The Tales of Hoffmann is an opéra fantastique by Jacques Offenbach. The French libretto was written by Jules Barbier, based on three short stories by E. T. A. Hoffmann, who is the protagonist of the story. It was Offenbach's final work; he died in October 1880, four months before the premiere.

The Opéra-Comique is a Parisian opera company, which was founded around 1714 by some of the popular theatres of the Parisian fairs. In 1762 the company was merged with, and for a time took the name of its chief rival the Comédie-Italienne at the Hôtel de Bourgogne, and was also called the Théâtre-Italien up to about 1793, when it again became most commonly known as the Opéra-Comique. Today the company's official name is Théâtre national de l'Opéra-Comique, and its theatre, with a capacity of around 1,248 seats, sometimes referred to as the Salle Favart, is located in Place Boïeldieu, in the 2nd arrondissement of Paris, not far from the Palais Garnier, one of the theatres of the Paris Opéra. The musicians and others associated with the Opéra-Comique have made important contributions to operatic history and tradition in France, and to French opera. Its current mission is to reconnect with its history, and discover its unique repertoire, to ensure production and dissemination of operas for the wider public. Mainstays of the repertory at the Opéra-Comique during its history have included the following works which have each been performed more than 1,000 times by the company: Cavalleria Rusticana, Le chalet, La dame blanche, Le domino noir, La fille du régiment, Lakmé, Manon, Mignon, Les noces de Jeannette, Le pré aux clercs, Tosca, La bohème, Werther and Carmen, the last having been performed more than 2,500 times.

Louise is an opera in four acts by Gustave Charpentier to an original French libretto by the composer, with some contributions by Saint-Pol-Roux, a symbolist poet and inspiration of the surrealists.

Paul Antonin Vidal was a French composer, conductor and music teacher mainly active in Paris.

Cendrillon (Cinderella) is an opera—described as a "fairy tale"—in four acts by Jules Massenet to a French libretto by Henri Caïn based on Perrault's 1698 version of the Cinderella fairy tale.

André Cluytens was a Belgian-born French conductor who was active in the concert hall, opera house and recording studio. His repertoire extended from Viennese classics through French composers to 20th century works. Although much of his career was spent in France, he was the first French conductor at Bayreuth in 1955; he also conducted the Ring and Parsifal at La Scala.
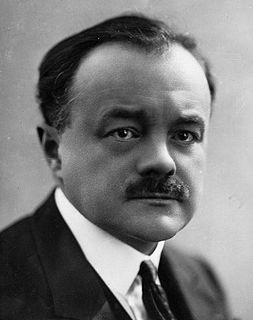
Albert Louis Wolff was a French conductor and composer of Dutch descent. Most of his career was spent in European venues, with the exception of two years that he spent as a conductor at the Metropolitan Opera and a few years in Buenos Aires during the Second World War. He is most known for holding the position of principal conductor with the Opéra-Comique in Paris for several years. He was married to the French mezzo-soprano Simone Ballard.

Mireille is an 1864 opera in five acts by Charles Gounod to a French libretto by Michel Carré after Frédéric Mistral's poem Mireio. The vocal score is dedicated to George V of Hanover.

Le roi d'Ys is an opera in three acts and five tableaux by the French composer Édouard Lalo, to a libretto by Édouard Blau, based on the old Breton legend of the drowned city of Ys. That city was, according to the legend, the capital of the kingdom of Cornouaille.

Macbeth is an opera in three acts, with music by Ernest Bloch to a libretto by Edmond Fleg, after the eponymous play of William Shakespeare. Bloch composed the opera between 1904 and 1906, but it did not receive its first performance until 30 November 1910 by the Opéra-Comique in Paris with Henri Albers in the title role and conducted by François Ruhlmann. Alex Cohen has written of quarrels within the cast that contributed to the opera's poorly received premiere.
Mârouf, savetier du Caire is an opéra comique by the French composer Henri Rabaud. The libretto, by Lucien Nepoty, is based on a tale from the Arabian Nights. Mârouf was first performed at the Opéra-Comique, Paris, on 15 May 1914. The premiere was a great success and Mârouf became Rabaud's most popular opera. The score makes great use of oriental colour. The United States premiere of the opera was given at the Metropolitan Opera on December 19, 1917, with Giuseppe De Luca in the title role, Frances Alda as Princess Saamcheddine, and Pierre Monteux conducting. The opera was revived at the Opéra-Comique in 2013 in a production by Jérôme Deschamps, with Jean-Sébastien Bou in the title role, conducted by Alain Altinoglu.

Pénélope is an opera in three acts by the French composer Gabriel Fauré. The libretto, by René Fauchois is based on Homer's Odyssey. It was first performed at the Salle Garnier, Monte Carlo on 4 March 1913. The piece is dedicated to Camille Saint-Saëns.

Fortunio is a comédie lyrique or opera in four acts and five tableaux by the French composer André Messager. The libretto by Gaston Arman de Caillavet and Robert de Flers is based on Alfred de Musset's 1835 comedy Le Chandelier.
Paul Adrien Bastide was a French conductor and composer.

Le chevalier d’Harmental is an opéra comique in five acts of 1896, with music by André Messager and a French libretto by Paul Ferrier, after Dumas père and Auguste Maquet. The play of the 1843 novel – in five acts, a prologue and ten tableaux – was first performed on 16 July 1849 at the Théâtre-Historique in Paris. The opera was first performed at the Opéra Comique in Paris on 5 May 1896, but ran for only six performances. It was seen at the Vienna Hofoper during the 1896-97 season.
Maurice Frigara was a French conductor of Corsican descent, mainly active in the opera house.
Puck is an opéra-féerique in three acts with music by Marcel Delannoy, premiered in 1949. The French libretto was adapted by André Boll from Shakespeare’s A Midsummer Night's Dream.

Le Marchand de Venise is a French opera in three acts by Reynaldo Hahn. The libretto was by Miguel Zamacoïs, after Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice. Hahn first started working on the opera during the First World War, imagining it as a 'Mozartian' work, with the role of Portia written specifically with the soprano Mary Garden in mind.

Le caïd, also spelled Le kaïd, is a comic opera in two acts composed by Ambroise Thomas to a libretto by Thomas Sauvage. It was premiered on 3 January 1849 by the Opéra-Comique at the second Salle Favart in Paris. The opera was originally titled Les boudjous.
Gustave Cloëz was a French conductor who was particularly active at the Paris Opéra-Comique in the mid-20th century, and made a significant number of recordings, often accompanying major singers of the time.