This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.
Year 429 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tricipitinus and Fidenas. The denomination 429 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Battle of Gaugamela, also called the Battle of Arbela, was the decisive battle of Alexander the Great's invasion of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. In 331 BC Alexander's army of the Hellenic League met the Persian army of Darius III near Gaugamela, close to the modern city of Dohuk in Iraqi Kurdistan. Though heavily outnumbered, Alexander emerged victorious due to his army's superior tactics and his deft employment of light infantry. It was a decisive victory for the Hellenic League and led to the fall of the Achaemenid Empire.

In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians (Παίονες).

The Pčinja District is one of nine administrative districts of Southern and Eastern Serbia. It covers the southern part of Serbia, bordering the disputed territory of Kosovo, Bulgaria and North Macedonia. Its administrative center is the city of Vranje.
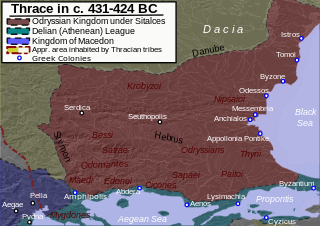
The Odrysian Kingdom was a state union of over 40 Thracian tribes and 22 kingdoms that existed between the 5th century BC and the 1st century AD. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria, spreading to parts of Southeastern Romania, parts of Northern Greece and parts of modern-day European Turkey.

Sitalces (Sitalkes) was one of the great kings of the Thracian Odrysian state. He was the son of Teres I, and on the sudden death of his father in 431 BC succeeded to the throne. Sitalces enlarged his kingdom by successful wars, and it soon comprised the whole territory from Abdera in the south to the mouths of the Danube in the north, and from the Black Sea in the east to the sources of the Struma in the west.

The Maedi were a Thracian tribe in antiquity. In historic times, they occupied the area between Paionia and Thrace, on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along the middle course of the Strymon, between the Kresna Gorge and the Rupel Pass. Strabo says that the Maedi bordered eastward on the Thunatae of Dardania, and that the Axius flowed through their territory.
Paeonian, sometimes spelled Paionian, is a poorly-attested, extinct language spoken by the ancient Paeonians until late antiquity.

The army of the Kingdom of Macedon was among the greatest military forces of the ancient world. It was created and made formidable by King Philip II of Macedon; previously the army of Macedon had been of little account in the politics of the Greek world, and Macedonia had been regarded as a second-rate power.

The Pieres were a Thracian tribe connected with the Brygi, that long before the archaic period in Greece occupied the narrow strip of plain land, or low hill, between the mouths of the Peneius and the Haliacmon rivers, at the foot of the great woody steeps of mount Olympus. This region was named after them as Pieria.

The Derrones were a Thracian or a Paionian tribe. Our knowledge of them comes from coins bearing variations of the legend of DERRONIKON (ΔΕΡΡΟΝΙΚΟΝ) - DERR (ΔΕΡΡ). The letters used in the coins are Greek, although this does not prove that the Derrones spoke the same language as their southern neighbours. These coins, which were perhaps made for export as much as for internal trade, are traditionally dated to 500-450 BC.

Kale-Krševica is an Ancient Macedonian archaeological site of more than 4 hectares and so far some 1,000 squares have been excavated with a former fortified town in the hills of Krševica overlooking Bujanovac and Vranje, to the south of Ristovac in southern Serbia. It has a history back to the 13th century BC as a settlement with elements of an acropolis, but main preserved characteristics is from the Greek-mediterranean style urban town in the 5th or 4th century BC with stone walls and necropolis. Finds of coins of Philip II, Alexander III, Cassander, Demetrios Poliorketes and Pelagia correspond in general to the chronological span of the archaeological material discovered so far in the course of excavations and may be considered the northernmost Ancient Macedonian city. The Paeonian tribe of Agrianes dwelled in this region, the Scordisci are believed to have razed the town to the ground in 279 BC. The town had at least 3,000 inhabitants in the 4th and 3rd century.

Odomanti or Odomantes were an ancient Thracian tribe. Some regard it as Paeonian, while others claim, that the tribe was with certainty Thracian. The Odomanti are noted by Herodotus, Thucydides, Stephanus of Byzantium and Pliny the Elder.

Almopians or Almopes were an ancient Paeonian tribe. They inhabited the region of Almopia in Lower Macedonia, which was named after the tribe. According to the Greek mythology, the founder of the tribe was thought to be the Giant demigod Almops whom they highly worshiped.

Siro-Paeonians or Siropaiones were an ancient Paeonian tribe inhabiting the ancient city of Siris and the Strymon plain. They were one of eight (Herodotus) or ten (Thucydides) tribes of Paeonia. They were situated from the Bisaltae and Odomanti to the south, Sinthi to the north, the Strymon to the east, Maedi to the west, and a mountain chain separating them from Crestonia. Their capital was Siris (Serres). They were defeated by Persian general Megabazus. They were expelled by the Persians to Asia Minor, where they are assumed to have founded Serraepolis.

Illyrian coinage which began in the 6th century BC continued up to the 1st century of Roman rule. It was the southern Illyrians who minted the first coins followed by the northern Illyrian during the Roman era. Illyrian coins have also been found in other areas apart from Illyria, such ancient Macedonia, Italy, Greece, Asia Minor and Egypt.