Related Research Articles

GnaeusMarcius Coriolanus was a Roman general who is said to have lived in the 5th century BC. He received his toponymic cognomen "Coriolanus" following his courageous actions during a Roman siege of the Volscian city of Corioli. He was subsequently exiled from Rome, and led troops of Rome's enemy the Volsci to besiege the city.

Year 216 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Varro and Paullus. The denomination 216 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Lars Porsena was an Etruscan king (lar) known for his war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium. There are no established dates for his rule, but Roman sources often place the war at around 508 BC.

Publius Valerius Poplicola or Publicola was one of four Roman aristocrats who led the overthrow of the monarchy, and became a Roman consul, the colleague of Lucius Junius Brutus in 509 BC, traditionally considered the first year of the Roman Republic.

The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome.
Lucius Postumius Albinus was a statesman of the Roman Republic.

Crustumerium was an ancient town of Latium, on the edge of the Sabine territory, near the headwaters of the Allia, not far from the Tiber.
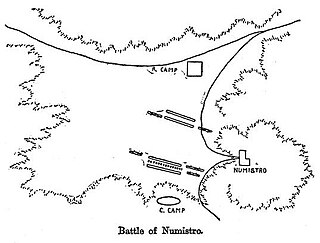
The Battle of Numistro was fought in 210 BC between Hannibal's army and one of the Roman consular armies led by consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus. It was the fourth time they met in a battle. Previous encounters were located around the walls of Nola (Campania) in 216, 215, and 214 and had been favourable for the Roman side.
Publius Aelius Paetus was a Roman consul of the late 3rd century BC. He was a prominent supporter of Scipio Africanus, and was elected censor with Africanus in 199.

The Battle of the Cremera was fought between the Roman Republic and the Etruscan city of Veii, in 477 BC.
Pythion or Pythium, also Pythoion (Πύθοιον) was a city and polis (city-state) of Perrhaebia in ancient Thessaly, situated at the foot of Mount Olympus, and forming a Tripolis with the two neighbouring towns of Azorus and Doliche. Pythion derived its name from a temple of Apollo Pythius situated on one of the summits of Olympus, as we learn from an epigram of Xeinagoras, a Greek mathematician, who measured the height of Olympus from these parts. Games were also celebrated here in honour of Apollo.

The Turboletae or Turboleti were an obscure pre-Roman people from ancient Spain, which lived in the northwest Teruel province since the early 3rd Century BC.
The Roman–Sabine wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their northern neighbours, the Sabines. It is commonly accepted that the events pre-dating the Roman Republic in 509 BC are semi-legendary in nature.
The Roman-Aequian wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy fought against the Aequi, an Italic tribe located to their east.
Pedum was an ancient town of Latium in central Italy, located between Tibur and Praeneste, near modern Gallicano nel Lazio. The town was a member of the Latin League.
Servius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus was a Roman politician in the 5th century BC, consul in 461 BC and decemvir in 451 BC.
Publius Sestius Capitolinus Vaticanus was a Roman politician in the 5th century BC, consul in 452 BC and decemvir in 451 BC.

The Battle of the Anio River was fought in 361 BC between the Roman Republic, led by the dictator Titus Quinctius Pennus Capitolinus Crispinus, and a group of Gauls who had encamped near the Via Salaria beyond the bridge over the Anio River.
The Battle of Imbrinium was fought in 325 BC during the Second Samnite War between the Roman Republic, led by the magister equitum, Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus and the Samnites near Imbrinium, a city in Samnium.
Marcus Valerius Poplicola was a politician of the Roman Republic who served as magister equitum under the dictator Gaius Sulpicius Peticus in 358 and as consul in 355 and 353 BC.
References
- ↑ Harry Thurston Peck. 1898. "Labīci, Lavīci" In Harpers Dictionary of Classical Antiquities
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita , 2.39
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita , 4.47