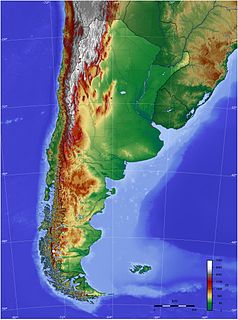
The geography of Argentina describes the geographic features of Argentina, a country located in southern South America. Bordered by the Andes in the west and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, neighboring countries are Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, and Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast.

An endorheic basin is a limited drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. Such a basin may also be referred to as a closed or terminal basin or as an internal drainage system or interior drainage basin.
Argentina is provided with a vast territory and a huge variety of climates and microclimates ranging from tundra and polar in the south to the tropical climate in the north, through a vast expanse of temperate climate and natural wonders like the Aconcagua, the highest mountain in the world outside the Himalayas, the widest river and estuary of the planet, the huge and mighty Iguazú Falls, some of the flattest and wide meadows-plains of planet Earth, culture, customs and cuisines famous internationally, a higher degree of development, good quality of life and people and relatively well prepared infrastructure make this country one of the most visited in America.

The Uruguay River is a river in South America. It flows from north to south and forms parts of the boundaries of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, separating some of the Argentine provinces of La Mesopotamia from the other two countries. It passes between the states of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil; forms the eastern border of the provinces of Misiones, Corrientes, and Entre Ríos in Argentina; and makes up the western borders of the departments of Artigas, Salto, Paysandú, Río Negro, Soriano, and Colonia in Uruguay.

Santa Cruz Province is a province of Argentina, located in the southern part of the country, in Patagonia. It borders Chubut Province to the north, and Chile to the west and south, with an Atlantic coast on its east. Santa Cruz is the second-largest province of the country, and the least densely populated in mainland Argentina.
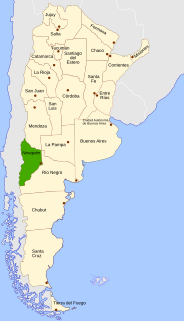
Neuquén is a province of Argentina, located in the west of the country, at the northern end of Patagonia. It borders Mendoza Province to the north, Rio Negro Province to the southeast, and Chile to the west. It also meets La Pampa Province at its northeast corner.

San Carlos de Bariloche, usually known as Bariloche, is a city in the province of Río Negro, Argentina, situated in the foothills of the Andes on the southern shores of Nahuel Huapi Lake. It is located within the Nahuel Huapi National Park. After development of extensive public works and Alpine-styled architecture, the city emerged in the 1930s and 1940s as a major tourism centre with skiing, trekking and mountaineering facilities. In addition, it has numerous restaurants, cafés, and chocolate shops. The city has a permanent population of 108,205 according to the 2010 census.
An inland port is a port on an inland waterway, such as a river, lake, or canal, which may or may not be connected to the sea. The term "inland port" is also used to refer to a dry port, which is an inland extension of a seaport, usually connected by rail to the docks. This article covers only ports that are covered by the first definition.

Los Alerces National Park is located in the Andes in Chubut Province in the Patagonian region of Argentina. Its western boundary coincides with the Chilean border. Successive glaciations have molded the landscape in the region creating spectacular features such as moraines, glacial cirques and clear-water lakes. The vegetation is dominated by dense temperate forests, which give way to alpine meadows higher up under the rocky Andean peaks. A highly distinctive and emblematic feature is its alerce forest; the globally threatened alerce tree is the second longest living tree species in the world. The alerce forests in the park are in an excellent state of conservation. The property is vital for the protection of some of the last portions of continuous Patagonian Forest in an almost pristine state and is the habitat for a number of endemic and threatened species of flora and fauna.

Nahuel Huapi Lake is a lake in the lake region of northern Patagonia between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén, in Argentina. The tourist center of Bariloche is on the southern shore of the lake.

Viedma Lake, approximately 50 miles long in southern Patagonia near the border between Chile and Argentina. It's a major elongated trough lake formed from melting glacial ice. Viedma Lake is the second largest lake in Argentina.

Mar Chiquita or Mar de Ansenuza is an endorheic salt lake located in the northeast of the province of Córdoba, in central Argentina. The northeast corner of the lake also extends into southeastern Santiago del Estero Province. It is the largest of the naturally occurring saline lakes in Argentina. The lake is located in parts of five departments in the two provinces.

The Los Ríos Region is one of Chile's 16 regions, the country's first-order administrative divisions. Its capital is Valdivia. It began to operate as a region on October 2, 2007, having been created by subdividing the Los Lagos Region in southern Chile. It consists of two provinces: Valdivia and the newly created Ranco Province, which was formerly part of Valdivia Province.

Lago Argentino is a lake in the Patagonian province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, at 50°2′S72°4′W. It is the biggest freshwater lake in Argentina, with a surface area of 1,415 km2 (546 sq mi). It has an average depth of 150 m (492 ft), and a maximum depth of 500 m (1,640 ft).

The lake known as O'Higgins in Chile and San Martín in Argentina is located around coordinates 48°50′S72°36′W in Patagonia, between the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region and the Santa Cruz Province.

The Puelo River has its origin in Lake Puelo in Argentine, and flows north-west through the Andes into Chile and the Reloncaví Estuary of the Reloncaví Sound at the northern end of the Gulf of Ancud.

The Pueyrredón/Cochrane Lake is a glacier fed lake located on the eastern edge of the southern Andes, straddling the border between Argentina and Chile. It is named after Lord Cochrane on the Chilean side and Pueyrredón on the Argentina side. The border is a peninsula that juts out into the lake on the north side. The border to the north of the lake follows the ridgeline of the last major expression of the eastern Andes. The Argentine portion of the lake has a surface of 150 km2 (58 sq mi), while the portion in Chile covers 175 km2 (68 sq mi).
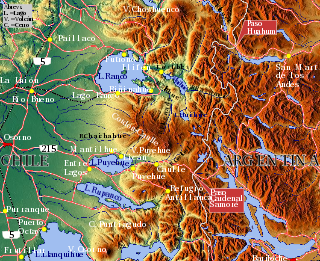
The Huahum River is a river in southern Chile and Argentina. It drains the waters of Lácar Lake in Argentina to Pirihueico Lake in Chile. The river gives name to Huahum Pass, an international mountain pass on the border between Chile and Argentina.

















