
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training, cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound.

A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids".
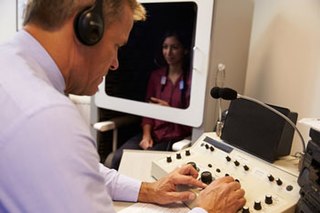
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
The Doctor of Audiology is a professional degree for an audiologist. The AuD program is designed to produce audiologists who are skilled in providing diagnostic, rehabilitative, and other services associated with hearing, balance, tinnitus management, and related audiological fields. These individuals help patients with hearing problems primarily by diagnosing hearing loss and fitting hearing assistive devices.

Pure-tone audiometry is the main hearing test used to identify hearing threshold levels of an individual, enabling determination of the degree, type and configuration of a hearing loss and thus providing a basis for diagnosis and management. Pure-tone audiometry is a subjective, behavioural measurement of a hearing threshold, as it relies on patient responses to pure tone stimuli. Therefore, pure-tone audiometry is only used on adults and children old enough to cooperate with the test procedure. As with most clinical tests, standardized calibration of the test environment, the equipment and the stimuli is needed before testing proceeds. Pure-tone audiometry only measures audibility thresholds, rather than other aspects of hearing such as sound localization and speech recognition. However, there are benefits to using pure-tone audiometry over other forms of hearing test, such as click auditory brainstem response (ABR). Pure-tone audiometry provides ear specific thresholds, and uses frequency specific pure tones to give place specific responses, so that the configuration of a hearing loss can be identified. As pure-tone audiometry uses both air and bone conduction audiometry, the type of loss can also be identified via the air-bone gap. Although pure-tone audiometry has many clinical benefits, it is not perfect at identifying all losses, such as ‘dead regions’ of the cochlea and neuropathies such as auditory processing disorder (APD). This raises the question of whether or not audiograms accurately predict someone's perceived degree of disability.
The ASA Silver Medal is an award presented by the Acoustical Society of America to individuals, without age limitation, for contributions to the advancement of science, engineering, or human welfare through the application of acoustic principles or through research accomplishments in acoustics. The medal is awarded in a number of categories depending on the technical committee responsible for making the nomination.
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes sounds. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the ear, but cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system. This is, in part, essentially a failure of the cocktail party effect found in most people.
Marion Downs was an American audiologist and Professor Emerita at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, who pioneered universal newborn hearing screening in the early 1960s, then spent more than 30 years trying to convince her peers to adopt the testing in hospitals and to place hearing aids on infants who showed hearing loss. She worked to alert the medical world to the developmental problems associated with childhood deafness. As a result of her efforts, 95 percent of all newborns in America today are screened for hearing loss. She devoted her professional life to the promotion of early identification of hearing loss in newborns, infants, and young children and to helping deaf and hard of hearing individuals lead fulfilling lives.
Tele-audiology is the utilization of telemedicine to provide audiological services and may include the full scope of audiological practice.
Ingo R. Titze is a voice scientist and executive director of the National Center for Voice and Speech and Adjunct Professor in the Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City. He also teaches at the Summer Vocology Institute, also housed at the University of Utah. He is a Distinguished Professor at the Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders at the University of Iowa and has written several books relating to the human voice.

Real ear measurement is the measurement of sound pressure level in a patient's ear canal developed when a hearing aid is worn. It is measured with the use of a silicone probe tube inserted in the canal connected to a microphone outside the ear and is done to verify that the hearing aid is providing suitable amplification for a patient's hearing loss. The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) and American Academy of Audiology (AAA) recommend real ear measures as the preferred method of verifying the performance of hearing aids. Used by audiologists and other hearing healthcare practitioners in the process of hearing aid fitting, real ear measures are the most reliable and efficient method for assessing the benefit provided by the amplification. Measurement of the sound level in the ear canal allows the clinician to make informed judgements on audibility of sound in the ear and the effectiveness of hearing aid treatment.
WS Audiology is a privately-owned manufacturer of hearing aids with headquarters in Denmark and Singapore with roots going back to 1878 and Siemens AG. The current company was created following the 2019 merger of Sivantos Group and Widex. Prior to that, Sivantos was spun off from Siemens after Siemens AG sold the company to EQT and Santo Holding in 2015. WS Audiology employs about 12,000 people in more than 125 countries. In fiscal year 2022-2023, the company generated revenue of €2.47 billion and adjusted EBITDA of €480 million.
Nan Bernstein Ratner is a professor in the Department of Hearing and Speech Sciences at the University of Maryland, College Park. Ratner is a board-recognized specialist in child language disorders.

Brian C.J. Moore FMedSci, FRS is an Emeritus Professor of Auditory Perception in the University of Cambridge and an Emeritus Fellow of Wolfson College, Cambridge. His research focuses on psychoacoustics, audiology, and the development and assessment of hearing aids.
Auditory science or hearing science is a field of research and education concerning the perception of sounds by humans, animals, or machines. It is a heavily interdisciplinary field at the crossroad between acoustics, neuroscience, and psychology. It is often related to one or many of these other fields: psychophysics, psychoacoustics, audiology, physiology, otorhinolaryngology, speech science, automatic speech recognition, music psychology, linguistics, and psycholinguistics.

Quentin Summerfield is a British psychologist, specialising in hearing. He joined the Medical Research Council Institute of Hearing Research in 1977 and served as its deputy director from 1993 to 2004, before moving on to a chair in psychology at The University of York. He served as head of the Psychology department from 2011 to 2017 and retired in 2018, becoming an emeritus professor. From 2013 to 2018, he was a member of the University of York's Finance & Policy Committee. From 2015 to 2018, he was a member of York University's governing body, the Council.
Elaine Saunders is an associate professor at the Swinburne University of Technology and executive director of Blamey Saunders, as well as an inventor, entrepreneur. She was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science Technology and Engineering in 2019. She is one of only nine women out of 160 to win the Clunies Ross award for entrepreneurship, and has won many other awards, as well as given numerous keynote addresses on the value of entrepreneurship and innovation in STEMM.
Sandra Gordon-Salant is an American audiologist. She is a professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, where she is also director of the doctoral program in clinical audiology. Gordon-Salant investigates the effects of aging and hearing loss on auditory processes, as well as signal enhancement devices for hearing-impaired listeners. She is the senior editor of the 2010 book, The Aging Auditory System. Gordon-Salant has served as editor of the Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research.

Richard Charles Dowell is an Australian audiologist, academic and researcher. He holds the Graeme Clark Chair in Audiology and Speech Science at University of Melbourne. He is a former director of Audiological Services at Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital.
Judy R. Dubno is an American scientist and researcher in the field of audiology. She is a distinguished university professor and director of research in the department of otolaryngology at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. She is recognized for her scientific contributions to the understanding of presbycusis, a condition of hearing loss that occurs gradually for many aging adults. She has been involved in the development and implementation of several new methods for assessing hearing loss, including the Hearing in Noise Test (HINT) and Speech Intelligibility Index (SII). She has won numerous awards for her work, including the Jerger Career Award for Research in Audiology in 2011. She served as President of the Acoustical Society of America from 2014 to 2015.







