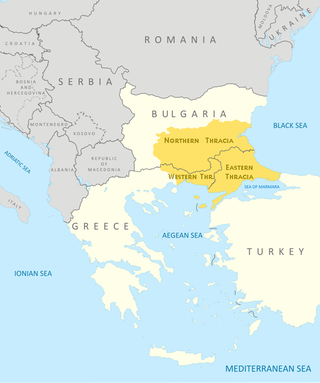
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece, and the European part of Turkey, roughly the Roman Province of Thrace. Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia.

The Thracians were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history. Thracians resided mainly in Southeast Europe in modern-day Bulgaria, Romania, North Macedonia and northern Greece, but also in north-western Anatolia in Turkey.

The Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at 2,191 meters (7,188 ft). The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge.

Eastern Macedonia and Thrace is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It consists of the northeastern parts of the country, comprising the eastern part of the region of Macedonia along with the region of Western Thrace, and the islands of Thasos and Samothrace.

Rhodope is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace. Its name is derived from the Rhodope Mountains, which cover the northern part of its territory. Together with the regional units Evros and Xanthi, it forms the geographical region of Western Thrace. The capital of the prefecture is the city of Komotini. The second largest town is Sapes. Most of the Muslims of Thrace, the only officially recognized minority in Greece, are settled in this area, where they form around half of the regional unit's population.

The Ilinden–Preobrazhenie Uprising, or simply the Ilinden Uprising, of August–October 1903, was an organized revolt against the Ottoman Empire, which was prepared and carried out by the Internal Macedonian-Adrianople Revolutionary Organization, with the support of the Supreme Macedonian-Adrianople Committee, which included mostly Bulgarian military personnel. The name of the uprising refers to Ilinden, a name for Elijah's day, and to Preobrazhenie which means Feast of the Transfiguration. Some historians describe the rebellion in the Serres revolutionary district as a separate uprising, calling it the Krastovden Uprising, because on September 14 the revolutionaries there also rebelled. The revolt lasted from the beginning of August to the end of October and covered a vast territory from the western Black Sea coast in the east to the shores of Lake Ohrid in the west.

Western Thrace or West Thrace also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographic and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lies east of the river Evros, forms the European part of Turkey, and the area to the north, in Bulgaria, is known as Northern Thrace.
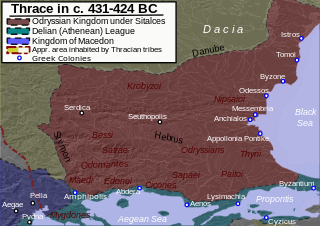
The Odrysian kingdom was an ancient Thracian state that thrived between the early 5th century BC and the early 3rd / late 1st century BC. Located in present-day Bulgaria, southeastern Romania, northern Greece and European Turkey, it was a tribal amalgam dominated by the Odrysians that was the first large political entity to develop in the eastern Balkans.

The Bessi or Bessae were a Thracian tribe that inhabited the upper valley of the Hebros and the lands between the Haemus and Rhodope mountain ranges in historical Thrace.

The Nestos, Mesta is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. It rises in the Rila Mountains and flows into the Aegean Sea near the island of Thasos. It plunges down towering canyons toward the Aegean Sea through mostly metamorphic formations. At the end, the main stream spreads over the coastal plain of Chrysoupolis and expands as a deltaic system with freshwater lakes and ponds forming the Nestos delta. The length of the river is 230 km (140 mi), of which 126 km (78 mi) flow through Bulgaria and the rest in Greece. Its drainage area is 5,184 km2 (2,002 sq mi), of which 66% is in Bulgaria. It forms some gorges in Rila and Pirin. The longest gorge between Pirin to the west and the Rhodope Mountains to the east is the 25-km long Momina Klisura in Bulgaria.

Perperikon, also Perpericum, is an ancient Thracian city located in the Eastern Rhodope Mountains, 15 km northeast of the present-day town of Kardzhali, Bulgaria on a 470 m high rocky hill, which is thought to have been a sacred place. The village of Gorna krepost is located at the foot of the hill and the gold-bearing Perpereshka River flows nearby. Perperikon is the largest megalith ensemble site in the Balkans. In the Middle Ages Perperikon served as a fortress.

The Thracian Sea is the northernmost part of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded by Macedonia and Thrace as well as northwestern Turkey. It connects to the Black Sea through the Dardanelles Straight, the Marmara Sea, and the Bosphorus Straight.

Topeiros is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit, Greece. The municipality has an area of 312.493 km2 and a population 9,473 (2021). The seat of the municipality is in Evlalo.

The Provisional Government of Western Thrace later Independent Government of Western Thrace, was a small, short-lived unrecognized republic established in Western Thrace from August 31 to October 25, 1913. It encompassed the area surrounded by the rivers Maritsa (Evros) in the east, Mesta (Nestos) in the west, the Rhodope Mountains in the north and the Aegean Sea in the south. Its total territory was approximately 8600 km².

East Thrace or eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically a part of Southeast Europe. It accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest city is Istanbul, which straddles the Bosporus between Europe and Asia. East Thrace is of historic importance as it is next to a major sea trade corridor and constitutes what remains of the once-vast Ottoman region of Rumelia. It is currently also of specific geostrategic importance because the sea corridor, which includes two narrow straits, provides access to the Mediterranean Sea from the Black Sea for the navies of five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and Georgia. The region also serves as a future connector of existing Turkish, Bulgarian, and Greek high-speed rail networks. Due to the guest worker agreement with Turkey and Germany, some Turks in Germany originally come from Eastern Thrace, mostly from the Kırklareli Province.

Thracia or Thrace is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD.

The history of Thracian warfare spans from the 10th century BC up to the 1st century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Thrace. It concerns the armed conflicts of the Thracian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Thracians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among Thracian tribes.
The Legend of Diyes is the story of the northward migration of the Thracian tribe Dii to the country of Odin. The Dii initially lived among the foothills of the Rhodope Mountains in Thrace.

Edonis or Edonida, also transliterated as Edonia, was an ancient region of Thrace which later became a district of Macedon. Its name is derived from the ancient Thracian inhabitants of the region, the Edonians. Later, the Greeks settled in the region, drove out the Edonians and built several colonies, including Amphipolis and Eion. It was bordered by Odomantice in the north, Bisaltia in the west, and the Aegean Sea in the south, and was separated from Thrace proper by the river Nestos in the east.

















