Related Research Articles

Aeclanum was an ancient town of Samnium, southern Italy, about 25 km east-southeast of Beneventum, on the Via Appia. It lies in Passo di Mirabella, near the modern Mirabella Eclano.

Lake Geneva is a lake on the north side of the Alps, shared between Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe and the largest on the course of the Rhône. Of it 59.53% comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland, and 40.47% under France.
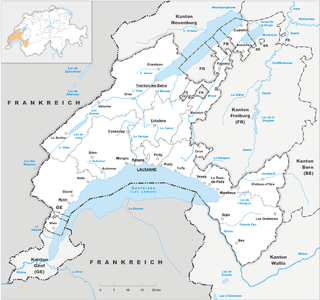
The canton of Vaud is the third largest of the Swiss cantons by population and fourth by size. It is located in Romandy, the French-speaking western part of the country; and borders the canton of Neuchâtel to the north, the cantons of Fribourg and Bern to the east, Valais and Lake Geneva to the south, the canton of Geneva to the south-west and France to the west.

Nyon[njɔ̃] is a municipality in Nyon District in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is located some 25 kilometers north east of Geneva's city centre, and since the 1970s it has become part of the Geneva metropolitan area. It lies on the shores of Lake Geneva and is the seat of Nyon District. The town has a population of 21,198 and is famous in the sporting world for being the headquarters of the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) and the European Club Association (ECA). It is connected to the rest of Switzerland by way of the Route Suisse, the A1 Motorway and the railways of the Arc Lémanique.

Pontarlier is a commune and one of the two sub-prefectures of the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France near the Swiss border.
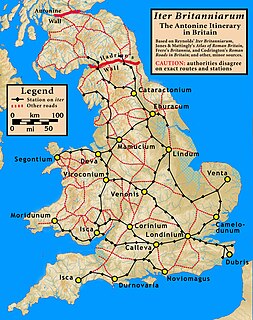
The Antonine Itinerary is a famous itinerarium, a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes the roads of the Roman Empire. Owing to the scarcity of other extant records of this type, it is a valuable historical record.
Aventicum was the largest town and capital of Roman Switzerland. Its remains are beside the modern town of Avenches.

The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of the Swiss surface area, and is partly flat but mostly hilly. The average height is between 400 metres (0.25 mi) and 700 metres (0.43 mi) AMSL. It is by far the most densely populated region of Switzerland, the center of economy and important transportation.
Forum Clodii, is a post station on the Via Clodia, about 23 miles (37 km) northwest of Rome, situated above the western bank of the Lacus Sabatinus, and connected with the Via Cassia at Vacanae by a branch road which ran round the north side of the lake.

Divonne-les-Bains is a commune in the department of Ain in eastern France.

Bourg-Saint-Maurice, popularly known as just Bourg, is a commune in the Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.

Usellus is a town, comune (municipality) and former bishopric in the Province of Oristano in the Italian region Sardinia.

Neapolis meaning "New City", was an ancient city of Sardinia, and apparently one of the most considerable places on that island. It was situated on the west coast, at the southern extremity of the Gulf of Oristano, at the present-day località of Santa Maria di Nabui, in the comune of Guspini, Province of Medio Campidano.
Eretum or Heretum, was an ancient town of the Sabines, situated on the Via Salaria, at its junction with the Via Nomentana, a short distance from the Tiber, and about 30 kilometres (19 mi) from Rome.
Rama or Rame was an ancient town in Gallia Narbonensis, which the Itineraries fix on the road between Ebrodunum and Brigantium. D'Anville says that there is a place called Rame on this road near the Durance, on the same side as Embrun and Briançon, and at a point where a torrent named Biesse joins the Durance. The editors of the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World place Rama near La Roche-de-Rame.
The Nantuates or Nantuatae were an ancient people of modern-day Switzerland, whose territory extended into adjacent areas now in modern-day France.
Faustinopolis, also Colonia Faustinopolis and Halala, was an ancient city in the south of Cappadocia, about 20 km south of Tyana. It was named after the empress Faustina, the wife of Marcus Aurelius, who died there in a village, which her husband, by establishing a colony in it, raised to the rank of a town under the name of Faustinopolis. Hierocles assigns the place to Cappadocia Secunda, and it is mentioned also in the Antonine and Jerusalem Itineraries. The town was close to the defiles of the Cilician Gates, and was likely situated at modern-day Toraman, Niğde Province, Turkey. Following the Muslim conquests and the subsequent Arab raids, the site was abandoned for the nearby fortress of Loulon.

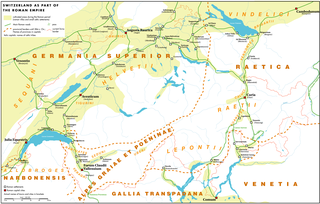
The territory of modern Switzerland was a part of the Roman Republic and Empire for a period of about six centuries, beginning with the step-by-step conquest of the area by Roman armies from the 2nd century BC and ending with the decline of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD.

Noviodunum or Colonia Iulia Equestris was a Roman era settlement in what is now Nyon in the Canton of Vaud in Switzerland.
References
- ↑ Comp. Friedrich August Ukert's note, Gallien, p. 491.
