| C83 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | July 11, 1947 |
| Date in force | June 15, 1974 |
| Classification | Workers in Non-Metropolitan Territories |
| Subject | Specific Categories of Workers |
| Previous | Social Policy (Non-Metropolitan Territories) Convention, 1947 |
| Next | Right of Association (Non-Metropolitan Territories) Convention, 1947 |
Labour Standards (Non-Metropolitan Territories) Convention, 1947 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1947 with the preamble stating:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals concerning the application of international labour standards in non-metropolitan territories,...
The treaty has been ratified only by the United Kingdom in 1950 and Australia in 1973. Australia has subsequently denounced the treaty, making it currently in force only for the United Kingdom.

The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, setting aside the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina.

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union are parties.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966, and in force from 23 March 1976 in accordance with Article 49 of the covenant. Article 49 allowed that the covenant would enter into force three months after the date of the deposit of the thirty-fifth instrument of ratification or accession. The covenant commits its parties to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. As of September 2019, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification. Notable holdouts are People's Republic of China and Cuba. North Korea tried to withdraw.
Ratification is a principal's approval of an act of its agent that lacked the authority to bind the principal legally. Ratification defines the international act in which a state indicates its consent to be bound to a treaty if the parties intended to show their consent by such an act. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usually accomplished by exchanging the requisite instruments, and in the case of multilateral treaties, the usual procedure is for the depositary to collect the ratifications of all states, keeping all parties informed of the situation.

The Convention on International Civil Aviation, also known as the Chicago Convention, established the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a specialized agency of the UN charged with coordinating international air travel. The Convention establishes rules of airspace, aircraft registration and safety, security, and sustainability, and details the rights of the signatories in relation to air travel. The Convention also contains provisions pertaining to taxation.
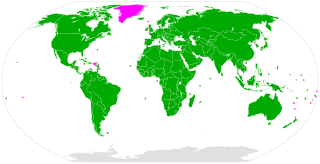
The Convention concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
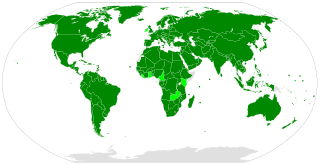
The Optional Protocol on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution and Child Pornography is a protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child and requires parties to prohibit the sale of children, child prostitution and child pornography.
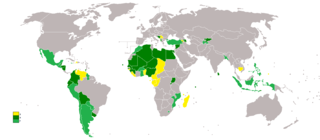
The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of August 2021 in 56 countries.
Social Policy Convention, 1947 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Convention concerning the Right of Association and the Settlement of Labour Disputes in Non-Metropolitan Territories is an International Labour Organization Convention on the rights of workers in non-metropoliton territories to form and be active in labour unions. As of 2013, the convention has been ratified by nine states: Belgium ; Fiji; France; Mauritania; Mauritius; New Zealand; Solomon Islands; Somalia; and the United Kingdom.
Labour Inspectorates Convention, 1947 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Social Policy Convention, 1962 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
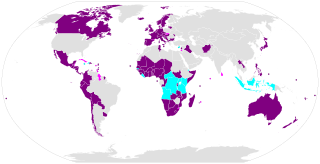
The Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) is an international treaty that prohibits all use, transfer, production, and stockpiling of cluster bombs, a type of explosive weapon which scatters submunitions ("bomblets") over an area. Additionally, the Convention establishes a framework to support victim assistance, clearance of contaminated sites, risk reduction education, and stockpile destruction. The convention was adopted on 30 May 2008 in Dublin, and was opened for signature on 3 December 2008 in Oslo. It entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states. As of July 2021, a total of 123 States have joined the Convention – 110 States Parties and 13 Signatories.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other "pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty, as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party.

The Convention on Domestic Workers, formally the Convention concerning Decent Work for Domestic Workers is a convention setting labour standards for domestic workers. It is the 189th ILO convention and was adopted during the 100th session of the International Labour Organization. It entered into force on 5 September 2013.
The International Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women and Children is a 1921 multilateral treaty of the League of Nations that addressed the problem of international trafficking of women and children.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.