Related Research Articles

Rennes is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the rivers Ille and Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department. In 2017, the urban area had a population of 357,327 inhabitants, and the larger metropolitan area had 739,974 inhabitants. The inhabitants of Rennes are called Rennais (masculine) or Rennaises (feminine) in French.

The 5th arrondissement of Paris is one of the 20 arrondissements of the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is referred to as le cinquième.

Gérard de Nerval was the pen name of the French writer, poet, and translator Gérard Labrunie, a major figure of French romanticism, best known for his novellas and poems, especially the collection Les Filles du feu, which included the novella Sylvie and the poem "El Desdichado". Through his translations, Nerval played a major role in introducing French readers to the works of German Romantic authors, including Klopstock, Schiller, Bürger and Goethe. His later work merged poetry and journalism in a fictional context and influenced Marcel Proust. His last novella, Aurélia ou le rêve et la vie, influenced André Breton and Surrealism.

The 2nd arrondissement of Paris is one of the 20 arrondissements of the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is colloquially referred to as deuxième. It is governed locally together with the 1st, 3rd and 4th arrondissement, with which it forms the 1st sector of Paris.

A grande école is a specialized top-level educational institution in France. Grandes écoles are part of an alternative educational system that operates alongside the mainstream French public university system, and take the shape of institutes dedicated to teaching, research and professional training in either pure natural and social sciences, or applied sciences such as engineering, architecture, business administration, or public policy and administration.

Paris-Panthéon-Assas University or Assas University, commonly known as Assas or Paris 2, is a university in Paris, often described as the top law school of France. It is considered as the direct inheritor of the Faculty of Law of Paris, the second-oldest faculty of Law in the world, founded in the 12th century.

The Archdiocese of Paris is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. It is one of twenty-three archdioceses in France. The original diocese is traditionally thought to have been created in the 3rd century by St. Denis and corresponded with the Civitas Parisiorum; it was elevated to an archdiocese on October 20, 1622. Before that date the bishops were suffragan to the archbishops of Sens.
The Institut d'Études politiques de Lyon also known as Sciences Po Lyon, is a grande école located in Lyon, France. It is one of ten Institutes of Political Studies in France, and was established in 1948 by Charles de Gaulle's provisional government following the model of the École Libre des Sciences Politiques. It is located at the Centre Berthelot within the buildings of a former military health college and operates as an autonomous institution within the University of Lyon. It is the first Institute of Political Studies to have joined the prestigious Conférence des Grandes écoles.

Saint Denis Street is a major north–south thoroughfare in Montreal, Quebec.

Saint Joseph University of Beirut is a private Catholic research university located in Beirut, Lebanon, which was founded in 1875 by French Jesuit missionaries and subsidized by the Government of France during the time when Lebanon was under Ottoman rule. It is widely recognized as one of the leading and most prestigious academic institutions in Lebanon and Middle East. The institution boasts a diverse and accomplished group of alumni, who have gone on to become leading figures in politics, law, academia, literature, sciences, arts, medicine, and religion. USJ's impressive roster of graduates includes seven of independent Lebanon's thirteen Presidents, a Speaker of the Parliament of Lebanon, two Presidents of the Council of Ministers of Lebanon, Governors of the Banque du Liban, hundreds of legislators and ministers, numerous judges, and high-ranking civil servants, among them Commanders of the Lebanese Armed Forces and executives of the Internal Security Forces. As the oldest and foremost French university in Lebanon, it not only promotes Lebanese culture but also upholds a policy of equal admission opportunity without consideration of ethno-religious affiliations. Furthermore, it advocates trilingual education, offering instruction in Arabic, French, and English. Additionally, it is known in Lebanon and the Middle East for its prominent university hospital, the Hôtel-Dieu de France, and for its prestigious and historical Faculty of Law, modern Lebanon's oldest law school and the first law school in Lebanon since the ancient Roman law school of Berytus.

UCLouvain Saint-Louis Brussels is an autonomous university campus specialized in social and human sciences part of UCLouvain and based in Brussels, Belgium.

Institut Mines-Télécom (IMT) is a French public academic institution dedicated to Higher Education and Research for Innovation in the fields of engineering and digital technology, organized as a Collegiate University. Created in 1996, it was originally known as the "Groupe des écoles des télécommunications", or GET, followed by the "Institut Télécom". The Mines schools, which were placed under the administrative supervision of the Ministry of Industry, joined the Institut in March 2012 when it took on its current name and gained the status of Grand établissement. It combines high academic and scientific legitimacy with a practical proximity to business and a unique positioning in 3 major transformations of the 21st century: Digital Affairs, Energy and Ecology, and Industry. Its training and research for innovation are rolled out in the Mines and Télécom Graduate Schools. The Institut falls under the administrative aegis of the General Council for the Economy, Industry, Energy and Technologies.
Émile-Dostaler O'Leary was a Canadian journalist and writer.

Le Soleil was a French daily newspaper. It was founded in 1873 and run by the journalists Édouard Hervé and Jean-Jacques Weiss. Le Soleil was a monarchist daily, more moderate than others, sold for five centimes at the end of the nineteenth and start of the twentieth century. It was located in the rue du Croissant. It was one of two French newspapers that gave the best coverage of international news, along with Le Temps.

Mont Pilat or the Pilat massif is a mountainous area in the east of the Massif Central of France.

The Faculty of Architecture, Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning, often called LOCI, is the 14th faculty of the University of Louvain, Belgium. It became an independent faculty in 2009, with the merger of three institutes founded between 1867 and 1882, and is active in Brussels (Saint-Gilles), Tournai and Louvain-la-Neuve.

A bourgeois of Paris was traditionally a member of one of the corporations or guilds that existed under the Ancien Régime. According to Article 173 of the Custom of Paris, a bourgeois had to possess a domicile in Paris as a tenant or owner for at least a year and a day. This qualification was also required for public offices such as provost of the merchants, alderman or consul, but unlike the bourgeois or citizens of other free cities, Parisians did not need letters of bourgeoisie to prove their status.

Denis Lalanne was a French sports journalist who specialized in tennis, rugby union, and golf.

Charles Mayer was a Canadian journalist, sportsperson and politician. He made a name in journalism as a sportswriter and municipal reporter with the newspaper La Patrie, and the magazine Le Petit Journal. He was the French-language publicist for the National Hockey League, and a radio sports commentator for the Montreal Royals and the Montreal Canadiens. He later became a press secretary for horse racing in Montreal, then was president of the Canadian Boxing Federation and vice-president of the National Boxing Association. He served six years on the Montreal City Council and campaigned for the city to host a Major League Baseball team and the Summer Olympic Games. He was one of the inaugural appointees to the National Fitness Council of Canada, was inducted into Canada's Sports Hall of Fame in 1971, and was posthumously recognized with the Elmer Ferguson Memorial Award in 1985 for his career as a hockey journalist.
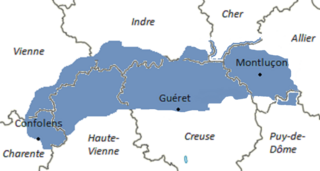
Marchois or Marchese is a transitional Occitan dialect between the Occitan language and the Oïl languages spoken in the historical region of La Marche, in northern Limousin and its region. Occitan and Oïl dialects meet there,.
References
- ↑ Monnet-Saint-Etienne, Université Jean; Saminadayar-Perrin, Corinne (2008). Qu'est-ce qu'un événement littéraire au XIXe siècle? (in French). Université de Saint-Etienne. p. 160. ISBN 978-2-86272-479-9.
- ↑ Heinrich-Heine-Gesellschaft; Heinrich-Heine-Institut; Düsseldorf, Heinrich-Heine-Institut (2016-08-09). Heine-Jahrbuch 2013: 52. Jahrgang (in German). Springer-Verlag. p. 129. ISBN 978-3-476-01198-5.