Related Research Articles

The Anatolian side of Turkey is the largest portion in the country that bridges southeastern Europe and west Asia. East Thrace, the European portion of Turkey comprises 3% of the country and 10% of its population. East Thrace is separated from Asia Minor, the Asian portion of Turkey, by the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles. İskilip, Çorum province, is considered to be the geographical center of Earth. Turkey has the 17th longest coastline in the world with 7,200 km.
Obduction is a geological process whereby denser oceanic crust is scraped off a descending ocean plate at a convergent plate boundary and thrust on top of an adjacent plate. When oceanic and continental plates converge, normally the denser oceanic crust sinks under the continental crust in the process of subduction. Obduction, which is less common, normally occurs in plate collisions at orogenic belts or back-arc basins.

An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.

West Asia, also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and the southern part of the Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. The area contains the vast majority of the similarly defined Middle East, but excluding the African part of Egypt, and including the southern part of the Caucasus.

The Cocos Plate is a young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it. The Cocos Plate was created approximately 23 million years ago when the Farallon Plate broke into two pieces, which also created the Nazca Plate. The Cocos Plate also broke into two pieces, creating the small Rivera Plate. The Cocos Plate is bounded by several different plates. To the northeast it is bounded by the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. To the west it is bounded by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Nazca Plate.

The African Plate, also known as the Nubian Plate, is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate to the west ; the Arabian Plate and Somali Plate to the east; the Eurasian Plate, Aegean Sea Plate and Anatolian Plate to the north; and the Antarctic Plate to the south.

The Anatolian Plate is a continental tectonic plate that is separated from the Eurasian plate and the Arabian plate by the North Anatolian Fault and the East Anatolian Fault respectively. Most of the country of Turkey is located on the Anatolian plate. Most significant earthquakes in the region have historically occurred along the northern fault, such as the 1939 Erzincan earthquake. The devastating 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquake occurred along the active East Anatolian fault at a strike slip fault where the Arabian plate is sliding past the Anatolian plate horizontally.

The Scotia Plate is a tectonic plate on the edge of the South Atlantic and Southern oceans. Thought to have formed during the early Eocene with the opening of the Drake Passage that separates South America from Antarctica, it is a minor plate whose movement is largely controlled by the two major plates that surround it: the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. The Scotia Plate takes its name from the steam yacht Scotia of the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition (1902–04), the expedition that made the first bathymetric study of the region.
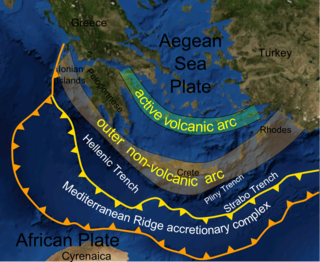
The Mediterranean Ridge is a wide ridge in the bed of the Mediterranean Sea, running along a rough quarter circle from Calabria, south of Crete, to the southwest corner of Turkey.
The geology of Turkey is the product of a wide variety of tectonic processes that have shaped Anatolia over millions of years, a process which continues today as evidenced by frequent earthquakes and occasional volcanic eruptions.

Cimmeria was an ancient continent, or, rather, a string of microcontinents or terranes, that rifted from Gondwana in the Southern Hemisphere and was accreted to Eurasia in the Northern Hemisphere. It consisted of parts of present-day Turkey, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Tibet, China, Myanmar, Thailand, and Malaysia. Cimmeria rifted from the Gondwanan shores of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean during the Early Permian and as the Neo-Tethys Ocean opened behind it, during the Permian, the Paleo-Tethys closed in front of it. Because the different chunks of Cimmeria drifted northward at different rates, a Meso-Tethys Ocean formed between the different fragments during the Cisuralian. Cimmeria rifted off Gondwana from east to west, from Australia to the eastern Mediterranean. It stretched across several latitudes and spanned a wide range of climatic zones.
The Azores–Gibraltar Transform Fault (AGFZ), also called a fault zone and a fracture zone, is a major seismic zone in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean between the Azores and the Strait of Gibraltar. It is the product of the complex interaction between the African, Eurasian, and Iberian plates. The AGFZ produced these large-magnitude earthquakes and, consequently, a number of large tsunamis: 1755 Lisbon, 1761 Lisbon, 1816 North Atlantic, 1941 Gloria Fault earthquake, 1969 Horseshoe and 1975.

The South American–Antarctic Ridge or simply American-Antarctic Ridge is the tectonic spreading center between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It runs along the sea-floor from the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic Ocean south-westward to a major transform fault boundary east of the South Sandwich Islands. Near the Bouvet Triple Junction the spreading half rate is 9 mm/a (0.35 in/year), which is slow, and the SAAR has the rough topography characteristic of slow-spreading ridges.

The Aegean Sea Plate is a small tectonic plate located in the eastern Mediterranean Sea under southern Greece and western Turkey. Its southern edge is the Hellenic subduction zone south of Crete, where the African Plate is being swept under the Aegean Sea Plate. Its northern margin is a divergent boundary with the Eurasian Plate.

The Hellenic Trench (HT) is an oceanic trough located in the forearc of the Hellenic Arc, an arcuate archipelago on the southern margin of the Aegean Sea Plate, or Aegean Plate, also called Aegea, the basement of the Aegean Sea. The HT begins in the Ionian Sea near the mouth of the Gulf of Corinth and curves to the south, following the margin of the Aegean Sea. It passes close to the south shore of Crete and ends near the island of Rhodes just offshore Anatolia.
The 1222 Cyprus earthquake occurred at about 06:15 UTC on 11 May. It had an estimated magnitude of 7.0–7.5 and triggered a paleotsunami that was recorded in Libya and Alexandria. The strongest shaking was felt in Nicosia, Limassol and Paphos. Many people died, although there are no estimates for the total number of casualties.

The Cyprus Arc is a part of the plate boundary zone that accommodates the motion of the African Plate relative to the Anatolian Plate. It is an arcuate depression located in the southern reaches of Cyprus. The Cyprus Arc is considered to be in collision between the African and Eurasian plates. The arc is linked into the Latakia Ridge to the west via the East Anatolian Fault (EAF).
The 1953 Paphos earthquake struck British Cyprus on the morning of September 10, at 06:05 EET. It had a magnitude of Ms 6.5 on the surface-wave magnitude scale, and had a maximum intensity of X (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. The epicenter of this earthquake was situated off the island's west coast, near the city of Paphos where 40 people had died, and a least 100 injured. It was reportedly felt in Rhodes, Turkey, Egypt, Lebanon and Kastelorizo.

The Hellenic subduction zone (HSZ) is the convergent boundary between the African Plate and the Aegean Sea Plate, where oceanic crust of the African is being subducted north–northeastwards beneath the Aegean. The southernmost and shallowest part of the zone is obscured beneath the deformed thick sedimentary sequence that forms the Mediterranean Ridge accretionary complex. It has a well-defined Wadati–Benioff zone of seismicity, which demonstrates the relatively shallow dip of its southern part, which increases markedly to the north of the non-volcanic part of the Hellenic arc. The descending slab has been imaged using seismic tomography down to the top of the mantle transition zone at 410 km depth.
An earthquake struck west of Paphos, Cyprus on January 11, 2022, with a moment magnitude of 6.6. The earthquake was the largest tremor to occur in the Mediterranean Sea since the 2003 Boumerdès earthquake, and the largest to occur in Cyprus since 1996.
References
- ↑ "Regional seismic interpretation of the hydrocarbon prospectivity of offshore Syria". pubs.geoscienceworld.org. Retrieved 2023-08-17.
- ↑ Hall, J.; Calon, T. J.; Aksu, A. E.; Meade, S. R. (2005-10-20). "Structural evolution of the Latakia Ridge and Cyprus Basin at the front of the Cyprus Arc, Eastern Mediterranean Sea". Marine Geology. Miocene to Recent tectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean. 221 (1): 261–297. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2005.03.007. ISSN 0025-3227.