. was an Internet software company. It was founded in 1990, in Champaign, Illinois, as an offshoot of the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, and later moved to Naperville, Illinois. Spyglass was created to commercialize and support technologies from the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). It focused on data visualization tools, such as graphing packages and 3D rendering engines.
This is a comparison of both historical and current web browsers based on developer, engine, platform(s), releases, license, and cost.

IrfanView is an image viewer, editor, organiser and converter program for Microsoft Windows. It can also play video and audio files, and has some image creation and painting capabilities. IrfanView is free for non-commercial use; commercial use requires paid registration. It is noted for its small size, speed, ease of use, and ability to handle a wide variety of graphic file formats. It was first released in 1996.
The Line Mode Browser is the second web browser ever created. The browser was the first demonstrated to be portable to several different operating systems. Operated from a simple command-line interface, it could be widely used on many computers and computer terminals throughout the Internet. The browser was developed starting in 1990, and then supported by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as an example and test application for the libwww library.

AOLpress is a discontinued HTML editor that was available from America Online (AOL). It was originally developed as NaviPress by the company NaviSoft before being bought by AOL. It was discontinued in 2000. However, the last version (2.0) may still be found on some Web sites for downloading.

Microsoft Internet Explorer 4 (IE4) is the fourth, and discontinued, version of the Internet Explorer graphical web browser that Microsoft unveiled in Spring of 1997, and released on September 22, 1997, primarily for Microsoft Windows, but also with versions available for the classic Mac OS, Solaris, and HP-UX and marketed as "The Web the Way You Want It".

ACDSee is an image organizer, viewer, and image editor program for Windows, macOS and iOS, developed by ACD Systems International Inc. ACDSee was originally distributed as a 16-bit application for Windows 3.0 and later supplanted by a 32-bit version for Windows 95. ACDSee Pro 6 adds native 64-bit support. The newest versions of ACDSee incorporate modern Digital Asset Management tools like Face Detection & Facial Recognition.

The Netscape web browser is the general name for a series of web browsers formerly produced by Netscape Communications Corporation, which eventually became a subsidiary of AOL. The original browser was once the dominant browser in terms of usage share, but as a result of the first browser war, it lost virtually all of its share to Internet Explorer due to Microsoft's anti-competitive bundling of Internet Explorer with Windows.
NetObjectsFusion (NOF) is a web design tool, from 1996 to 2001 developed and distributed by NetObjects, Inc., marketed from 2001 until 2009 by Web.com, which bought the application in 2001, and from July 2009 on distributed again by the re-established NetObjects, Inc.
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. It further provides for the capture or input of information which may be returned to the presenting system, then stored or processed as necessary. The method of accessing a particular page or content is achieved by entering its address, known as a Uniform Resource Identifier or URI. This may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content. Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to navigate their browsers to related resources. A web browser can also be defined as an application software or program designed to enable users to access, retrieve and view documents and other resources on the Internet.

UdiWWW is an early, now discontinued freeware graphical HTML 3.2 web browser for 16-bit and 32-bit Microsoft Windows. It was written and developed by Bernd Richter in C/C++ from 1995 to 1996. Following the release of version 1.2 in April 1996, Richter ceased development, stating "let Microsoft with the ActiveX Development Kit do the rest."