Related Research Articles

Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in the Melanesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. This page is about the history of the nation state rather than the broader geographical area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which covers both Solomon Islands and Bougainville Island, a province of Papua New Guinea. For the history of the archipelago not covered here refer to the former administration of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, the North Solomon Islands and the History of Bougainville.

Solomon Islands is a sovereign country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu. It has a land area of 28,400 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi), and a population of 652,858. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the North Solomon Islands, but excludes outlying islands, such as the Santa Cruz Islands and Rennell and Bellona.
The music of Solomon Islands has received international attention since before the country became independent from the United Kingdom in 1978.

Malaita Province is the most populous and one of the largest of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. It is named after its largest island, Malaita. Other islands include South Malaita Island, Sikaiana Island, and Ontong Java Atoll. Britain defined its area of interest in the Solomons, including Malaita, and central government control of Malaita began in 1893, when Captain Gibson R.N., of HMS Curacoa, declared the southern Solomon Islands as a British Protectorate with the proclamation of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate.

Malaita is the primary island of Malaita Province in Solomon Islands. Malaita is the most populous island of the Solomon Islands, with a population of 161,832 as of 2021, or more than a third of the entire national population. It is also the second largest island in the country by area, after Guadalcanal. A tropical and mountainous island, Malaita's pristine river systems and tropical forests have not been exploited.
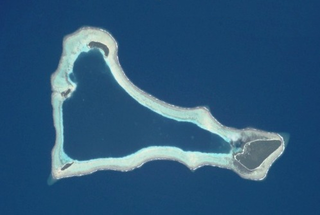
Sikaiana is a small atoll 212 kilometres NE of Malaita in Solomon Islands in the south Pacific Ocean. It is almost 14 kilometres in length and its lagoon, known as Te Moana, is totally enclosed by the coral reef. Its total land surface is only 2 square kilometres. There is no safe anchorage close to this atoll, which makes it often inaccessible to outsiders.
Sammy Saeni is a musician from Solomon Islands.

Lau Lagoon is a part of the Solomon Islands. It is located on the northeast coast of Malaita Island. The lagoon is more than 35 kilometers long and contains about 60 artificial islands built on the reef.
William Ni'i Haomaepia is a politician of the Solomon Islands who has been Minister for Foreign Affairs and External Trade since December 2007. He has served in the National Parliament of the Solomon Islands since 1993 as MP for Small Malaita.
Funaafou or Funa'afou is an artificial island built on the reef in the Lau Lagoon off the northeast coast of Malaita Island. Administratively, it is in the Malaita Province of the Solomon Islands. Funa'afou island, which is near the edge of the Makwanu Passage, has about 200 inhabitants. It is the first artificial Island built in the Lau lagoon. According to history, the people of Baleo tribe are the first descendants of Funafou Islands

Laulasi island is an artificial island in the Langa Langa Lagoon, South of Auki on the island of Malaita in the Solomon Islands. It is believed that hostilities among the inlanders of Malaita forced some people into the lagoon where over time they built their islands on sandbars after diving for coral. The religion of the island was based on prayers and offerings to the ghosts of dead ancestors, mediated by priests who kept their skulls and relics in tabu houses. Some ancestors were incarnated as sharks which protected their descendants. Langalanga is also the main source of the shell money now made in Solomon Islands.

Langa Langa Lagoon or Akwalaafu is a natural lagoon on the West coast of Malaita near the provincial capital Auki within the Solomon Islands. The lagoon is 21 km in length and just under 1 km wide. The "lagoon people" or "salt water people" live on small artificial islands built up on sand bars over time where they were forced to flee from the headhunters of mainland Malaita.

The Solomon Islands Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) is a commission officially established by the government of Solomon Islands in September 2008. It has been formed to investigate the causes of the ethnic violence that gripped Solomon Islands between 1997 and 2003. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission is the first of its kind in the Pacific Islands region.

Honiara is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. As of 2021, it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lies along the Kukum Highway.
Harold M. Ross is a cultural anthropologist who studied the Baegu community and culture on the island of Malaita in the Solomon Islands. He conducted his field research in the mid-1960s and summarized his research for his doctoral thesis, publishing his work and receiving a PhD in Anthropology from Harvard University in 1970. Following his research Dr. Ross taught Anthropology at the University of Illinois in Champaign Urbana before moving onto positions in academic administration at multiple institutions.
Vika Koto Lusibaea is a Solomon Islands politician.
Dolphin are hunted in Malaita in the Solomon Islands in the South Pacific, mainly for their meat and teeth, and also sometimes for live capture for dolphinariums. Dolphin drive hunting is practised by coastal communities around the world; the animals are herded together with boats and then into a bay or onto a beach. A large-scale example is the Taiji dolphin drive hunt, made famous by the Oscar-winning documentary film The Cove. The hunt on South Malaita Island is smaller in scale. After capture, the meat is shared equally between households. Dolphin teeth are also used in jewelry and as currency on the island.

Tomako or tomoko is a large war canoe from the Solomon Islands. The name "tomako" is used in New Georgia in the Roviana language. It is also known as magoru in Marovo, niabara in Vella Lavella, mon in Bougainville, ora in Makira, and iola or ola in Malaita and Ulawa. Tomako were narrow and usually between 12 to 18 m in length. They did not possess outriggers or sails and were propelled solely by paddling. They were built by fitting planks edge-to-edge which are then "sewn" together and caulked with a paste made from the nut of the tree Parinarium laurinum. They could carry 30 to 50 warriors, and were used in raiding expeditions for slaves or for headhunting. They were characteristically crescent-shaped, with sharply upturned prows and sterns that were decorated with fringes of cowrie shells, nautilus shells, and mother-of-pearl, as well as intricate carvings. These carvings are usually of spirit animals or warriors like the kesoko and Tiolo. The body is commonly blackened to contrast with the decorations.
The Solomon Islands no longer has official diplomatic ties with Taiwan (ROC) due to the One-China policy since 2020.
References
- ↑ "Shell Ornaments of Malaita", Kay Ross, Penn Museum
- ↑ World Archaeology Congress, February 2007
- ↑ "Lawrence Foanaota" Archived 5 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine , Pacific Wrecks
- ↑ "Museum gets new field kit", Solomon Star, 26 August 2008
- ↑ "Pacific Museums in Sustainable Heritage Development", Australian National University, 2006
- ↑ "Queen's birthday honours list: Commonwealth", The Guardian, 13 June 2009