Related Research Articles

Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a type of mass spectrometry that uses an inductively coupled plasma to ionize the sample. It atomizes the sample and creates atomic and small polyatomic ions, which are then detected. It is known and used for its ability to detect metals and several non-metals in liquid samples at very low concentrations. It can detect different isotopes of the same element, which makes it a versatile tool in isotopic labeling.
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.

An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines.

Secondary-ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is a technique used to analyze the composition of solid surfaces and thin films by sputtering the surface of the specimen with a focused primary ion beam and collecting and analyzing ejected secondary ions. The mass/charge ratios of these secondary ions are measured with a mass spectrometer to determine the elemental, isotopic, or molecular composition of the surface to a depth of 1 to 2 nm. Due to the large variation in ionization probabilities among elements sputtered from different materials, comparison against well-calibrated standards is necessary to achieve accurate quantitative results. SIMS is the most sensitive surface analysis technique, with elemental detection limits ranging from parts per million to parts per billion.
A microprobe is an instrument that applies a stable and well-focused beam of charged particles to a sample.

In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of biomolecules and various organic molecules, which tend to be fragile and fragment when ionized by more conventional ionization methods. It is similar in character to electrospray ionization (ESI) in that both techniques are relatively soft ways of obtaining ions of large molecules in the gas phase, though MALDI typically produces far fewer multi-charged ions.

Isotope-ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS) is a specialization of mass spectrometry, in which mass spectrometric methods are used to measure the relative abundance of isotopes in a given sample.

The history of mass spectrometry has its roots in physical and chemical studies regarding the nature of matter. The study of gas discharges in the mid 19th century led to the discovery of anode and cathode rays, which turned out to be positive ions and electrons. Improved capabilities in the separation of these positive ions enabled the discovery of stable isotopes of the elements. The first such discovery was with the element neon, which was shown by mass spectrometry to have at least two stable isotopes: 20Ne and 22Ne. Mass spectrometers were used in the Manhattan Project for the separation of isotopes of uranium necessary to create the atomic bomb.

Spark ionization is a method used to produce gas phase ions from a solid sample. The prepared solid sample is vaporized and partially ionized by an intermittent discharge or spark. This technique is primarily used in the field of mass spectrometry. When incorporated with a mass spectrometer the complete instrument is referred to as a spark ionization mass spectrometer or as a spark source mass spectrometer (SSMS).

Protein mass spectrometry refers to the application of mass spectrometry to the study of proteins. Mass spectrometry is an important method for the accurate mass determination and characterization of proteins, and a variety of methods and instrumentations have been developed for its many uses. Its applications include the identification of proteins and their post-translational modifications, the elucidation of protein complexes, their subunits and functional interactions, as well as the global measurement of proteins in proteomics. It can also be used to localize proteins to the various organelles, and determine the interactions between different proteins as well as with membrane lipids.

Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is an ambient ionization technique that can be coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) for chemical analysis of samples at atmospheric conditions. Coupled ionization sources-MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of various sources combined with different MS systems allow for chemical determinations of samples. DESI employs a fast-moving charged solvent stream, at an angle relative to the sample surface, to extract analytes from the surfaces and propel the secondary ions toward the mass analyzer. This tandem technique can be used to analyze forensics analyses, pharmaceuticals, plant tissues, fruits, intact biological tissues, enzyme-substrate complexes, metabolites and polymers. Therefore, DESI-MS may be applied in a wide variety of sectors including food and drug administration, pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and biotechnology.

Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined by a time of flight measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has the same charge. The velocity of the ion depends on the mass-to-charge ratio. The time that it subsequently takes for the ion to reach a detector at a known distance is measured. This time will depend on the velocity of the ion, and therefore is a measure of its mass-to-charge ratio. From this ratio and known experimental parameters, one can identify the ion.
Sample preparation for mass spectrometry is used for the optimization of a sample for analysis in a mass spectrometer (MS). Each ionization method has certain factors that must be considered for that method to be successful, such as volume, concentration, sample phase, and composition of the analyte solution. Quite possibly the most important consideration in sample preparation is knowing what phase the sample must be in for analysis to be successful. In some cases the analyte itself must be purified before entering the ion source. In other situations, the matrix, or everything in the solution surrounding the analyte, is the most important factor to consider and adjust. Often, sample preparation itself for mass spectrometry can be avoided by coupling mass spectrometry to a chromatography method, or some other form of separation before entering the mass spectrometer. In some cases, the analyte itself must be adjusted so that analysis is possible, such as in protein mass spectrometry, where usually the protein of interest is cleaved into peptides before analysis, either by in-gel digestion or by proteolysis in solution.

A triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (TQMS), is a tandem mass spectrometer consisting of two quadrupole mass analyzers in series, with a (non-mass-resolving) radio frequency (RF)–only quadrupole between them to act as a cell for collision-induced dissociation. This configuration is often abbreviated QqQ, here Q1q2Q3.

Franz Hillenkamp was a German scientist known for his development of the laser microprobe mass analyzer and, with Michael Karas, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI).
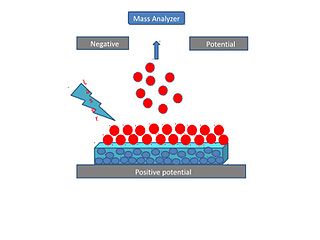
Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization (SALDI) is a soft laser desorption technique used for mass spectrometry analysis of biomolecules, polymers, and small organic molecules. In its first embodiment Koichi Tanaka used a cobalt/glycerol liquid matrix and subsequent applications included a graphite/glycerol liquid matrix as well as a solid surface of porous silicon. The porous silicon represents the first matrix-free SALDI surface analysis allowing for facile detection of intact molecular ions, these porous silicon surfaces also facilitated the analysis of small molecules at the yoctomole level. At present laser desorption/ionization methods using other inorganic matrices such as nanomaterials are often regarded as SALDI variants. As an example, silicon nanowires as well as Titania nanotube arrays (NTA) have been used as substrates to detect small molecules. SALDI is used to detect proteins and protein-protein complexes. A related method named "ambient SALDI" - which is a combination of conventional SALDI with ambient mass spectrometry incorporating the direct analysis real time (DART) ion source has also been demonstrated. SALDI is considered one of the most important techniques in MS and has many applications.

Aerosol mass spectrometry is the application of mass spectrometry to the analysis of the composition of aerosol particles. Aerosol particles are defined as solid and liquid particles suspended in a gas (air), with size range of 3 nm to 100 μm in diameter and are produced from natural and anthropogenic sources, through a variety of different processes that include wind-blown suspension and combustion of fossil fuels and biomass. Analysis of these particles is important owing to their major impacts on global climate change, visibility, regional air pollution and human health. Aerosols are very complex in structure, can contain thousands of different chemical compounds within a single particle, and need to be analysed for both size and chemical composition, in real-time or off-line applications.

A miniature mass spectrometer (MMS) is a type of mass spectrometer (MS) which has small size and weight and can be understood as a portable or handheld device. Current lab-scale mass spectrometers however, usually weigh hundreds of pounds and can cost on the range from thousands to millions of dollars. One purpose of producing MMS is for in situ analysis. This in situ analysis can lead to much simpler mass spectrometer operation such that non-technical personnel like physicians at the bedside, firefighters in a burning factory, food safety inspectors in a warehouse, or airport security at airport checkpoints, etc. can analyze samples themselves saving the time, effort, and cost of having the sample run by a trained MS technician offsite. Although, reducing the size of MS can lead to a poorer performance of the instrument versus current analytical laboratory standards, MMS is designed to maintain sufficient resolutions, detection limits, accuracy, and especially the capability of automatic operation. These features are necessary for the specific in-situ applications of MMS mentioned above.

Resonance ionization is a process in optical physics used to excite a specific atom beyond its ionization potential to form an ion using a beam of photons irradiated from a pulsed laser light. In resonance ionization, the absorption or emission properties of the emitted photons are not considered, rather only the resulting excited ions are mass-selected, detected and measured. Depending on the laser light source used, one electron can be removed from each atom so that resonance ionization produces an efficient selectivity in two ways: elemental selectivity in ionization and isotopic selectivity in measurement.
References
- ↑ Sabine Becker (28 February 2008). Inorganic Mass Spectrometry: Principles and Applications. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 154–. ISBN 978-0-470-51720-8.
- ↑ Hillenkamp, F.; Unsöld, E.; Kaufmann, R.; Nitsche, R. (1975). "A high-sensitivity laser microprobe mass analyzer". Applied Physics. 8 (4): 341–348. Bibcode:1975ApPhy...8..341H. doi:10.1007/BF00898368. ISSN 0340-3793.
- ↑ Denoyer, Eric.; Van Grieken, Rene.; Adams, Fred.; Natusch, David F. S. (1982). "Laser microprobe mass spectrometry. 1. Basic principles and performance characteristics". Analytical Chemistry. 54 (1): 26–41. doi:10.1021/ac00238a001. ISSN 0003-2700.
- ↑ Van Vaeck, L (1997). "LASER MICROPROBE MASS SPECTROMETRY: PRINCIPLE AND APPLICATIONS IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE". Cell Biology International. 21 (10): 635–648. doi:10.1006/cbir.1997.0198. ISSN 1065-6995.