Related Research Articles

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is a national public health institute in the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.

A mental disorder, also called a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitting, or occur as a single episode. Many disorders have been described, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. Such disorders may be diagnosed by a mental health professional.

Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. About 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kills about half of those affected. The classic symptoms of active TB are a chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically called consumption due to the weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution, which establishes the agency's governing structure and principles, states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health." It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with six semi-autonomous regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.

The United States Department of Health & Human Services (HHS), also known as the Health Department, is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government with the goal of protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW).
A health system, also sometimes referred to as health care system or as healthcare system, is the organization of people, institutions, and resources that deliver health care services to meet the health needs of target populations.
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution, patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in defined populations.
Health is a state of physical, mental and social well-being in which disease and infirmity are absent.

Health care, health-care, or healthcare is the maintenance or improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, recovery, or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals in allied health fields. Physicians and physician associates are a part of these health professionals. Dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, medicine, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training and other health professions are all part of health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.

Public health has been defined as "the science and art of preventing disease”, prolonging life and improving quality of life through organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals. Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The public can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of health takes into account physical, psychological, and social well-being. As such, according to the World Health Organization, it is not merely the absence of disease or infirmity and more recently, a resource for everyday living.

Mental health is the level of psychological well-being or an absence of mental illness. It is the state of someone who is "functioning at a satisfactory level of emotional and behavioral adjustment". From the perspectives of positive psychology or of holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mental health includes "subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, inter-generational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others". The WHO further states that the well-being of an individual is encompassed in the realization of their abilities, coping with normal stresses of life, productive work, and contribution to their community. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health".

The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, also known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or colloquially as Obamacare, is a United States federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 amendment, it represents the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the passage of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965.

Occupational safety and health (OSH), also commonly referred to as health and safety, occupational health and safety (OHS), occupational health, or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of occupational safety and health program/department etc.

Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus is an Ethiopian biologist, public health researcher and official who has served since 2017 as Director-General of the World Health Organization. Tedros is the first non-physician and first African in the role; he was endorsed by the African Union. He has held two high-level positions in the government of Ethiopia: Minister of Health from 2005 to 2012 and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2012 to 2016.
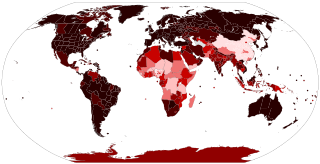
This article provides a general overview and documents the status of locations affected by SARS-CoV-2, the virus which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The first human cases of COVID-19 were identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, Hubei, China, and has resulted in an ongoing pandemic. As of 7 September 2020, more than 27.2 million cases have been reported across 188 countries and territories with more than 890,000 deaths; more than 18.1 million people have recovered.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the United States is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019. As of September 2020, there were over 6,000,000 cases of COVID-19 and 180,000 COVID-19-related deaths in the U.S.

COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main branches detect either the presence of the virus or of antibodies produced in response to infection. Tests for viral presence are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the country in late January 2020. As of 7 September 2020 there have been 350,100 confirmed cases and 41,554 deaths of confirmed cases, the world's sixth-highest death rate per hundred thousand population. There were 57,226 deaths where the death certificate mentioned COVID-19 by 21 August. More than 90% of those dying had underlying illnesses or were over 60 years old. The infection rate is higher in care homes than in the community. There has been large regional variation in the outbreak's severity.
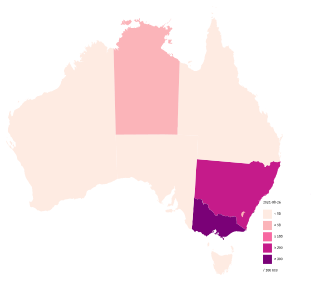
The COVID-19 pandemic in Australia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of the coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first confirmed case in Australia was identified on 25 January 2020, in Victoria, when a man who had returned from Wuhan, China, tested positive for the virus.
References
- ↑ Grupenhoff, J.T. (1982). National Health Directory. Science and Health Publications. ISSN 0147-2771 . Retrieved 2015-03-08.
| This article about a member of the Ohio House of Representatives is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |