The Chalcolithic, a name derived from the Greek: χαλκός khalkós, "copper" and from λίθος líthos, "stone" or Copper Age, also known as the Eneolithic or Aeneolithic is an archaeological period which researchers usually regard as part of the broader Neolithic. In the context of Eastern Europe, archaeologists often prefer the term "Eneolithic" to "Chalcolithic" or other alternatives.

In Old World archaeology, Mesolithic is the period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia roughly 20,000 to 8,000 BP. The term is less used of areas further east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa.

The Rosetta Stone is a granodiorite stele, found in 1799, inscribed with three versions of a decree issued at Memphis, Egypt, in 196 BC during the Ptolemaic dynasty on behalf of King Ptolemy V. The top and middle texts are in Ancient Egyptian using hieroglyphic script and Demotic script, respectively, while the bottom is in Ancient Greek. As the decree has only minor differences between the three versions, the Rosetta Stone proved to be the key to deciphering Egyptian hieroglyphs, thereby opening a window into ancient Egyptian history.
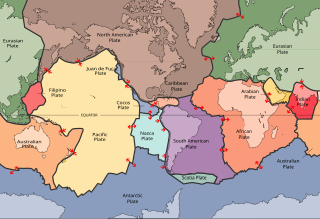
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet, or natural satellite, that is defined by its rigid mechanical properties. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater. The outermost shell of a rocky planet, the crust, is defined on the basis of its chemistry and mineralogy.

A sarcophagus is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word "sarcophagus" comes from the Greek σάρξ sarx meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν phagein meaning "to eat"; hence sarcophagus means "flesh-eating", from the phrase lithos sarkophagos, "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself.

Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fractures and spaces, deep underground, where the water table and hydrothermal fluids provide the means for chemical precipitation. Individual crystals are rare but do occur as slender to acicular prisms. Pseudomorphs after more tabular or blocky azurite crystals also occur.

Staurolite is a red brown to black, mostly opaque, nesosilicate mineral with a white streak. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, has a Mohs hardness of 7 to 7.5 and the chemical formula: Fe2+2Al9O6(SiO4)4(O,OH)2. Magnesium, zinc and manganese substitute in the iron site and trivalent iron can substitute for aluminium.
In geometry, parallel lines are lines in a plane which do not meet; that is, two lines in a plane that do not intersect or touch each other at any point are said to be parallel. By extension, a line and a plane, or two planes, in three-dimensional Euclidean space that do not share a point are said to be parallel. However, two lines in three-dimensional space which do not meet must be in a common plane to be considered parallel; otherwise they are called skew lines. Parallel planes are planes in the same three-dimensional space that never meet.

Natrolite is a tectosilicate mineral species belonging to the zeolite group. It is a hydrated sodium and aluminium silicate with the formula Na2Al2Si3O10 · 2H2O. The type locality is Hohentwiel, Hegau, Germany.

An acrolith is a composite sculpture made of stone and other materials, as in the case of a figure whose clothed parts are made of wood, while the exposed flesh parts such as head, hands, and feet are made of marble. The wood was covered either by drapery or by gilding. This type of statuary was common and widespread in Classical antiquity.

Litharge (from Greek lithargyros, lithos (stone) + argyros (silver) λιθάργυρος) is one of the natural mineral forms of lead(II) oxide, PbO. Litharge is a secondary mineral which forms from the oxidation of galena ores. It forms as coatings and encrustations with internal tetragonal crystal structure. It is dimorphous with the orthorhombic form massicot. It forms soft (Mohs hardness of 2), red, greasy-appearing crusts with a very high specific gravity of 9.14–9.35. PbO may be prepared by heating lead metal in air at approximately 600 °C (lead melts at only 300 °C). At this temperature it is also the end product of oxidation of other lead oxides in air. This is often done with a set of bellows pumping air over molten lead and causing the oxidized product to slip or fall off the top into a receptacle, where it quickly solidifies in minute scales.

The Ruthwell Cross is a stone Anglo-Saxon cross probably dating from the 8th century, when the village of Ruthwell, now in Scotland, was part of the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Northumbria.
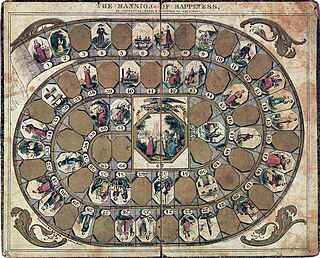
The Mansion of Happiness: An Instructive Moral and Entertaining Amusement is a children's board game inspired by Christian morality. Players race about a 66-space spiral track depicting virtues and vices with their goal being the Mansion of Happiness at track's end. Instructions upon virtue spaces advance players toward the goal while those upon vice spaces force them to retreat.

The mineral aggregate heliotrope, also known as bloodstone, is a variety of jasper or chalcedony. The "classic" bloodstone is green jasper (chalcedony) with red inclusions of hematite.
In geometry, a vertex is a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedra are vertices.
The Winnipegosis komatiite belt is an approximately 150 x 30 km linear greenstone belt located in Manitoba, Canada. It has no surface exposure, and was identified based on geophysical signatures and drilling during mining exploration by Cominco during the 1990s. The belt has an age of 1870 ± 7 Ma, and is predominantly composed of basaltic and komatiitic volcanic rocks, with minor intrusive igneous and sedimentary rocks. The belt is considered part of the larger Circum-Superior Large Igneous Province, and was likely generated by a mantle plume.
These are the results of the women's team all-around competition, one of six events for female competitors in artistic gymnastics at the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal. There were a total of 14 events: 6 for women and 8 for men. The compulsory and optional rounds took place on July 18 and 19 at the Montreal Forum.

Moulsford railway station was on the original route of the Great Western Railway, being one of three intermediate stations provided when the line was extended from Reading to Steventon in 1840.
The Inland Type Foundry was an American type foundry established in 1894 in Saint Louis, Missouri and later with branch offices in Chicago and New York City. Although it was founded to compete directly with the "type trust", and was consistently profitable, it was eventually sold to ATF.
Gagae or Gagai was a town on the southeast coast of ancient Lycia, in what is now the province of Antalya, from which the Gagates lapis derived its name. The ruins are located in Kumluca district, Antalya Province, Turkey. Excavations in 2007 revealed an upper and lower acropolis and evidence of Rhodian colonization.














