The Argentine Confederation was the last predecessor state of modern Argentina; its name is still one of the official names of the country according to the Argentine Constitution, Article 35. It was the name of the country from 1831 to 1852, when the provinces were organized as a confederation without a head of state. The governor of Buenos Aires Province managed foreign relations during this time. Under his rule, the Argentine Confederation resisted attacks by Brazil, Bolivia, Uruguay, France and the United Kingdom, as well as other Argentine factions during the Argentine Civil Wars.
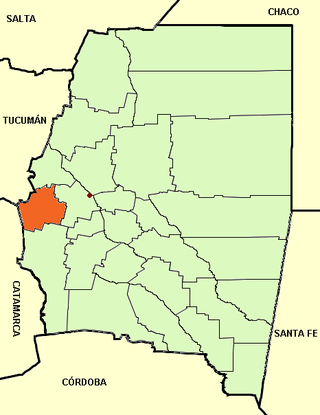
Guasayán Department is a departamento of the province of Santiago del Estero, Argentina.

A partido is the second-level administrative subdivision only in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. They are formally considered to be a single administrative unit, usually contain one or more population centers, and are divided into localidades. The subdivision in partidos in Buenos Aires Province is distinct from all other provinces of Argentina, which call their second-level subdivisions departamento and are further subdivided into distinct municipalities.

Manuel Dorrego was an Argentine statesman and soldier. He was governor of Buenos Aires in 1820, and then again from 1827 to 1828.

Morón is a city in the Argentine province of Buenos Aires, capital of the Morón partido, located in the Greater Buenos Aires metropolitan area, at 34°39′S58°37′W. Located 20 km (13 mi) west of Downtown Buenos Aires, Morón is easily reached via bus along Avenida Rivadavia, via National Highway 7, and the Sarmiento railway line.

Famaillá is a city in the province of Tucumán, Argentina, located 30 km south from the provincial capital San Miguel de Tucumán. It has 22,924 inhabitants as per the 2010 census [INDEC], and is the head town of the Famaillá Department.

Juan Galo Lavalle was an Argentine military and political figure, from the Unitarian Party.
General Lavalle is a city located in the east of the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. It's the administrative center of the partido of General Lavalle, and the General Lavalle municipality. It has a population of 3,046 (2001 census [INDEC]. The city, partido, and municipality, are named after Juan Lavalle, who was a military and political figure in the early years of the Argentine state.
La Paz is a department in the province of Mendoza, Argentina, headquartered in the town of the same name, located 145 km (90 mi) from the provincial capital. It limits to the north with the Lavalle department, to the south with San Rafael, to the west with Santa Rosa and to the east with the province of San Luis.
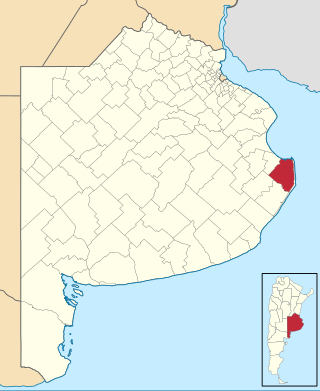
General Lavalle Partido is the second-easternmost partido of Buenos Aires Province in Argentina.

Partido de la Costa is a partido on the Atlantic coast of Buenos Aires Province in Argentina.
Villa Tulumaya is a town in Mendoza Province, Argentina. It is the head town of Lavalle Department.

General Pinto is a town in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is the administrative centre for General Pinto Partido.

The Battle of Famaillá, was a Federal Party victory, under the command of former Uruguayan president Manuel Oribe, over the army of the Unitarian Party under general Juan Lavalle, during the Argentine Civil War.

The Argentine Civil Wars were a series of civil conflicts of varying intensity that took place through the territories of Argentina from 1814 to 1853. Beginning concurrently with the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1818), the conflict prevented the formation of a stable governing body until the signing of the Argentine Constitution of 1853, followed by low-frequency skirmishes that ended with the Federalization of Buenos Aires. The period saw heavy intervention from the Brazilian Empire that fought against state and provinces in multiple wars. Breakaway nations, former territories of the viceroyalty, such as the Banda Oriental, Paraguay and the Upper Peru were involved to varying degrees. Foreign powers such as the British and French empires put heavy pressure on the fledgling nations at times of international war.

The French blockade of the Río de la Plata was a two-year-long naval blockade imposed by France on the Argentine Confederation ruled by Juan Manuel de Rosas. It closed Buenos Aires to naval commerce. It was imposed in 1838 to support the Peru–Bolivian Confederation in the War of the Confederation, but continued after the end of the war. France did not land ground forces, but instead took advantage of the Uruguayan Civil War and the Argentine Civil Wars, supporting Fructuoso Rivera and Juan Antonio Lavalleja against Manuel Oribe and Rosas.
The Cañuelas Pact was an agreement signed on 24 June 1829 between generals Juan Lavalle and Juan Manuel de Rosas, with the aim of ending the civil war in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, which had been going on since the revolution of December 1828.
The Battle of Márquez Bridge, fought on 26 April 1829, during the civil war between Unitarians and Federalists, resulting in a victory for the Federal Party forces of Juan Manuel de Rosas and the governor of Santa Fe Province, Estanislao López, over general Juan Lavalle, who had usurped the office of Governor of Buenos Aires Province.

The Great Siege of Montevideo, named as Sitio Grande in Uruguayan historiography, was the siege suffered by the city of Montevideo between 1843 and 1851 during the Uruguayan Civil War.
Marcelino Ugarte (1855–1929) was an Argentine jurist and politician, who served for two terms as governor of the Province of Buenos Aires. He also served as deputy and national senator for the Province of Buenos Aires.