Carl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue, Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.

In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple image segments, also known as image regions or image objects. The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze. Image segmentation is typically used to locate objects and boundaries in images. More precisely, image segmentation is the process of assigning a label to every pixel in an image such that pixels with the same label share certain characteristics.
Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems use cameras, ultrasonic, electromagnetic or a combination or fields to capture and relay the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's precise movements in relation to the patient, to computer monitors in the operating room or to augmented reality headsets. This is generally performed in real-time though there may be delays of seconds or minutes depending on the modality and application.

Gluteoplasty denotes the plastic surgery and the liposuction procedures for the correction of the congenital, traumatic, and acquired defects and deformities of the buttocks and the anatomy of the gluteal region; and for the aesthetic enhancement of the contour of the buttocks.

Computer-assisted orthopedic surgery or computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery is a discipline where computer technology is applied pre-, intra- and/or post-operatively to improve the outcome of orthopedic surgical procedures. Although records show that it has been implemented since the 1990s, CAOS is still an active research discipline which brings together orthopedic practitioners with traditionally technical disciplines, such as engineering, computer science and robotics.
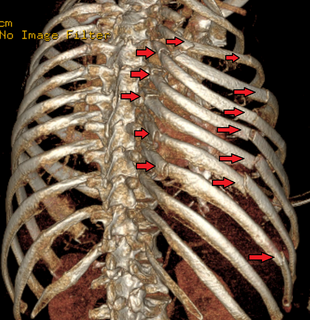
Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath.
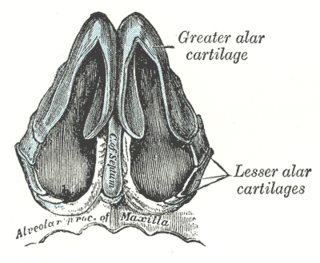
The nasal cartilages are structures within the nose that provide form and support to the nasal cavity. The nasal cartilages are made up of a flexible material called hyaline cartilage in the distal portion of the nose. There are five individual cartilages that make up the nasal cavity: septal nasal cartilage, lateral nasal cartilage, major alar cartilage, minor alar cartilage, and vomeronasal cartilage.
The Latham appliance is a medical appliance used to repair cleft lip and cleft palate in young children.

The surgical segment navigator (SSN) is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the surgical tool navigator (STN), the surgical microscope navigator (SMN) and the 6DOF manipulator (MKM), developed by Carl Zeiss.
Patient registration is used to correlate the reference position of a virtual 3D dataset gathered by computer medical imaging with the reference position of the patient. This procedure is crucial in computer assisted surgery, in order to insure the reproducitibility of the preoperative registration and the clinical situation during surgery. The use of the term "patient registration" out of this context can lead to a confusion with the procedure of registering a patient into the files of a medical institution.
Bone segment navigation is a surgical method used to find the anatomical position of displaced bone fragments in fractures, or to position surgically created fragments in craniofacial surgery. Such fragments are later fixed in position by osteosynthesis. It has been developed for use in craniofacial and oral and maxillofacial surgery.
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for surgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions. CAS is also known as computer-aided surgery, computer-assisted intervention, image-guided surgery, digital surgery and surgical navigation, but these are terms that are more or less synonymous with CAS. CAS has been a leading factor in the development of robotic surgery.

The surgical planning is the preoperative method of pre-visualising a surgical intervention, in order to predefine the surgical steps and furthermore the bone segment navigation in the context of computer-assisted surgery. The surgical planning is most important in neurosurgery and oral and maxillofacial surgery. The transfer of the surgical planning to the patient is generally made using a medical navigation system.

OrthoCAD Network Research Cell is a federally funded research and development facility in the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India. The Laboratory's primary function is the design and development of reconstruction systems for orthopaedic and other applications, the current focus is on mega-implants for limb-saving surgery, mainly for children affected by bone cancer. The Cell later led to the establishment of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (incubation) Centre (BETiC).

Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is the application of computer graphics to create or contribute to images in art, printed media, video games, simulators, computer animation and VFX in films, television programs, shorts, commercials, and videos. The images may be dynamic or static, and may be two-dimensional (2D), although the term "CGI" is most commonly used to refer to the 3-D computer graphics used for creating characters, scenes and special effects in films and television, which is described as "CGI animation".
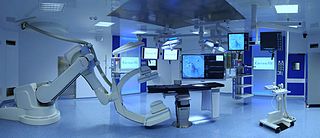
A hybrid operating room is a surgical theatre that is equipped with advanced medical imaging devices such as fixed C-Arms, X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanners or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners. These imaging devices enable minimally-invasive surgery. Minimally-invasive surgery is intended to be less traumatic for the patient and minimize incisions on the patient and perform surgery procedure through one or several small cuts.
Computer-assisted interventions (CAI) is a field of research and practice, where medical interventions are supported by computer-based tools and methodologies. Examples include:
The Dextroscope is a medical equipment system that creates a Virtual Reality (VR) environment in which surgeons can plan neurosurgical and other surgical procedures.
Rüdiger Marmulla is a German cranio-maxillofacial surgeon.

Gregory D. Hager is the Mandell Bellmore Professor of Computer Science and founding director of the Johns Hopkins Malone Center for Engineering in Healthcare at Johns Hopkins University.